Name: Astronomy Study Guide Part 1 Define Astronomy
... Month- Length of time for the moon to revolve around earth Year- Length of time for Earth to revolve around sun 365.25 days Calendar- years, months, and days based on our celestial objects Leap Year- Feb 29 once every 4 years to make up for our 365.25 day solar year ...
... Month- Length of time for the moon to revolve around earth Year- Length of time for Earth to revolve around sun 365.25 days Calendar- years, months, and days based on our celestial objects Leap Year- Feb 29 once every 4 years to make up for our 365.25 day solar year ...
Simple Winter Star - Dark Sky Discovery
... On the other side of Polaris is a W of stars (or an M depending on which way up it happens to be; the stars appear to rotate anti-clockwise round Polaris once every 24 hours). This is the constellation of Cassiopeia. These stars in the northern sky are the same all year round, so you will always be ...
... On the other side of Polaris is a W of stars (or an M depending on which way up it happens to be; the stars appear to rotate anti-clockwise round Polaris once every 24 hours). This is the constellation of Cassiopeia. These stars in the northern sky are the same all year round, so you will always be ...
Chapter 26
... through the middle with arms extending off the bar. 3. Elliptical- spherical or oval with no spiral arms 4. Irregular- very disorganized appearance, lots of dust and gas ...
... through the middle with arms extending off the bar. 3. Elliptical- spherical or oval with no spiral arms 4. Irregular- very disorganized appearance, lots of dust and gas ...
Milky Way galaxy - Uplift North Hills Prep
... Besides the usual stars, clusters of stars, galaxies, and clusters and super- clusters of galaxies, the universe contains a number of other interesting objects. Among these are stars known as red giants, white dwarfs, neutron stars, black holes and exploding stars called novae and supernovae. In ad ...
... Besides the usual stars, clusters of stars, galaxies, and clusters and super- clusters of galaxies, the universe contains a number of other interesting objects. Among these are stars known as red giants, white dwarfs, neutron stars, black holes and exploding stars called novae and supernovae. In ad ...
Life Cycle of Star Flipbook
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
The Sky - HiSPARC
... now famous list of 110 Messier objects.4 Messier was a comet hunter, he became frustrated by objects strongly resembling comets but which were in fact not comets. In modern catalogues the original Messier objects can still be recognised by their names; M001 to M110. Herschel was impressed by Messier ...
... now famous list of 110 Messier objects.4 Messier was a comet hunter, he became frustrated by objects strongly resembling comets but which were in fact not comets. In modern catalogues the original Messier objects can still be recognised by their names; M001 to M110. Herschel was impressed by Messier ...
Stargazing Rules 01162013
... Moon is shaped like a "C", it bulges to the left. 18. Even though most of the objects we observe in the night sky appear not to move in relation to each other, in reality they are all moving at great speed relative to us and to each other. They appear not to be moving because of their great distanc ...
... Moon is shaped like a "C", it bulges to the left. 18. Even though most of the objects we observe in the night sky appear not to move in relation to each other, in reality they are all moving at great speed relative to us and to each other. They appear not to be moving because of their great distanc ...
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears
... have surface temperatures aS low as 3,000oC, while the hottest stars have surface temperatures ten times higher. The temperature of a star determines its color-from cool, red stars to hot, blue ones. The table below Shows how temperature and star color are related. Recall that the sun is a medium-te ...
... have surface temperatures aS low as 3,000oC, while the hottest stars have surface temperatures ten times higher. The temperature of a star determines its color-from cool, red stars to hot, blue ones. The table below Shows how temperature and star color are related. Recall that the sun is a medium-te ...
a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as
... Yvonne looks at the stars in the night sky through a telescope. She sees four stars that have different colors. One star is blue, one is white, one looks yellow, and the fourth looks red. Which star is the coolest? a. the red star b. the blue star c. the white star d. the yellow star Answer: b How a ...
... Yvonne looks at the stars in the night sky through a telescope. She sees four stars that have different colors. One star is blue, one is white, one looks yellow, and the fourth looks red. Which star is the coolest? a. the red star b. the blue star c. the white star d. the yellow star Answer: b How a ...
The Constellation Lepus, the Hare
... John Russell Hind and has been reputed to be the most beautiful star in the sky. There is one Messier Object in Lepus, M79, discovered in 1780 by Pierre Méchain. It is a globular cluster of magnitude 8.0, 42,000 light-years from Earth. One of the few globular clusters visible in the Northern Hemisph ...
... John Russell Hind and has been reputed to be the most beautiful star in the sky. There is one Messier Object in Lepus, M79, discovered in 1780 by Pierre Méchain. It is a globular cluster of magnitude 8.0, 42,000 light-years from Earth. One of the few globular clusters visible in the Northern Hemisph ...
Characteristics of Stars Stars Analyzing Starlight Star Characteristics
... by analyzing the spectra of the light that a star emits ...
... by analyzing the spectra of the light that a star emits ...
CHAPTER 2 NOTES (STARS AND GALAXIES)
... Galaxy- huge collection of stars 3 types of galaxies are: 1. spiral- arms like a pinwheel ex our galaxy- Milky Way 2. elliptical- nearly spherical to flatdisks (older than other galaxies) 3. irregular- no orderly or definite shape, not very common Milky Way Galaxy- pinwheel shaped disk with bulge in ...
... Galaxy- huge collection of stars 3 types of galaxies are: 1. spiral- arms like a pinwheel ex our galaxy- Milky Way 2. elliptical- nearly spherical to flatdisks (older than other galaxies) 3. irregular- no orderly or definite shape, not very common Milky Way Galaxy- pinwheel shaped disk with bulge in ...
The Life Cycle of a Star Webquest
... 18. If you were in a spaceship would you be able to see a star twinkling? ____________ Why? ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 18. If you were in a spaceship would you be able to see a star twinkling? ____________ Why? ______________________________________________________________________________ ...
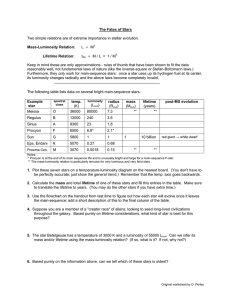
The Fates of Stars Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation:
... 1. Plot these seven stars on a temperature-luminosity diagram on the nearest board. (You don't have to be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. ...
... 1. Plot these seven stars on a temperature-luminosity diagram on the nearest board. (You don't have to be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. ...
source
... 1. Plot these seven stars on a temperature-luminosity diagram on the nearest board. (You don't have to be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. ...
... 1. Plot these seven stars on a temperature-luminosity diagram on the nearest board. (You don't have to be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.