Night Sky Checklist Year-Round Unaided Eye Astronomy
... The Little Dipper is a part of the constellation Ursa Minor, the Smaller Bear. It’s quite faint and may not be visible inside a city. Since it’s always in the north, getting well out of town in that direction will make it easier to find. Polaris, also known as The North Star, lies almost exactly in ...
... The Little Dipper is a part of the constellation Ursa Minor, the Smaller Bear. It’s quite faint and may not be visible inside a city. Since it’s always in the north, getting well out of town in that direction will make it easier to find. Polaris, also known as The North Star, lies almost exactly in ...
Startalk
... A big glowing ball of gas! Contains mainly H and He They have a core that is dense and super hot! Nuclear fusion is the source of their energy! ...
... A big glowing ball of gas! Contains mainly H and He They have a core that is dense and super hot! Nuclear fusion is the source of their energy! ...
Vocabulary Review
... a star that has collapsed under gravity to the point that the electrons and protons have smashed together to form ...
... a star that has collapsed under gravity to the point that the electrons and protons have smashed together to form ...
Name: ______________________________# __________ Study Guide is due WEDNESDAY November 2
... Study Guide is due WEDNESDAY November 2nd 1.5 Quarter Assessment Test is FRIDAY Nov. 4th 1.5 Quarter Assessment Study Guide 1. What branch of earth science deals with studying the objects in space? ...
... Study Guide is due WEDNESDAY November 2nd 1.5 Quarter Assessment Test is FRIDAY Nov. 4th 1.5 Quarter Assessment Study Guide 1. What branch of earth science deals with studying the objects in space? ...
Astronomy Unit Test – Chapter 21
... 23. What category of star is Sirius B? 24. Which giant is the brightest? 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compa ...
... 23. What category of star is Sirius B? 24. Which giant is the brightest? 25. Predict what will happen when the sun runs out of fuel. 26. What is used to classify stars? 27. At which phase of the moon could a solar eclipse occur? 28. A star is twice as massive as the sun. How will its lifespan compa ...
Starry Starry Night Vocabulary
... Protostar: The hot core at the center of the collapsing cloud of gas and dust that one day becomes a star. This is the early stage in the process of star formation. Solar flare: A sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness on the sun or other star. A solar flare occurs when magnetic energy t ...
... Protostar: The hot core at the center of the collapsing cloud of gas and dust that one day becomes a star. This is the early stage in the process of star formation. Solar flare: A sudden, rapid, and intense variation in brightness on the sun or other star. A solar flare occurs when magnetic energy t ...
Galaxy Classification - Starry Night Education
... Milky Way galaxy? a. The plane of the solar system is coincident with the plane of the galaxy. b. The plane of the solar system is perpendicular to that of the Milky Way. c. The plane of the solar system is inclined at a small angle to the plane of the galaxy. d. The angle between the plane of the s ...
... Milky Way galaxy? a. The plane of the solar system is coincident with the plane of the galaxy. b. The plane of the solar system is perpendicular to that of the Milky Way. c. The plane of the solar system is inclined at a small angle to the plane of the galaxy. d. The angle between the plane of the s ...
1 - Quia
... a star. Use all of the stages listed below in your flow chart. Also include information about when a star moves from one cycle to the next. Use your textbook as a reference, and consult additional reference sources if needed. a. nebula b. protostar c. main sequence star d. red giant e. white dwarf f ...
... a star. Use all of the stages listed below in your flow chart. Also include information about when a star moves from one cycle to the next. Use your textbook as a reference, and consult additional reference sources if needed. a. nebula b. protostar c. main sequence star d. red giant e. white dwarf f ...
Spring Constellations
... Leo, the lion. Directly under the Big Dipper, the brightest star is Regulus (king of the stars, 80 LY away & 100X sun’s brightness.) 2nd brightest star is Denebola, lion’s hindquarters. Regulus is almost exactly on the ecliptic. This part of the sky with the Bear & Lion is the “carnivore’s corner.” ...
... Leo, the lion. Directly under the Big Dipper, the brightest star is Regulus (king of the stars, 80 LY away & 100X sun’s brightness.) 2nd brightest star is Denebola, lion’s hindquarters. Regulus is almost exactly on the ecliptic. This part of the sky with the Bear & Lion is the “carnivore’s corner.” ...
III. Contents of The Universe
... B. Stars – balls of hot gas that emit light The Sun is the closest star to us 1. Multiple Star System most stars that we see in the sky are parts of multiple star systems revolve around each other. two stars = binary star system. ex. Algol, eclipsing binary ...
... B. Stars – balls of hot gas that emit light The Sun is the closest star to us 1. Multiple Star System most stars that we see in the sky are parts of multiple star systems revolve around each other. two stars = binary star system. ex. Algol, eclipsing binary ...
The Sun and the Stars
... • Luminosity is a term that astronomers use when describing the total amount of energy it radiated by the star ( the twinkle) • It can be measured more precisely as a star’s total energy output per second, measured in Joules per second (J/s) • When discussion stars we always compare with the sun, so ...
... • Luminosity is a term that astronomers use when describing the total amount of energy it radiated by the star ( the twinkle) • It can be measured more precisely as a star’s total energy output per second, measured in Joules per second (J/s) • When discussion stars we always compare with the sun, so ...
Chapter 20 The Universe
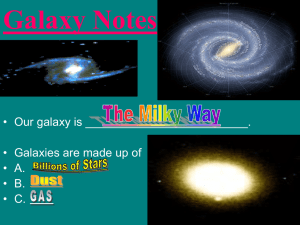
... Sirius (Dog star) only 9 light years away Proxima Centauri (closest) 4.25 light yrs Other than sun Galaxy- large grouping of stars -our solar system is part of Milky Way Galaxy - what we see as the Milky Way is only the edge (spiral galaxy) ...
... Sirius (Dog star) only 9 light years away Proxima Centauri (closest) 4.25 light yrs Other than sun Galaxy- large grouping of stars -our solar system is part of Milky Way Galaxy - what we see as the Milky Way is only the edge (spiral galaxy) ...
Where a limit?
... Gagarin JU.A.quantit of flights: 1 Call sign: "Cedar" the Touch: 01 hour, 48 minutes. A world championship: the first cosmonaut of a planet (on April, 12th, 1961 has made flight by spaceship "East"); the maximum cargo lifted into an orbit — 4725 kg; мах. Flight height — 327 km that remains a record ...
... Gagarin JU.A.quantit of flights: 1 Call sign: "Cedar" the Touch: 01 hour, 48 minutes. A world championship: the first cosmonaut of a planet (on April, 12th, 1961 has made flight by spaceship "East"); the maximum cargo lifted into an orbit — 4725 kg; мах. Flight height — 327 km that remains a record ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... h. space object that causes craters i. the force that exists between any two bodies in the universe j. process that developed the three layers of Earth and Moon’s interior k. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born l. the time in the life of a star when it generates energy by fus ...
... h. space object that causes craters i. the force that exists between any two bodies in the universe j. process that developed the three layers of Earth and Moon’s interior k. a large cloud of gas and dust in space where stars are born l. the time in the life of a star when it generates energy by fus ...
Astronomy Campus Assessment
... Scientists measure the movement of distant galaxies to learn more about the origin of the universe. You researched scientific data that showed that light from a distant galaxy is red-shifted. How would you evaluate the data? A. It indicates that the expansion of the universe has stopped, and so it d ...
... Scientists measure the movement of distant galaxies to learn more about the origin of the universe. You researched scientific data that showed that light from a distant galaxy is red-shifted. How would you evaluate the data? A. It indicates that the expansion of the universe has stopped, and so it d ...
the life cycle of stars
... • A star can be classified as one type of star early in its life, and as a different type of star as it gets older. • A star is classified differently as its properties change. ...
... • A star can be classified as one type of star early in its life, and as a different type of star as it gets older. • A star is classified differently as its properties change. ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.