* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stars are classified by how hot they are (temperature)
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
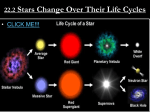
Stars Color of stars Different colors of gas denote different temperatures EX: flames in a fire can tell you the parts of the flame that are hotter than other parts White and clear blue are hotter than yellow Composition of Stars Spectrum- rainbow of colors Spectrograph – an instrument used by astronomers to spread starlight out into its colors (similar to a prism) Stars are made of various gases that produce different spectrum of light Classifying stars Stars are classified by how hot they are (temperature) and luminosity (brightness) How bright is that star? Magnitude is used to indicate how bright one object is compared with another A smaller number means a brighter star EX: Our sun is about +5. A blue star, which are the brightest, have an absolute magnitude of -10 Also used to show brightness of astronomical objects Venus shines with an apparent magnitude of 4.6 Full moon shines with an apparent magnitude of -12.5 Distances to the stars Light-year: distance light travels in one year Speed of light is ~300,000km/s (186,000mi/s) or 9.5 trillion km in one year Easier to use light year than km/s North Star is 431 light years away, or 4,080,000,000,000,000km Motion of the Stars Due to Earth's rotation, we see the sun rise and set, and stars come and go in the night Stars do move in space, but because they are so distant, their motion is hard for us to measure Over thousands of years, their movement would be obvious H-R diagram 1911, Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung plotted the temperature and brightness of stars on a graph 1913, American astronomer Henry Norris Russell made similar graphs Although they used different data, they came up with the same graphs Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram H-R Diagram When stars get old Most stars stay in main sequence for a long time, but not forever Average stars (our sun) turn into red giants and then white dwarfs More massive stars may explode and become violent – supernova Supernova Death of a large star by explosion After the explosion, two things can happen Neutron star (pulsar – spinning neutron star) Black holes Black Holes An object with more than three solar masses squeezed into a ball. So small and massive and its gravity is so strong that not even light can escape Doesn't gobble up other stars, but can pull in material from the nearby star