An Atlas of Stellar Spectra
... The problem of a classification according to luminosity is a difficult one. In the first place, lines or blends which may be useful at one spectral type may be quite insensitive at another. In fact, some lines which show a positive absolute-magnitude effect for some spectral classes may show a negat ...
... The problem of a classification according to luminosity is a difficult one. In the first place, lines or blends which may be useful at one spectral type may be quite insensitive at another. In fact, some lines which show a positive absolute-magnitude effect for some spectral classes may show a negat ...
Astronomy Astrophysics
... is a 16 detector-array infrared camera that samples 1.65 deg2 . Each 2048 × 2048 detector is sensitive over λ = 0.8–2.5 μm and delivers images with an average pixel scale of 0.34 arcsec px−1 . A single exposure corresponds to a patchy individual “pawprint” coverage on the sky. To fill the gaps and t ...
... is a 16 detector-array infrared camera that samples 1.65 deg2 . Each 2048 × 2048 detector is sensitive over λ = 0.8–2.5 μm and delivers images with an average pixel scale of 0.34 arcsec px−1 . A single exposure corresponds to a patchy individual “pawprint” coverage on the sky. To fill the gaps and t ...
constellations - Richmond and Glen Allen Weather
... What is a constellation? Constellation is derived from the Latin "constellatus," set with stars; from "com-," together, and "stellare," to shine; stella, a star. A constellation is a group of stars, which might form a pattern or shape within a specific area of the sky and is often named after people ...
... What is a constellation? Constellation is derived from the Latin "constellatus," set with stars; from "com-," together, and "stellare," to shine; stella, a star. A constellation is a group of stars, which might form a pattern or shape within a specific area of the sky and is often named after people ...
365 days of SKYWATCHING
... study - the Moon. Its rugged craters, high mountains and vast seas offer some of the finest details to be found in any astronomical target. It changes every night as the terminator - the line between sunset and shadow - progresses over the surface, revealing new details. Unlike a star chart, Moon fea ...
... study - the Moon. Its rugged craters, high mountains and vast seas offer some of the finest details to be found in any astronomical target. It changes every night as the terminator - the line between sunset and shadow - progresses over the surface, revealing new details. Unlike a star chart, Moon fea ...
Book Describing Techniques to Detect Transiting ExoPlanets
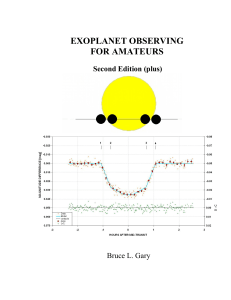
... of planets must exist! This is the message from the tally of ~ 400 extra-solar planetary systems (as of mid-2009). Among them are 60 exoplanets that transit in front of their star (46 that are brighter than 14th magnitude), and the number is growing with a doubling time of 1.1 years. It is important ...
... of planets must exist! This is the message from the tally of ~ 400 extra-solar planetary systems (as of mid-2009). Among them are 60 exoplanets that transit in front of their star (46 that are brighter than 14th magnitude), and the number is growing with a doubling time of 1.1 years. It is important ...
A spectroscopic study of detached binary systems using precise radial velocities
... Several months after this thesis began, a high-resolution spectrograph, Hercules, commenced operations at the Mt John University Observatory, to be used in conjuction with the 1metre McLellan telescope. For late-type stars, the anticipated velocity precision was . 10 m s−1 . The primary goals of thi ...
... Several months after this thesis began, a high-resolution spectrograph, Hercules, commenced operations at the Mt John University Observatory, to be used in conjuction with the 1metre McLellan telescope. For late-type stars, the anticipated velocity precision was . 10 m s−1 . The primary goals of thi ...
Tuomas Kangas
... Stars are divided into spectral classes depending on their effective (surface) temperatures, which determine their intrinsic colors. The sequence from hottest to coolest is O–B–A–F–G–K–M, followed by the even cooler brown dwarfs. O-type stars are blue, with temperatures T & 20000 K, while red M-type ...
... Stars are divided into spectral classes depending on their effective (surface) temperatures, which determine their intrinsic colors. The sequence from hottest to coolest is O–B–A–F–G–K–M, followed by the even cooler brown dwarfs. O-type stars are blue, with temperatures T & 20000 K, while red M-type ...
Search For Gas Giants Around Late-m Dwarfs - STARS
... We carried out a near-infrared radial velocity search for Jupiter-mass planets around 36 late M dwarfs. This survey was the first of its kind undertaken to monitor radial velocity variability of these faint dwarfs. For this unique survey we employed the 10-m Keck II on Mauna Kea in Hawaii. With a re ...
... We carried out a near-infrared radial velocity search for Jupiter-mass planets around 36 late M dwarfs. This survey was the first of its kind undertaken to monitor radial velocity variability of these faint dwarfs. For this unique survey we employed the 10-m Keck II on Mauna Kea in Hawaii. With a re ...
act_science_bellringers
... 24. H—“ Gravity causes part of a cloud of gas and dust to collapse and heat up”; gravitational force is the only one mentioned in the passage. 25. B—“ hydrogen to make helium in a shell surrounding its center.” This answer comes straight from the passage, and the question directs you to find the ans ...
... 24. H—“ Gravity causes part of a cloud of gas and dust to collapse and heat up”; gravitational force is the only one mentioned in the passage. 25. B—“ hydrogen to make helium in a shell surrounding its center.” This answer comes straight from the passage, and the question directs you to find the ans ...
Astronomy Astrophysics - Niels Bohr Institutet
... A major effort has been devoted to the determination of new isochrone ages for all stars for which this is possible. Particular attention has been given to a realistic treatment of statistical biases and error estimates, as standard techniques tend to underestimate these effects and introduce spurious ...
... A major effort has been devoted to the determination of new isochrone ages for all stars for which this is possible. Particular attention has been given to a realistic treatment of statistical biases and error estimates, as standard techniques tend to underestimate these effects and introduce spurious ...
Altas Farnese
... near the north pole (cf. Section A.2.2). (7) The ecliptic crosses the equator 5° west of the colure lines. This arrangement is wrong by definition, as precession moves the sky along the ecliptic, suggesting that the sculptor made the change because of his lack of astronomical knowledge. (8) The stri ...
... near the north pole (cf. Section A.2.2). (7) The ecliptic crosses the equator 5° west of the colure lines. This arrangement is wrong by definition, as precession moves the sky along the ecliptic, suggesting that the sculptor made the change because of his lack of astronomical knowledge. (8) The stri ...
Selected observation targets at a glance per constellation
... rotational velocity of 245 km/s. White main sequence star, evolving into a subgiant. A massive asteroid belt was confirmed in the star’s orbit in 2001. This was the first extra-solar asteroid belt discovered. 17 Leporis, SS Leporis, a spectroscopic binary, components belong to the spectral classes A ...
... rotational velocity of 245 km/s. White main sequence star, evolving into a subgiant. A massive asteroid belt was confirmed in the star’s orbit in 2001. This was the first extra-solar asteroid belt discovered. 17 Leporis, SS Leporis, a spectroscopic binary, components belong to the spectral classes A ...