Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears
... Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the observer. The absolute magnitude of stars is measured on a Scale ...
... Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the observer. The absolute magnitude of stars is measured on a Scale ...
Extra Questions Stellar properties
... How many times brighter or dimmer than the Sun is it? 3 Barnard’s star, the star with the largest known proper motion in the skjy can be seen only with a telescope because its apparent magnitude is +9.54. Its distance from Earth is 1.81 parsecs. How much closer to Earth would it have to be in order ...
... How many times brighter or dimmer than the Sun is it? 3 Barnard’s star, the star with the largest known proper motion in the skjy can be seen only with a telescope because its apparent magnitude is +9.54. Its distance from Earth is 1.81 parsecs. How much closer to Earth would it have to be in order ...
Astronomy word grid
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
PH507 - University of Kent
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
Main Sequence Stars
... The rst classi cation of stars was suggested by Einar Hertzsprung in Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate bein ...
... The rst classi cation of stars was suggested by Einar Hertzsprung in Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate bein ...
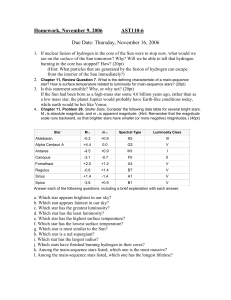
Homework, August 29, 2002 AST110-6
... e. Which star has the highest surface temperature? f. Which star has the lowest surface temperature? g. Which star is most similar to the Sun? h. Which star is a red supergiant? i. Which star has the largest radius? j. Which stars have finished burning hydrogen in their cores? k. Among the main-sequ ...
... e. Which star has the highest surface temperature? f. Which star has the lowest surface temperature? g. Which star is most similar to the Sun? h. Which star is a red supergiant? i. Which star has the largest radius? j. Which stars have finished burning hydrogen in their cores? k. Among the main-sequ ...
Regulus the Star njw
... The star’s name regulus comes from the Latin word Rex which means King It is associated with many cultures like the Greeks , Arabs, and Ancient Babylon It also is know as one of the four Royal Stars of the Heavens ...
... The star’s name regulus comes from the Latin word Rex which means King It is associated with many cultures like the Greeks , Arabs, and Ancient Babylon It also is know as one of the four Royal Stars of the Heavens ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
Another exAmple: expository mode
... known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. I ...
... known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. I ...
Physical properties of stars
... Absolute magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star Apparent magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their apparent magnitude. Absolute motion- the actual motion of stars in spa ...
... Absolute magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star Apparent magnitude depends on: The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their apparent magnitude. Absolute motion- the actual motion of stars in spa ...
astronomy 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... 6. What does the lifetime of a star depend on? IT’S MASS. 7. What is a supernova? EXPLOSION OF A HIGH MASS STAR. 8. What is a star system? A GROUP OF TWO OR MORE STARS. 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What ...
... 6. What does the lifetime of a star depend on? IT’S MASS. 7. What is a supernova? EXPLOSION OF A HIGH MASS STAR. 8. What is a star system? A GROUP OF TWO OR MORE STARS. 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What ...
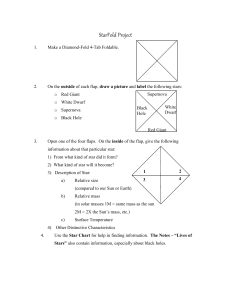
Use this form to take notes in class about stars
... “clump” together? ______________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. What causes the center of the “core” to heat up? ...
... “clump” together? ______________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. What causes the center of the “core” to heat up? ...
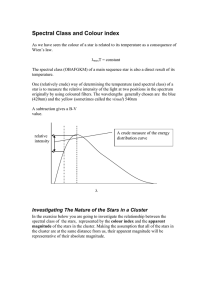
Spectral Class and Colour index
... Spectral Class and Colour index As we have seen the colour of a star is related to its temperature as a consequence of Wien’s law. λmaxT = constant The spectral class (OBAFGKM) of a main sequence star is also a direct result of its temperature. One (relatively crude) way of determining the temperatu ...
... Spectral Class and Colour index As we have seen the colour of a star is related to its temperature as a consequence of Wien’s law. λmaxT = constant The spectral class (OBAFGKM) of a main sequence star is also a direct result of its temperature. One (relatively crude) way of determining the temperatu ...
1 - Pitt County Schools
... 3. What factors determine a star’s apparent magnitude? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. The H-R diagram shows the relationship between what two factors? _________________________ ...
... 3. What factors determine a star’s apparent magnitude? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ 4. The H-R diagram shows the relationship between what two factors? _________________________ ...
Homework 7
... 2. Why are carbonaceous chondritic meteorites thought to be the oldest pristine material from the inner solar system? ...
... 2. Why are carbonaceous chondritic meteorites thought to be the oldest pristine material from the inner solar system? ...
The distance that light travels in a year is 9.5 trillion km. The
... Space Quiz Review – Go to 2-103 Tomorrow SC.8.E.5.1 SC.8.E.5.2 SC.8.E.5.3 SC.8.E.5.4 SC.8.E.5.5 ...
... Space Quiz Review – Go to 2-103 Tomorrow SC.8.E.5.1 SC.8.E.5.2 SC.8.E.5.3 SC.8.E.5.4 SC.8.E.5.5 ...