* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Notes – #6 Our Sky Through Binoculars and Telescopes 1
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting instrument wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
James Webb Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
European Southern Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Jodrell Bank Observatory wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of the telescope wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
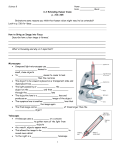
Name: ___________________________ Notes – #6 Our Sky Through Binoculars and Telescopes 1. Binoculars and telescopes do three things: A. Collect more _______________________ B. Make objects look ____________________ C. ________________ the image 2. The bending of light as it passes through a lens is called _______________________. 3. Who made a better working version of the refracting telescope? 4. Newton realized that a lens brings light of different colors to a different ____________. This distortion is called __________________________________. 5. Who was the first person to build a working reflecting telescope? 6. A reflecting telescope uses a __________________ to focus the light instead of a lens. 7. M31, the Andromeda Galaxy, is ___________________________ light years away. 8. In the sword region of the Orion constellation, what will you see? 9. On what object can you see craters and mountains with a pair of binoculars? 10. Why can you see craters on the Moon more easily at the dark/light boundary (i.e. the terminator)? 11. What did Galileo see when he pointed his telescope at Jupiter? 12. Does Venus have phases (like the Moon phases)? 13. The head of Cygnus (The Swan) is a __________________ star system. 14. A large grouping of stars clustered together is called a _________________________. 15. True or False: New stars are forming within the Orion Nebula.