* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
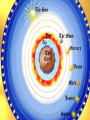
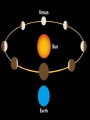
Download What is the difference between geocentric and heliocentric theories?
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
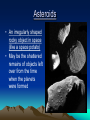
SHOW ME! 10 volunteers 1 sun 9 planets Geocentric vs Heliocentric • “Geo” means Earth • “Helio” means sun Ancient Observations • The ancient Greeks observed the sky and noticed that the moon, sun, and stars seemed to move in a circle around the Earth. • It seemed that the Earth was not moving and everything in the heavens revolved around the Earth. • As it turned out, it was very difficult to prove that the planets did not revolve around the Earth without leaving the planet. Geocentric Theory • Ancient Greeks such as Aristotle believed that the universe was perfect and finite, with the Earth at the exact center. • This is the geocentric theory, which stated, the planets, moon, sun, and stars revolve around the Earth. Ptolemy (85-165 AD) • In AD 140 the Greek astronomer Ptolemy revised the geocentric model to explain all the planetary motions. • His model had the planets move in little circles that also moved in bigger circles. • This belief persisted for about 1500 years. Copernicus (1473-1543) • In the early 1500’s the polish astronomer Copernicus suggested that the Sun, not Earth, was the center of the solar system and the planets revolved around it. • This is the Helios means “sun” Heliocentric Theory. in Greek. Galileo (year 1609) • One of the first to use a telescope to see objects in space Isaac Newton (1687) • Showed that all objects in the universe attract each other by gravity What is a galaxy? • A galaxy is a large grouping of stars, gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. 1. Spiral 3Types of Galaxies 3. Irregular 2. Elliptical Spiral Galaxies • Shaped like flattened disks with one or more spiral arms. • Our galaxy, Milky Way, is a spiral galaxy. • Our solar system is located in one of the spiral arms. Elliptical Galaxies • About 1/3 of all galaxies. • massive, round blobs of stars. • Round or elliptical in shape. • Contain very little gas or dust. • Because of little gas, no new stars are forming. • The largest and smallest galaxies are elliptical galaxies. Irregular Galaxies • No defined shape • Do not fit into any other category. • Chaotic mix of stars, gas and dust • Usually found near large spiral galaxies who may be distorting their shape. THINGS IN OUR SKY!!! • A natural satellite is any celestial body in space that orbits around a larger body. Meteorite, Meteoroid, Meteor? What’s the difference? Meteorite vs. Meteoroid • Meteoroid = while in space a meteorite is called a meteoroid • Meteorite = a small rock or rocky grain that strikes Earth’s surface • So the difference is just based on where the rock is when you are describing it Meteor • Sometimes called a “Shooting Star” • When a meteorite enters Earth’s atmosphere, friction causes them to burn up, producing a streak of light Comets • Bodies in space made up of ice, dust, small gritty particles • Sometimes called “dirty snowballs” • When close to the sun, ice vaporizes, producing a spectacular streak of gas, referred to as a “tail” • Many in a regular orbit around the sun Comets Famous Comets • Comet Hale-Bopp • Halley’s Comet • Comet Kohoutek Asteroids • An irregularly shaped rocky object in space (like a space potato) • May be the shattered remains of objects left over from the time when the planets were formed How big are asteroids? • Larger than meteoroids • (In fact, the main difference between meteoroids and asteroids is their size.) • Size ranges from 10 feet across to bigger than a mountain Asteroids • Approx. 150,000 asteroids in the Solar System • Most are in a band that orbit the sun between Mars and Jupiter (Asteroid Belt) • Why are there all of those asteroids between Mars and Jupiter and not another planet?