The Periodic Table OL Page 1 of 2 G. Galvin Name: Periodic Table
... 1. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of the elements recur periodically, i.e. the properties displayed by the element are repeated at regular intervals in oth ...
... 1. Mendeleev: Arranged the elements in order of increasing weight. Defn: Mendeleev’s Periodic Law: When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic weight, the properties of the elements recur periodically, i.e. the properties displayed by the element are repeated at regular intervals in oth ...
Chapter 6 Vocabulary crossword puzzle
... 3. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially filled 6. Measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound; the element named Cesium has the lowest amount, while the element named Fluorine has the highest amount 7. Term that refers to a se ...
... 3. Elements in which the highest occupied s and p sublevels are partially filled 6. Measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons when the atom is in a compound; the element named Cesium has the lowest amount, while the element named Fluorine has the highest amount 7. Term that refers to a se ...
here
... electrons to be the “bonding/reactive” electrons. Then give an example of an element that would be likely to bond and one that would not be likely to bond based on your explanation. ...
... electrons to be the “bonding/reactive” electrons. Then give an example of an element that would be likely to bond and one that would not be likely to bond based on your explanation. ...
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW Electron Configurations Explain the
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
... Explain the relationship between energy levels and sublevels and atomic orbitals. Describe the shapes of the s & p orbitals. Recall the reason for the x, y, z, axes. Apply the Pauli exclusion principle, the aufbau principle, and Hund’s rule to write electron configurations using orbital diag ...
Power point on the Periodic Table
... Vertical columns in the periodic table: group Numbered from 1 to 18 Elements in the same family (group) share similar physical and chemical properties The group also tells you the amount of valence electrons ...
... Vertical columns in the periodic table: group Numbered from 1 to 18 Elements in the same family (group) share similar physical and chemical properties The group also tells you the amount of valence electrons ...
C2_Chemistry_Summary_Topic_1
... Keywords: proton, neutron, electron, shells, negative, atomic number, mass number ...
... Keywords: proton, neutron, electron, shells, negative, atomic number, mass number ...
Periodic Table of Elements * Study Guide
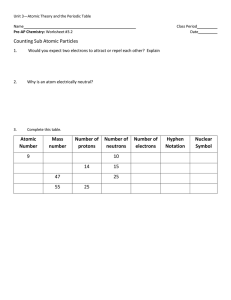
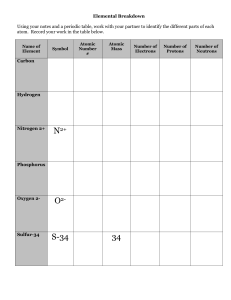
... Study and understand the following: Atomic Structure: How to find an element’s: atomic number atomic mass what two particles make up the atomic mass? what makes up the atom’s volume? # of protons Electrical charge of proton, electron, neutron # of electrons # of neutrons group # ...
... Study and understand the following: Atomic Structure: How to find an element’s: atomic number atomic mass what two particles make up the atomic mass? what makes up the atom’s volume? # of protons Electrical charge of proton, electron, neutron # of electrons # of neutrons group # ...
Dmitri MendeleevанааA Russian chemist, noticed a repeating
... Dmitri Mendeleev A Russian chemist, noticed a repeating pattern of chemical properties in the elements that were known at the time. Mendeleev arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic mass to form something close to the modern day periodic table. The pattern of repeating ord ...
... Dmitri Mendeleev A Russian chemist, noticed a repeating pattern of chemical properties in the elements that were known at the time. Mendeleev arranged the elements in the order of increasing atomic mass to form something close to the modern day periodic table. The pattern of repeating ord ...
Summative Assessment Study Guide Name: Due date: SPS1
... SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process half-life as related to radioactive decay. d. Describe nuclear energy, its pra ...
... SPS3. Students will distinguish the characteristics and components of radioactivity. a. Differentiate among alpha and beta particles and gamma radiation. b. Differentiate between fission and fusion. c. Explain the process half-life as related to radioactive decay. d. Describe nuclear energy, its pra ...
Ch. 4: Atoms and the Periodic Table – Study Guide
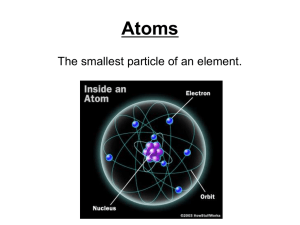
... Ch. 4: Atoms and the Periodic Table – Study Guide The first person who suggested that matter was made up of atoms was the Greek philosopher Democritus. The word atom comes from the Greek word that means “unable to be divided.” Dalton’s atomic theory stated that every element was made of atoms that c ...
... Ch. 4: Atoms and the Periodic Table – Study Guide The first person who suggested that matter was made up of atoms was the Greek philosopher Democritus. The word atom comes from the Greek word that means “unable to be divided.” Dalton’s atomic theory stated that every element was made of atoms that c ...
File
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
What is the history of chemistry and elements
... 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinations with other elements in ...
... 2400 year ago Greek philosophers proposed that everything was made of four basic substances – air, water, fire, and earth. Today chemists know that there are 100+ basic substances, or elements. Everything on Earth is made of these elements or combinations with other elements in ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ...
L.O.
... 11. Describe the atom as having a vary small positively charged nucleus with negatively charged electrons moving around outside the nucleus describe the location and charge of the proton, neutron and electron ...
... 11. Describe the atom as having a vary small positively charged nucleus with negatively charged electrons moving around outside the nucleus describe the location and charge of the proton, neutron and electron ...
Chapter 6 Review“The Periodic Table”
... 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What does the number 84 represent in the name krypton-84? 6. What is the correct complete symbol for an atom of tritium? 7. Dalton said that atoms were indivisible and atoms ...
... 3. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. 4. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. 5. What does the number 84 represent in the name krypton-84? 6. What is the correct complete symbol for an atom of tritium? 7. Dalton said that atoms were indivisible and atoms ...
CHEMISTRY TERMS Period: Elements in the same horizontal row
... Period: Elements in the same horizontal row with the same ground state energy level. Periodic Law: Elements list in order of their atomic numbers that fall into reoccurring groups. Ionic Radius: the radius of an atom’s ion, measured by the distance between ions in a crystal lattice. Atomic Radius: o ...
... Period: Elements in the same horizontal row with the same ground state energy level. Periodic Law: Elements list in order of their atomic numbers that fall into reoccurring groups. Ionic Radius: the radius of an atom’s ion, measured by the distance between ions in a crystal lattice. Atomic Radius: o ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.