Clarke`s column neurons as the focus of a corticospinal corollary circuit
... and excitatory inputs to Clarke’s column neurons established local spinal circuits with the capacity to mark or modulate incoming proprioceptive input. Together, our genetic, anatomical and physiological results indicate that Clarke’s column spinocerebellar neurons nucleate local spinal corollary ci ...
... and excitatory inputs to Clarke’s column neurons established local spinal circuits with the capacity to mark or modulate incoming proprioceptive input. Together, our genetic, anatomical and physiological results indicate that Clarke’s column spinocerebellar neurons nucleate local spinal corollary ci ...
Do superior colliculus projection zones in the inferior pulvinar
... without further processing so that neurons labelled with FB could be located. Another series was processed for myelin according to the procedure of Gallyas (1979), and the third series was processed for CO following the procedures of Wong-Riley (1979). Both the myelin and CO procedures allowed us to ...
... without further processing so that neurons labelled with FB could be located. Another series was processed for myelin according to the procedure of Gallyas (1979), and the third series was processed for CO following the procedures of Wong-Riley (1979). Both the myelin and CO procedures allowed us to ...
The occipitoparietal pathway of the macaque monkey: comparison
... the fundus of the superior temporal area (FST). Although these observations could be interpreted as supporting the anatomicalhierarchical model, the evidence is still inconclusive, mainly because comparisons have been made between areas belonging to the occipitoparietal and occipitotemporal pathways ...
... the fundus of the superior temporal area (FST). Although these observations could be interpreted as supporting the anatomicalhierarchical model, the evidence is still inconclusive, mainly because comparisons have been made between areas belonging to the occipitoparietal and occipitotemporal pathways ...
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... modified neural structures. The very "damage" is not the development of the pathological process. He plays the role of the causes and conditions of this development, which is carried out its own endogenous mechanisms of nervous system damage. At the level of relations interneuronal such integration ...
... modified neural structures. The very "damage" is not the development of the pathological process. He plays the role of the causes and conditions of this development, which is carried out its own endogenous mechanisms of nervous system damage. At the level of relations interneuronal such integration ...
Descending Inhibitory Systems
... of descending pathways may vary from excitation to inhibition depending on the response characteristics and laminar location of the spinal dorsal horn neuron (Laird and Cervero, 1990); this is in line with the evidence showing a differential effect of specific brain areas upon superficial versus dee ...
... of descending pathways may vary from excitation to inhibition depending on the response characteristics and laminar location of the spinal dorsal horn neuron (Laird and Cervero, 1990); this is in line with the evidence showing a differential effect of specific brain areas upon superficial versus dee ...
Lillienfeld: Chapter 3 lecture PowerPoint
... • During learning, long-term potentiation occurs and makes synapses perform better. • There is only limited recovery following brain injury or serious illness. ...
... • During learning, long-term potentiation occurs and makes synapses perform better. • There is only limited recovery following brain injury or serious illness. ...
Neural correlates of incidental and directed facial emotion
... three nodes, with consequent dysregulation in their interactions that may increase vulnerability to mood and anxiety disorders in adolescence (Nelson et al., 2005). One way to test whether an increase in prefrontal regulation of sub-cortical activity is a possible bio-behavioral mechanism for the de ...
... three nodes, with consequent dysregulation in their interactions that may increase vulnerability to mood and anxiety disorders in adolescence (Nelson et al., 2005). One way to test whether an increase in prefrontal regulation of sub-cortical activity is a possible bio-behavioral mechanism for the de ...
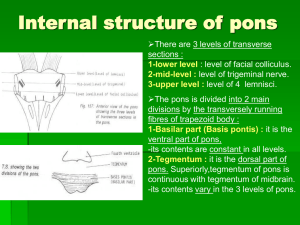
07-pons + midbrain2009-03-24 08:441.9 MB
... by stroke,tumour or multiple sclerosis causes : 1-epsilateral cranial nerve dysfunction + contralateral spastic hemiparesis. 2-hyperreflexia & an extensor plantar response (upper motor neurone lesion). 3-contalateral hemisensory loss. 4-ipsilateral incoordination (ataxia). 5-it can affect eye moveme ...
... by stroke,tumour or multiple sclerosis causes : 1-epsilateral cranial nerve dysfunction + contralateral spastic hemiparesis. 2-hyperreflexia & an extensor plantar response (upper motor neurone lesion). 3-contalateral hemisensory loss. 4-ipsilateral incoordination (ataxia). 5-it can affect eye moveme ...
슬라이드 1 - Brain Facts
... Under conditions of persistent injury, C fibers fire repetitively and the response of dorsal horn neurons increase progressively (“wind-up” phenomenon). This is due to activation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type glutamate receptor and diffusion of substance P that sensitizes adjacent neurons ...
... Under conditions of persistent injury, C fibers fire repetitively and the response of dorsal horn neurons increase progressively (“wind-up” phenomenon). This is due to activation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type glutamate receptor and diffusion of substance P that sensitizes adjacent neurons ...
[PDF]
... eGFPþ neuron. Neurons were selected for analysis based on expression of eGFP throughout the cell body and its processes. Cells were excluded if they exhibit excessive overlapping with adjacent eGFP expressing neurons, their morphology is not intact, they have membrane varicosities, or they show sign ...
... eGFPþ neuron. Neurons were selected for analysis based on expression of eGFP throughout the cell body and its processes. Cells were excluded if they exhibit excessive overlapping with adjacent eGFP expressing neurons, their morphology is not intact, they have membrane varicosities, or they show sign ...
Ventral Medial Nucleus Neurons Send Thalamocortical Afferents
... 2004; Kuramoto et al. 2011) and relays basal ganglia information to the cerebral cortex including motor areas. Thus, the VM is at least partly associated with the motor function as well as with other cortical functions. In addition to the VM, the ventral anterior and ventral lateral nuclear complex ...
... 2004; Kuramoto et al. 2011) and relays basal ganglia information to the cerebral cortex including motor areas. Thus, the VM is at least partly associated with the motor function as well as with other cortical functions. In addition to the VM, the ventral anterior and ventral lateral nuclear complex ...
- Northumbria Research Link
... in higher brain areas whereas TMS measurements reflect neuronal responsiveness of a different portion of the CNS (motor cortex & spine), specifically related to motor function. Based on this, the two methods focus on somewhat different brain areas/function so it is difficult to directly compare resu ...
... in higher brain areas whereas TMS measurements reflect neuronal responsiveness of a different portion of the CNS (motor cortex & spine), specifically related to motor function. Based on this, the two methods focus on somewhat different brain areas/function so it is difficult to directly compare resu ...
kwanPNAS08
... are generated sequentially so that early-born neurons occupy the deep layers and later-born neurons migrate past older neurons to settle in more superficial layers. The molecular mechanisms that regulate the laminar position and identity of projection neurons are being unraveled (3, 7). Previous stu ...
... are generated sequentially so that early-born neurons occupy the deep layers and later-born neurons migrate past older neurons to settle in more superficial layers. The molecular mechanisms that regulate the laminar position and identity of projection neurons are being unraveled (3, 7). Previous stu ...
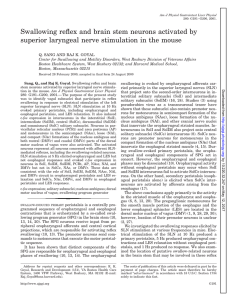
Circuit Architecture of VTA Dopamine Neurons Revealed by
... neurons, we used DAT-Cre mice, in which Cre mimics the expression pattern of the plasma membrane dopamine transporter (Bäckman et al., 2006; Lammel et al., 2015), and GAD2Cre mice, in which Cre mimics the expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase-2 (Taniguchi et al., 2011), an enzyme that coverts g ...
... neurons, we used DAT-Cre mice, in which Cre mimics the expression pattern of the plasma membrane dopamine transporter (Bäckman et al., 2006; Lammel et al., 2015), and GAD2Cre mice, in which Cre mimics the expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase-2 (Taniguchi et al., 2011), an enzyme that coverts g ...
Visually induced and spontaneous behavior in the zebrafish
... Behavior is often conceived as resulting from a stimulus-response association. Under this paradigm, understanding the nervous system is reduced to finding the relation between a sensory input and a motor output. Yet, in naturally behaving animals, motor actions influence sensory perceptions just as ...
... Behavior is often conceived as resulting from a stimulus-response association. Under this paradigm, understanding the nervous system is reduced to finding the relation between a sensory input and a motor output. Yet, in naturally behaving animals, motor actions influence sensory perceptions just as ...
Acceleration of visually cued conditioned fear through the
... groups indicated that c-fos expression was significantly higher for all groups that showed cued fear responses after one session of conditioning than for the light-conditioned sham lesion group, which did not (P < 0.01, t-test; Fig. 4d). This is consistent with the hypothesis that activation of the ...
... groups indicated that c-fos expression was significantly higher for all groups that showed cued fear responses after one session of conditioning than for the light-conditioned sham lesion group, which did not (P < 0.01, t-test; Fig. 4d). This is consistent with the hypothesis that activation of the ...
Swallowing reflex and brain stem neurons activated by superior
... SLN stimulation at 5 Hz elicited oropharyngeal and LES but not esophageal responses and evoked c-fos expression in neurons in SolI, SolIM, SolDM, PCRt, AP, NAsc, NAl, and DMVc but not in SolCe, NAc, or DMVr. These data are consistent with the role of SolI, SolIM, SolDM, NAsc, NAl, and DMVc circuit i ...
... SLN stimulation at 5 Hz elicited oropharyngeal and LES but not esophageal responses and evoked c-fos expression in neurons in SolI, SolIM, SolDM, PCRt, AP, NAsc, NAl, and DMVc but not in SolCe, NAc, or DMVr. These data are consistent with the role of SolI, SolIM, SolDM, NAsc, NAl, and DMVc circuit i ...
FREE Sample Here
... MOD: Module 2-1 Neurons: The Body’s Wiring OBJ: 2.3 KEY: Evaluate/Explain NOT: www Which of the following is NOT true of action potentials? A) They are generated according to an all-or-none principle. B) They all travel at the same speed. C) They are electrical charges that shoot down the axon. D) T ...
... MOD: Module 2-1 Neurons: The Body’s Wiring OBJ: 2.3 KEY: Evaluate/Explain NOT: www Which of the following is NOT true of action potentials? A) They are generated according to an all-or-none principle. B) They all travel at the same speed. C) They are electrical charges that shoot down the axon. D) T ...
gross_neuroanatomy-1
... Precuneus is one of the most relevant nodes of the “default mode network” a set of brain regions that exhibit high metabolic consumption and it seems to be associated with conscious processing of stimuli and awareness ...
... Precuneus is one of the most relevant nodes of the “default mode network” a set of brain regions that exhibit high metabolic consumption and it seems to be associated with conscious processing of stimuli and awareness ...
Mouse Nerve Growth Factor Prevents Degeneration of Axotomized
... replaced with normal saline at a continuous, slow intravenous drip throughout surgery. Under sterile conditions, the dura was exposed through a lo-mm trephine hole drilled 10-20 mm anterior to the interaural line. The sagittal sinus was retracted and the 2 hemispheres separated. The body of the fomi ...
... replaced with normal saline at a continuous, slow intravenous drip throughout surgery. Under sterile conditions, the dura was exposed through a lo-mm trephine hole drilled 10-20 mm anterior to the interaural line. The sagittal sinus was retracted and the 2 hemispheres separated. The body of the fomi ...
The Dorsal Visual System Predicts Future and Remembers Past Eye
... the lateral and ventral intraparietal areas (LIP, VIP), and the middle temporal (MT) and medial superior temporal (MST) areas. As reported previously, neurons showed tonic eye-position-related activity during fixation. In addition, they showed a variety of transient changes in activity around the ti ...
... the lateral and ventral intraparietal areas (LIP, VIP), and the middle temporal (MT) and medial superior temporal (MST) areas. As reported previously, neurons showed tonic eye-position-related activity during fixation. In addition, they showed a variety of transient changes in activity around the ti ...
Changes in the N1-P2 Complex after Speech
... there is tremendous potential for clinical application. The N1-P2 complex could be used to monitor neurophysiologic changes during speech-sound acquisition after cochlear implantation, hearing aid use, or any other form of auditory learning. More importantly, physiologic correlates of perception cou ...
... there is tremendous potential for clinical application. The N1-P2 complex could be used to monitor neurophysiologic changes during speech-sound acquisition after cochlear implantation, hearing aid use, or any other form of auditory learning. More importantly, physiologic correlates of perception cou ...
L
... are determined by the region of brain in which the seizure occurs. The seizure occupies a limited volume of cerebral cortex. Complex Partial Seizure: consciousness is impaired.The seizure occupies a larger volume of cerebral cortex such that normal thinking is impaired. Often, complex partial seizur ...
... are determined by the region of brain in which the seizure occurs. The seizure occupies a limited volume of cerebral cortex. Complex Partial Seizure: consciousness is impaired.The seizure occupies a larger volume of cerebral cortex such that normal thinking is impaired. Often, complex partial seizur ...
Research in Mammalian Mastication1
... or (2) mastication arises de novo with development of completely separate neuromuscular elements associated with dental eruption (Bosma, 1967; Moyers, 1973). Dr. Herring presents new data on this problem. The possibility exists that developmental timing of masticatory muscles, nerves, and neurons is ...
... or (2) mastication arises de novo with development of completely separate neuromuscular elements associated with dental eruption (Bosma, 1967; Moyers, 1973). Dr. Herring presents new data on this problem. The possibility exists that developmental timing of masticatory muscles, nerves, and neurons is ...
Proprioception: - e
... feedback mechanisms that generate an appropriate corrective torque based on body-sway motion detected primarily by visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensory system. Thus, proprioception largely contributes to postural regulation. When proprioceptive information was altered (tendon vibration con ...
... feedback mechanisms that generate an appropriate corrective torque based on body-sway motion detected primarily by visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensory system. Thus, proprioception largely contributes to postural regulation. When proprioceptive information was altered (tendon vibration con ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.






![[PDF]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008803384_1-36fd0609f80954d0c3765babde2de933-300x300.png)