Georgetown University Liberal Studies Graduate Program Spring
... The word “renaissance” means “rebirth” and thus the use of the term inevitably yields the question: rebirth of what? While it becomes clear, as one follows the period that has received that label, that much of classical, Greek and Roman, culture is re-achieving the center of the stage, this realizat ...
... The word “renaissance” means “rebirth” and thus the use of the term inevitably yields the question: rebirth of what? While it becomes clear, as one follows the period that has received that label, that much of classical, Greek and Roman, culture is re-achieving the center of the stage, this realizat ...
AP Euro Jeopardy
... The Corpus Hermeticum contained writings on which topics? The occult, theology and philosphy ...
... The Corpus Hermeticum contained writings on which topics? The occult, theology and philosphy ...
UNIT ONE STUDY GUIDE 2015
... 1. ANALYZE HOW THE Hundred Years’ War, Black Death, and Great Schism (Avignon Papacy) led to the Renaissance. Include and define the following: vernacular writing, simony, pluralism, indulgences, Avignon Papacy, and Great Schism [Daily Questions Videos and Duncan Notes; look in your book for definit ...
... 1. ANALYZE HOW THE Hundred Years’ War, Black Death, and Great Schism (Avignon Papacy) led to the Renaissance. Include and define the following: vernacular writing, simony, pluralism, indulgences, Avignon Papacy, and Great Schism [Daily Questions Videos and Duncan Notes; look in your book for definit ...
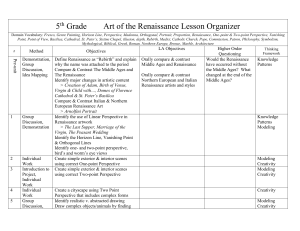
5th Grade Art of the Renaissance Lesson Organizer Domain
... Point, Point of View, Basilica, Cathedral, St. Peter’s, Sistine Chapel, illusion, depth, Rebirth, Medici, Catholic Church, Pope, Commission, Patron, Philosophy, Symbolism, Mythological, Biblical, Greek, Roman, Northern Europe, Bronze, Marble, Architecture LA Objectives Higher Order Thinking ...
... Point, Point of View, Basilica, Cathedral, St. Peter’s, Sistine Chapel, illusion, depth, Rebirth, Medici, Catholic Church, Pope, Commission, Patron, Philosophy, Symbolism, Mythological, Biblical, Greek, Roman, Northern Europe, Bronze, Marble, Architecture LA Objectives Higher Order Thinking ...
Week 17
... Does Machiavelli think a Prince should be loved or hated? Why? What does covetous mean? What is meant by preparations? Why is Machiavelli seen as controversial? What traits make a good head of state? ...
... Does Machiavelli think a Prince should be loved or hated? Why? What does covetous mean? What is meant by preparations? Why is Machiavelli seen as controversial? What traits make a good head of state? ...
The Renaissance
... needed wealthy patrons to support it. Political changes in the ruling class of Italy shortly before this period had led to the rulers of most of the major city states being “new men” without much of a political history. They attempted to legitimise themselves with conspicuous display, with ostentati ...
... needed wealthy patrons to support it. Political changes in the ruling class of Italy shortly before this period had led to the rulers of most of the major city states being “new men” without much of a political history. They attempted to legitimise themselves with conspicuous display, with ostentati ...
Medieval Period… Middle Ages… Dark Ages… Who cares?
... The Middle Ages: Birth of an Idea The phrase “Middle Ages” tells us more about the Renaissance that followed it than it does about the era itself. Starting around the 14th century, European thinkers, writers and artists began to look back and celebrate the art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome. ...
... The Middle Ages: Birth of an Idea The phrase “Middle Ages” tells us more about the Renaissance that followed it than it does about the era itself. Starting around the 14th century, European thinkers, writers and artists began to look back and celebrate the art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome. ...
WH_Chpt1_Sect2
... events/individual’s impact on the Renaissance and Reformation (should include a brief statement[2-3 sentences] of what happened and a picture. They will be expected to add 10 events or individual contributions from every section of the text assigned for reading (totaling 30 items). This will be an o ...
... events/individual’s impact on the Renaissance and Reformation (should include a brief statement[2-3 sentences] of what happened and a picture. They will be expected to add 10 events or individual contributions from every section of the text assigned for reading (totaling 30 items). This will be an o ...
Review Sheet Renaissance Test
... Hundred Years War, Black Death, Rise of Nations, Rise of Towns and Trade What was the Renaissance? Time period of achievement and recovery in Europe AFTER the Middle Ages Means rebirth in French Why did the Renaissance start in Italy (2 reasons)? Great wealth was generated in Northern Italy ...
... Hundred Years War, Black Death, Rise of Nations, Rise of Towns and Trade What was the Renaissance? Time period of achievement and recovery in Europe AFTER the Middle Ages Means rebirth in French Why did the Renaissance start in Italy (2 reasons)? Great wealth was generated in Northern Italy ...
Chapt. 13 - Northern Renaissance
... Printing Press c. 1440 Gutenburg’s Bible was the first European book printed using moveable type- the printing press Printing encouraged scholarly research and increase desire of public to gain knowledge (access to works of the past) Lay piety Ideas of the Renaissance and Reformation could not ...
... Printing Press c. 1440 Gutenburg’s Bible was the first European book printed using moveable type- the printing press Printing encouraged scholarly research and increase desire of public to gain knowledge (access to works of the past) Lay piety Ideas of the Renaissance and Reformation could not ...
Italian Renaissance Toward the end of the 14th century AD, a
... were living in a new age. The barbarous, unenlightened “Middle Ages” were over, they said; the new age would be a rebirth of learning and literature, art and culture. This was the birth of the period now known as the Renaissance. For centuries, scholars have agreed that the Italian Renaissance (anot ...
... were living in a new age. The barbarous, unenlightened “Middle Ages” were over, they said; the new age would be a rebirth of learning and literature, art and culture. This was the birth of the period now known as the Renaissance. For centuries, scholars have agreed that the Italian Renaissance (anot ...
Renaissance
... Renaissance spread from Italy as scholars from other areas visited Italian city-states & took the new ideas they saw back Kings bought Renaissance art, helping to spread new ideas Renaissance ideas spread to the Holy Roman Empire (Germany), England, France, Belgium, Netherlands ...
... Renaissance spread from Italy as scholars from other areas visited Italian city-states & took the new ideas they saw back Kings bought Renaissance art, helping to spread new ideas Renaissance ideas spread to the Holy Roman Empire (Germany), England, France, Belgium, Netherlands ...
the middle ages - Educator Pages
... most people, including the nobility, were illiterate. Boys were educated in music and the most important musicians were priests and worked for the church as liturgical singers. Women were not allowed to sing in church but did make music in convents. The church also frowned upon instruments. Instrume ...
... most people, including the nobility, were illiterate. Boys were educated in music and the most important musicians were priests and worked for the church as liturgical singers. Women were not allowed to sing in church but did make music in convents. The church also frowned upon instruments. Instrume ...
Renaissance Art PowerPoint
... Hellenistic or Roman copy of lost bronze original made between 350 and 325 BC Rediscovered in late 15th century ...
... Hellenistic or Roman copy of lost bronze original made between 350 and 325 BC Rediscovered in late 15th century ...
The Renaissance Man
... heretic, as he deserves, to be brought personally before us, or to be securely guarded until those who have captured him inform us, whereupon we will order the appropriate manner of proceeding against the said Luther. Those who will help in his capture will be rewarded generously for their good work ...
... heretic, as he deserves, to be brought personally before us, or to be securely guarded until those who have captured him inform us, whereupon we will order the appropriate manner of proceeding against the said Luther. Those who will help in his capture will be rewarded generously for their good work ...
details
... • Should not be considered an appendage to Italian art • But, Italian influence was strong – Painting in OIL, developed in Flanders – The differences between the two cultures: – Italy change was inspired by humanism with its emphasis on the revival of the values of classical antiquity – Northern E ...
... • Should not be considered an appendage to Italian art • But, Italian influence was strong – Painting in OIL, developed in Flanders – The differences between the two cultures: – Italy change was inspired by humanism with its emphasis on the revival of the values of classical antiquity – Northern E ...
AP EURO - Blind Brook
... humanists shared the ideas of Ficino and Pico about the wisdom of ancient texts, but they viewed humanist learning as a way to bring about reform of the church and deepen people’s spiritual lives. 2. These humanists thought that the best elements of classical and Christian cultures should be combine ...
... humanists shared the ideas of Ficino and Pico about the wisdom of ancient texts, but they viewed humanist learning as a way to bring about reform of the church and deepen people’s spiritual lives. 2. These humanists thought that the best elements of classical and Christian cultures should be combine ...
Rediscovering the Classical Tradition Through Art
... their importance, rather than how they would appear in the real world. •Little emotion ...
... their importance, rather than how they would appear in the real world. •Little emotion ...
expo renaissance
... foodstuffs to Europe, but it took considerable time for many of these things to become generally accepted and known. Here is a list of some of the foods which did not come into use until late or after the Renaissance. ...
... foodstuffs to Europe, but it took considerable time for many of these things to become generally accepted and known. Here is a list of some of the foods which did not come into use until late or after the Renaissance. ...
Protestant Reformation Identify and or define for historical
... 11. How did classical architecture influence the architecture of the Renaissance? Give examples 12. Know what was unique about the book “The Prince” by Machiavelli” and why it is considered Humanist 13. Be able to describe why science was still very dangerous during the Renaissance 14. What was the ...
... 11. How did classical architecture influence the architecture of the Renaissance? Give examples 12. Know what was unique about the book “The Prince” by Machiavelli” and why it is considered Humanist 13. Be able to describe why science was still very dangerous during the Renaissance 14. What was the ...
Northern Renaissance
... northern Europe and later to England. The printing press helped humanist ideas (Humanism) to spread, as did people who traveled. • Northern Renaissance refers to the culture in places we know today as Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, and the Netherlands. Like Italian artists, northern artists wanted th ...
... northern Europe and later to England. The printing press helped humanist ideas (Humanism) to spread, as did people who traveled. • Northern Renaissance refers to the culture in places we know today as Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, and the Netherlands. Like Italian artists, northern artists wanted th ...
Humanism
... .themselves as ushering in the modern age, as distinct from the ancient and medieval eras Study of the Renaissance might well center on five interrelated issues. First, although Renaissance thinkers often tried to associate themselves with classical antiquity and to dissociate themselves from the Mi ...
... .themselves as ushering in the modern age, as distinct from the ancient and medieval eras Study of the Renaissance might well center on five interrelated issues. First, although Renaissance thinkers often tried to associate themselves with classical antiquity and to dissociate themselves from the Mi ...
World History
... into Catholic & Protestant groups • Humanism had an impact on movement that demanded reform of the Roman Catholic Church • Desiderius Erasmus – criticized the Church in his work The Praise of Folly for emphasizing practices (rites) over principles ...
... into Catholic & Protestant groups • Humanism had an impact on movement that demanded reform of the Roman Catholic Church • Desiderius Erasmus – criticized the Church in his work The Praise of Folly for emphasizing practices (rites) over principles ...
Renaissance in Scotland

The Renaissance in Scotland was a cultural, intellectual and artistic movement in Scotland, from the late fifteenth century to the beginning of the seventeenth century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late fourteenth century and reaching northern Europe as a Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century. It involved an attempt to revive the principles of the classical era, including humanism, a spirit of scholarly enquiry, scepticism, and concepts of balance and proportion. Since the twentieth century the uniqueness and unity of the Renaissance has been challenged by historians, but significant changes in Scotland can be seen to have taken place in education, intellectual life, literature, art, architecture, music and politics.The court was central to the patronage and dissemination of Renaissance works and ideas. It was also central to the staging of lavish display that portrayed the political and religious role of the monarchy. The Renaissance led to the adoption of ideas of imperial monarchy, encouraging the Scottish crown to join the new monarchies by asserting imperial jurisdiction and distinction. The growing emphasis on education in the Middle Ages became part of a humanist and then Protestant programme to extend and reform learning. It resulted in the expansion of the school system and the foundation of six university colleges by the end of the sixteenth century. Relatively large numbers of Scottish scholars studied on the continent or in England and some, such as Hector Boece, John Mair, Andrew Melville and George Buchanan, returned to Scotland to play a major part in developing Scottish intellectual life. Vernacular works in Scots began to emerge in the fifteenth century, while Latin remained a major literary language. With the patronage of James V and James VI, writers included William Stewart, John Bellenden, David Lyndsay, William Fowler and Alexander Montgomerie.In the sixteenth century, Scottish kings, particularly James V, built palaces in a Renaissance style, beginning at Linlithgow. The trend soon spread to members of the aristocracy. Painting was strongly influenced by Flemish art, with works commissioned from the continent and Flemings serving as court artists. While church art suffered iconoclasm and a loss of patronage as a result of the Reformation, house decoration and portraiture became significant for the wealthy, with George Jamesone emerging as the first major named artist in the early seventeenth century. Music also incorporated wider European influences although the Reformation caused a move from complex polyphonic church music to the simpler singing of metrical psalms. Combined with the Union of Crowns in 1603, the Reformation also removed the church and the court as sources of patronage, changing the direction of artistic creation and limiting its scope. In the early seventeenth century the major elements of the Renaissance began to give way to Stoicism, Mannerism and the Baroque.