Northern Renaissance
... • Growing wealth in Northern Europe supported Renaissance ideas. • Northern Renaissance thinkers merged humanist ideas with Christianity. • The movable type printing press and the production and sale of books (Gutenberg Bible) helped disseminate ideas. Northern Renaissance writers • Erasmus—The Prai ...
... • Growing wealth in Northern Europe supported Renaissance ideas. • Northern Renaissance thinkers merged humanist ideas with Christianity. • The movable type printing press and the production and sale of books (Gutenberg Bible) helped disseminate ideas. Northern Renaissance writers • Erasmus—The Prai ...
Renaissance - Rowan County Schools
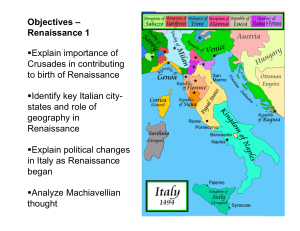
... Increased trade with Asia and other regions Growth of large, wealthy city-states in Italy Renewed interest in the classical learning of ancient Greece and Rome Rise of rich and powerful merchants, who became patrons of the arts Increased desire for scientific and technical knowledge Desire to beauti ...
... Increased trade with Asia and other regions Growth of large, wealthy city-states in Italy Renewed interest in the classical learning of ancient Greece and Rome Rise of rich and powerful merchants, who became patrons of the arts Increased desire for scientific and technical knowledge Desire to beauti ...
Section Summary Key Terms and People Academic Vocabulary
... devoted themselves to religious study. In the Renaissance, people began to study poetry, history, and art. These subjects are part of the humanities. This emphasis on human achievement was called humanism. This led to a renewed interest in the classical writings of the Greeks and Romans. Dante Aligh ...
... devoted themselves to religious study. In the Renaissance, people began to study poetry, history, and art. These subjects are part of the humanities. This emphasis on human achievement was called humanism. This led to a renewed interest in the classical writings of the Greeks and Romans. Dante Aligh ...
Chapter 13
... Hapsburgs gained international power Maximilian I (1493 – 1519) Charles, Maximilian’s grandson, became heir to the Habsburg, Burgundian, and Spanish lines, making him the leading monarch of his age ...
... Hapsburgs gained international power Maximilian I (1493 – 1519) Charles, Maximilian’s grandson, became heir to the Habsburg, Burgundian, and Spanish lines, making him the leading monarch of his age ...
Renaissance Intro Info and Worksheet
... was made up of several independent states. They were prosperous and a centre for international trade. They employed rich bankers, merchants and lawyers who could afford to build fine houses, buy books and employ musicians and artists. The rival city states competed with each other to be the richest ...
... was made up of several independent states. They were prosperous and a centre for international trade. They employed rich bankers, merchants and lawyers who could afford to build fine houses, buy books and employ musicians and artists. The rival city states competed with each other to be the richest ...
Connect the Sentence answers
... annulment which the Catholic Church would not grant him. Thus, Henry went to the English courts, got an annulment, married Anne Boleyn and had a daughter, Elizabeth. He charged Anne of adultery and had her beheaded. During this marriage to Anne, Henry went to the English Parliament and asked for the ...
... annulment which the Catholic Church would not grant him. Thus, Henry went to the English courts, got an annulment, married Anne Boleyn and had a daughter, Elizabeth. He charged Anne of adultery and had her beheaded. During this marriage to Anne, Henry went to the English Parliament and asked for the ...
The Renaissance (1300-1600)
... b. Ideas will dominate European social & political life for hundreds of years The Vernacular Replaces Latin in Literature 1. During the Middle Ages, Latin was the language of the Church and of educated people 2. Over the centuries other tongues had been evolving through everyday usage a. French, Ita ...
... b. Ideas will dominate European social & political life for hundreds of years The Vernacular Replaces Latin in Literature 1. During the Middle Ages, Latin was the language of the Church and of educated people 2. Over the centuries other tongues had been evolving through everyday usage a. French, Ita ...
Renaissance Art Document
... Ages, many people felt as if the world was indeed being born again. The Renaissance witnessed a remaking of nearly all of society’s institutions: political, economic, social, educational, and family. It was also a time when leading thinkers revisited the great or classical ideas of ancient Greece an ...
... Ages, many people felt as if the world was indeed being born again. The Renaissance witnessed a remaking of nearly all of society’s institutions: political, economic, social, educational, and family. It was also a time when leading thinkers revisited the great or classical ideas of ancient Greece an ...
Chp 12
... and architects change over the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries? • What is the purpose of applying linear perspective to painting? • What were the differences in the ways painters in Italian cities and those in Flanders achieved depth and dimension in their work? • How did the scholarly interests ...
... and architects change over the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries? • What is the purpose of applying linear perspective to painting? • What were the differences in the ways painters in Italian cities and those in Flanders achieved depth and dimension in their work? • How did the scholarly interests ...
The Renaissance - Barren County Schools
... • Michelangelo’s David, housed in Florence’s Accademia Gallery, is one of the most famous works of art, period. • Most people know that this work is a masterpiece by Michelangelo begun in the year 1501, that it’s sculpted in marble, it’s over life-size, and that it represents the biblical figure of ...
... • Michelangelo’s David, housed in Florence’s Accademia Gallery, is one of the most famous works of art, period. • Most people know that this work is a masterpiece by Michelangelo begun in the year 1501, that it’s sculpted in marble, it’s over life-size, and that it represents the biblical figure of ...
World History and Geography
... earth as important for people and he thought the Church wrong to ignore the real world in which people lived. He said the educated person should study humans i.e. history, languages, literature and ethics. 13. Giovanni Boccaccio - He was a noted humanist who wrote both poetry and prose. He used the ...
... earth as important for people and he thought the Church wrong to ignore the real world in which people lived. He said the educated person should study humans i.e. history, languages, literature and ethics. 13. Giovanni Boccaccio - He was a noted humanist who wrote both poetry and prose. He used the ...
Il Duomo St. Peter`s St. Paul`s US capital (Florence) (Rome) (London)
... • By the end of the 15th century, Italian city-states no longer had a monopoly on Asian goods – Other nations want to get wealthy through trade – Explorations by Spain and Portugal in the late 1400s opened new trade routes to Asia ...
... • By the end of the 15th century, Italian city-states no longer had a monopoly on Asian goods – Other nations want to get wealthy through trade – Explorations by Spain and Portugal in the late 1400s opened new trade routes to Asia ...
Renaissance Society and Humanist Culture
... Why was Florence the site of the first cultural flowering in Italy? Describe the political conditions in fifteenth century Italy. What were the major characteristics of Italian Renaissance art and literature? Be able to identify some of the major Renaissance figures and examples of their work. 5. Wh ...
... Why was Florence the site of the first cultural flowering in Italy? Describe the political conditions in fifteenth century Italy. What were the major characteristics of Italian Renaissance art and literature? Be able to identify some of the major Renaissance figures and examples of their work. 5. Wh ...
The Renaissance - Duluth High School
... • The Courtier – Book written that described the Renaissance ideal for men • Upper class women were as well educated as men during the Renaissance, HOWEVER most women had less political, economic and social influence than women of the Middle Ages • Florence was the leading city during the Renaissanc ...
... • The Courtier – Book written that described the Renaissance ideal for men • Upper class women were as well educated as men during the Renaissance, HOWEVER most women had less political, economic and social influence than women of the Middle Ages • Florence was the leading city during the Renaissanc ...
The Italian Renaissance
... -During the new age, the Renaissance, people began to focus on refinement, personal achievement, and learning. The word Renaissance comes from a Latin word that means rebirth or revival. The term is used to describe a renewed attention to ideas from classical Greek and Roman culture. This renewal fi ...
... -During the new age, the Renaissance, people began to focus on refinement, personal achievement, and learning. The word Renaissance comes from a Latin word that means rebirth or revival. The term is used to describe a renewed attention to ideas from classical Greek and Roman culture. This renewal fi ...
Name: Date: :___ The Renaissance Objective: Students will
... Humanism was the most significant intellectual movement of the Renaissance. It blended concern for the history and actions of human beings with religious concerns. The humanists were scholars and artists who studied subjects that they believed would help them better understand the problems of humani ...
... Humanism was the most significant intellectual movement of the Renaissance. It blended concern for the history and actions of human beings with religious concerns. The humanists were scholars and artists who studied subjects that they believed would help them better understand the problems of humani ...
Directions: Explore the various websites related to the
... Answer the questions using complete sentences. Introduction to the Renaissance 1. What does the term Renaissance mean? 2. Name some artists that were well known during this time period? 3. What are some of the significant achievements of this era? Basic Renaissance Beliefs 4. Who was the perfect ren ...
... Answer the questions using complete sentences. Introduction to the Renaissance 1. What does the term Renaissance mean? 2. Name some artists that were well known during this time period? 3. What are some of the significant achievements of this era? Basic Renaissance Beliefs 4. Who was the perfect ren ...
Renaissance Review Packet
... (modernization) in many areas of life– from government to science to the arts to religion • Renaissance: reawakened interest in classical learning, Middle Ages: some preservation of classical heritage, but not a focus • Renaissance: think about here and now, Middle Ages: think about what happens whe ...
... (modernization) in many areas of life– from government to science to the arts to religion • Renaissance: reawakened interest in classical learning, Middle Ages: some preservation of classical heritage, but not a focus • Renaissance: think about here and now, Middle Ages: think about what happens whe ...
The Italian Renaissance - Mr. Ryan Teaches History
... change in many ways, political, social, economic, and cultural. Perhaps most important were the changes that took place in the way people viewed themselves and their world. ...
... change in many ways, political, social, economic, and cultural. Perhaps most important were the changes that took place in the way people viewed themselves and their world. ...
Renaissance
... greater understanding of Christianity, but they stressed the use of reason over accepted dogma • Students from England, Holland, France, and Germany went to Italy for the ‘new learning’ • New universities opened across northern Europe, especially in Germany (Wittenberg was founded in ...
... greater understanding of Christianity, but they stressed the use of reason over accepted dogma • Students from England, Holland, France, and Germany went to Italy for the ‘new learning’ • New universities opened across northern Europe, especially in Germany (Wittenberg was founded in ...
Music: An Appreciation by Roger Kamien
... Rebirth of human learning and creativity Time of great explorers Humanism Fascination w/ ancient Greece & Rome Visual art becomes more realistic • Mythology is favorite subject • Nude body, as in ancient times, is shown ...
... Rebirth of human learning and creativity Time of great explorers Humanism Fascination w/ ancient Greece & Rome Visual art becomes more realistic • Mythology is favorite subject • Nude body, as in ancient times, is shown ...
Renaissance in Scotland

The Renaissance in Scotland was a cultural, intellectual and artistic movement in Scotland, from the late fifteenth century to the beginning of the seventeenth century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late fourteenth century and reaching northern Europe as a Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century. It involved an attempt to revive the principles of the classical era, including humanism, a spirit of scholarly enquiry, scepticism, and concepts of balance and proportion. Since the twentieth century the uniqueness and unity of the Renaissance has been challenged by historians, but significant changes in Scotland can be seen to have taken place in education, intellectual life, literature, art, architecture, music and politics.The court was central to the patronage and dissemination of Renaissance works and ideas. It was also central to the staging of lavish display that portrayed the political and religious role of the monarchy. The Renaissance led to the adoption of ideas of imperial monarchy, encouraging the Scottish crown to join the new monarchies by asserting imperial jurisdiction and distinction. The growing emphasis on education in the Middle Ages became part of a humanist and then Protestant programme to extend and reform learning. It resulted in the expansion of the school system and the foundation of six university colleges by the end of the sixteenth century. Relatively large numbers of Scottish scholars studied on the continent or in England and some, such as Hector Boece, John Mair, Andrew Melville and George Buchanan, returned to Scotland to play a major part in developing Scottish intellectual life. Vernacular works in Scots began to emerge in the fifteenth century, while Latin remained a major literary language. With the patronage of James V and James VI, writers included William Stewart, John Bellenden, David Lyndsay, William Fowler and Alexander Montgomerie.In the sixteenth century, Scottish kings, particularly James V, built palaces in a Renaissance style, beginning at Linlithgow. The trend soon spread to members of the aristocracy. Painting was strongly influenced by Flemish art, with works commissioned from the continent and Flemings serving as court artists. While church art suffered iconoclasm and a loss of patronage as a result of the Reformation, house decoration and portraiture became significant for the wealthy, with George Jamesone emerging as the first major named artist in the early seventeenth century. Music also incorporated wider European influences although the Reformation caused a move from complex polyphonic church music to the simpler singing of metrical psalms. Combined with the Union of Crowns in 1603, the Reformation also removed the church and the court as sources of patronage, changing the direction of artistic creation and limiting its scope. In the early seventeenth century the major elements of the Renaissance began to give way to Stoicism, Mannerism and the Baroque.























