Ch.-17-Review
... - What was the Renaissance a rebirth of? - What was the Medici family’s contribution to the Renaissance? - What was the first full-sized book printed by Gutenberg? - What are indulgences? - Who declared himself head of the English Church in 1534? - What is a “Renaissance man”? - What are the reasons ...
... - What was the Renaissance a rebirth of? - What was the Medici family’s contribution to the Renaissance? - What was the first full-sized book printed by Gutenberg? - What are indulgences? - Who declared himself head of the English Church in 1534? - What is a “Renaissance man”? - What are the reasons ...
Renaissance Music
... General Facts After the dark ages, the period of enlightenment The rebirth of humanism More artistic ...
... General Facts After the dark ages, the period of enlightenment The rebirth of humanism More artistic ...
Renaissance - Nelson County School District
... General Facts After the dark ages, the period of enlightenment The rebirth of humanism More artistic ...
... General Facts After the dark ages, the period of enlightenment The rebirth of humanism More artistic ...
The Intellectual and artistic renaissance
... • Humanism: secularism and emphasis on the individual • Study of classics (literary works of ancient Greece & Rome) ...
... • Humanism: secularism and emphasis on the individual • Study of classics (literary works of ancient Greece & Rome) ...
The Renaissance
... you think this affected the spread of the Renaissance? Erasmus- Holland o The Praise of Folly- satire of traditional medieval society o Criticized the Church and the ceremony, believed it wasn’t in line with the original roots of Christianity Sir Thomas More- England o Utopia- satire mocking the wea ...
... you think this affected the spread of the Renaissance? Erasmus- Holland o The Praise of Folly- satire of traditional medieval society o Criticized the Church and the ceremony, believed it wasn’t in line with the original roots of Christianity Sir Thomas More- England o Utopia- satire mocking the wea ...
Renaissance Intellectual Movements Humanism Focused on human
... Return to the ideals of Greece and Rome ...
... Return to the ideals of Greece and Rome ...
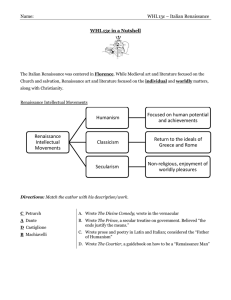
Italian Renaissance Humanism
... Humanism was based on the classics of Greece & Rome. They studied poetry, philosophy, & history. (B) Petrarch used forgotten Latin and he emphasized using pure classical Latin. (A) ...
... Humanism was based on the classics of Greece & Rome. They studied poetry, philosophy, & history. (B) Petrarch used forgotten Latin and he emphasized using pure classical Latin. (A) ...
Ch 12 sec 2 - Somerset Academy
... Study of the classics, the literary works ancient Greece & Rome. Humanist studied: grammar, rhetoric, poetry, moral philosophy, and history Petrarch, Called the father of Italian Renaissance Humanism, began emphasis on using pure classic Latin Humanist believed: Duty to life active civic life Put st ...
... Study of the classics, the literary works ancient Greece & Rome. Humanist studied: grammar, rhetoric, poetry, moral philosophy, and history Petrarch, Called the father of Italian Renaissance Humanism, began emphasis on using pure classic Latin Humanist believed: Duty to life active civic life Put st ...
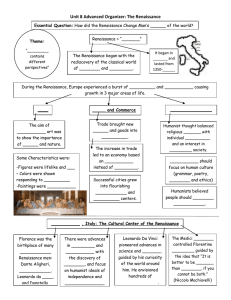
Italy – Birthplace of the Renaissance I. The word
... B. Thriving cities (urban areas where ideas can be freely shared). C. There was a wealthy merchant class as a result of new banking and manufacturing. D. Access to the classical heritage of Greece and Rome III. Characteristics of the Renaissance A. The Renaissance was an age of recovery from disaste ...
... B. Thriving cities (urban areas where ideas can be freely shared). C. There was a wealthy merchant class as a result of new banking and manufacturing. D. Access to the classical heritage of Greece and Rome III. Characteristics of the Renaissance A. The Renaissance was an age of recovery from disaste ...
The Renaissance
... What is "The Renaissance" A period of "rebirth" in Europe Reawakening of interest in art, literature, science, and classical civilizations ...
... What is "The Renaissance" A period of "rebirth" in Europe Reawakening of interest in art, literature, science, and classical civilizations ...
Renaissance Art PPT - Scott County Schools
... Pieta, David, Sistine Chapel Depicts biblical history of world from Creation to the Flood., – Four years he laied on his back on a platform just a few inches below the chapel ceiling. ...
... Pieta, David, Sistine Chapel Depicts biblical history of world from Creation to the Flood., – Four years he laied on his back on a platform just a few inches below the chapel ceiling. ...
- Bright Star Schools
... focus on human culture (grammar, poetry, ________ and ethics) Humanists believed people should ________ ____________. ...
... focus on human culture (grammar, poetry, ________ and ethics) Humanists believed people should ________ ____________. ...
Renaissance Review - Joy Eldridge at VHS
... 2. The ability to make art 3-D 5. Rebirth in Classical culture of arts and learning that took place from ~1300-1600 6. Michelangelo's most famous statue 9. Michelangelo's most famous painting was on this ceiling 11. Petrarch gathered Greek and Roman works into one of these 12. Renaissance sculptor a ...
... 2. The ability to make art 3-D 5. Rebirth in Classical culture of arts and learning that took place from ~1300-1600 6. Michelangelo's most famous statue 9. Michelangelo's most famous painting was on this ceiling 11. Petrarch gathered Greek and Roman works into one of these 12. Renaissance sculptor a ...
RenaissanceReformati..
... • Changed from an agricultural society to an Urban Society • It was a study of Roman and Greek cultures. ...
... • Changed from an agricultural society to an Urban Society • It was a study of Roman and Greek cultures. ...
Review Sheet 9R Renaissance – Reformation – Catholic Reformation
... 2. Who wrote The Prince. What is the central message of the book? 3. Describe 2 ways in which the printing press revolutionized Europe in the 16th c. – Gutenberg bible, Luther 95 Thesis, Castiglione, The Prince 4. Why did many Christians call for Church reform? Include historical pieces of evidence ...
... 2. Who wrote The Prince. What is the central message of the book? 3. Describe 2 ways in which the printing press revolutionized Europe in the 16th c. – Gutenberg bible, Luther 95 Thesis, Castiglione, The Prince 4. Why did many Christians call for Church reform? Include historical pieces of evidence ...
Renaissance
... • Dominant intellectual movement of Renaissance • Philosophy that people were rational human beings • Emphasized the dignity and worth of the individual • Humanities: promotion of a new educational curriculum – Included grammar, rhetoric, history, poetry, and ethics ...
... • Dominant intellectual movement of Renaissance • Philosophy that people were rational human beings • Emphasized the dignity and worth of the individual • Humanities: promotion of a new educational curriculum – Included grammar, rhetoric, history, poetry, and ethics ...
Renaissance
... • Dominant intellectual movement of Renaissance • Philosophy that people were rational human beings • Emphasized the dignity and worth of the individual • Humanities: promotion of a new educational curriculum – Included grammar, rhetoric, history, poetry, and ethics ...
... • Dominant intellectual movement of Renaissance • Philosophy that people were rational human beings • Emphasized the dignity and worth of the individual • Humanities: promotion of a new educational curriculum – Included grammar, rhetoric, history, poetry, and ethics ...
Renaissance/Reformation Review Sheet
... Renaissance/Reformation Review Sheet For the test you will need to know the following terms/ideas. When completing this review sheet you should know the basic information for each item listed (who, what, when, where, why, how is it important) Renaissance- def. 3 Characteristics of the Renaissance 3 ...
... Renaissance/Reformation Review Sheet For the test you will need to know the following terms/ideas. When completing this review sheet you should know the basic information for each item listed (who, what, when, where, why, how is it important) Renaissance- def. 3 Characteristics of the Renaissance 3 ...
Renaissance in Scotland

The Renaissance in Scotland was a cultural, intellectual and artistic movement in Scotland, from the late fifteenth century to the beginning of the seventeenth century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late fourteenth century and reaching northern Europe as a Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century. It involved an attempt to revive the principles of the classical era, including humanism, a spirit of scholarly enquiry, scepticism, and concepts of balance and proportion. Since the twentieth century the uniqueness and unity of the Renaissance has been challenged by historians, but significant changes in Scotland can be seen to have taken place in education, intellectual life, literature, art, architecture, music and politics.The court was central to the patronage and dissemination of Renaissance works and ideas. It was also central to the staging of lavish display that portrayed the political and religious role of the monarchy. The Renaissance led to the adoption of ideas of imperial monarchy, encouraging the Scottish crown to join the new monarchies by asserting imperial jurisdiction and distinction. The growing emphasis on education in the Middle Ages became part of a humanist and then Protestant programme to extend and reform learning. It resulted in the expansion of the school system and the foundation of six university colleges by the end of the sixteenth century. Relatively large numbers of Scottish scholars studied on the continent or in England and some, such as Hector Boece, John Mair, Andrew Melville and George Buchanan, returned to Scotland to play a major part in developing Scottish intellectual life. Vernacular works in Scots began to emerge in the fifteenth century, while Latin remained a major literary language. With the patronage of James V and James VI, writers included William Stewart, John Bellenden, David Lyndsay, William Fowler and Alexander Montgomerie.In the sixteenth century, Scottish kings, particularly James V, built palaces in a Renaissance style, beginning at Linlithgow. The trend soon spread to members of the aristocracy. Painting was strongly influenced by Flemish art, with works commissioned from the continent and Flemings serving as court artists. While church art suffered iconoclasm and a loss of patronage as a result of the Reformation, house decoration and portraiture became significant for the wealthy, with George Jamesone emerging as the first major named artist in the early seventeenth century. Music also incorporated wider European influences although the Reformation caused a move from complex polyphonic church music to the simpler singing of metrical psalms. Combined with the Union of Crowns in 1603, the Reformation also removed the church and the court as sources of patronage, changing the direction of artistic creation and limiting its scope. In the early seventeenth century the major elements of the Renaissance began to give way to Stoicism, Mannerism and the Baroque.