Lecture Notes World History II Ch
... power. Machiavelli argued the prince’s attitude toward power should be based on understanding that human nature is self-interested. A prince, therefore should not act on moral principles but on behalf of the interests of the state. Machiavelli was among the first to abandon morality as the basis f ...
... power. Machiavelli argued the prince’s attitude toward power should be based on understanding that human nature is self-interested. A prince, therefore should not act on moral principles but on behalf of the interests of the state. Machiavelli was among the first to abandon morality as the basis f ...
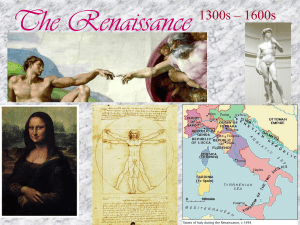
The Renaissance - Lakewood City School District
... had hoped to return Catholicism to England, but severed ties once Mary Queen of Scots was executed. • He attacked England’s Naval fleet, and the English Navy defeated the Spanish Armada, making England the greatest military power in all of Europe. ...
... had hoped to return Catholicism to England, but severed ties once Mary Queen of Scots was executed. • He attacked England’s Naval fleet, and the English Navy defeated the Spanish Armada, making England the greatest military power in all of Europe. ...
The Renaissance - St. John`s College HS
... problematic (see Hundred Years War) and now strong centrally-run States looked out for the welfare of their people. • Especially since professional, standing armies made up of commoners (not knights or nobles) were most effective on the field of battle, the common subjects of these States became mor ...
... problematic (see Hundred Years War) and now strong centrally-run States looked out for the welfare of their people. • Especially since professional, standing armies made up of commoners (not knights or nobles) were most effective on the field of battle, the common subjects of these States became mor ...
Document
... 45. What type of government does the following list describe? monarchy There is one ruler. The ruler usually inherited power. The ruler passed on leadership to his son. 46. The crusades have been called ‘history’s most successful failure.” What would best explain this expression? The Crusades ...
... 45. What type of government does the following list describe? monarchy There is one ruler. The ruler usually inherited power. The ruler passed on leadership to his son. 46. The crusades have been called ‘history’s most successful failure.” What would best explain this expression? The Crusades ...
Renaissance
... Classicism? (“old school” is cool) = belief or admiration of Greco-Roman culture HUMANISM = philosophical movement during the Renaissance that stressed life on Earth, and the quality of being human. Rejected living only for the afterlife of Christianity (Middle Ages view). ...
... Classicism? (“old school” is cool) = belief or admiration of Greco-Roman culture HUMANISM = philosophical movement during the Renaissance that stressed life on Earth, and the quality of being human. Rejected living only for the afterlife of Christianity (Middle Ages view). ...
The Renaissance - WVW World History
... • Renaissance thinkers had an interest in ancient Rome • Italy’s location supported trade • Trade made Italian merchants wealthy • These wealthy merchants became patrons of their cities ...
... • Renaissance thinkers had an interest in ancient Rome • Italy’s location supported trade • Trade made Italian merchants wealthy • These wealthy merchants became patrons of their cities ...
The Renaissance Begins
... Roman Ruins Many city states competing for fame Italy’s cities very wealthy – Could afford to pay painters, sculptors, architects, and other artists An add on their website (competition lives)- WELCOME TO FLORENCE- The splendid city of Michelangelo and Dante and the world's celebrated jewel of R ...
... Roman Ruins Many city states competing for fame Italy’s cities very wealthy – Could afford to pay painters, sculptors, architects, and other artists An add on their website (competition lives)- WELCOME TO FLORENCE- The splendid city of Michelangelo and Dante and the world's celebrated jewel of R ...
17.1 Italy Birthplace of the Renaissance
... ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in Rome He spent hours each day laying stretched on his back on top of a high scaffold with paint ...
... ceiling of the Sistine Chapel in Rome He spent hours each day laying stretched on his back on top of a high scaffold with paint ...
Chapter 28 – Florence: The Cradle of the Renaissance Section 1
... Leave this section blank. We will do it together in class. Section 2 1. Because of its ideal location on the Arno River, Florence became a center for trade and commerce. It also was dominated by the Medici family, who helped Florence become a banking center for Europe. 2. The city’s residents could ...
... Leave this section blank. We will do it together in class. Section 2 1. Because of its ideal location on the Arno River, Florence became a center for trade and commerce. It also was dominated by the Medici family, who helped Florence become a banking center for Europe. 2. The city’s residents could ...
Jan van Eyck Mona Lisa and Last Supper
... Dante’s poem, Divine Comedy, goes through the various levels of _______________. ...
... Dante’s poem, Divine Comedy, goes through the various levels of _______________. ...
Medieval Europe had been a fragmented feudal
... Niccolo Machiavelli- Author of important political treatise “The Prince” Had served as a minor government official in the Republican government of Florence Wrote to stress that rulers must be concerned with “the way things are, not the way they wish them to be.” Wanted the Italian city- states to un ...
... Niccolo Machiavelli- Author of important political treatise “The Prince” Had served as a minor government official in the Republican government of Florence Wrote to stress that rulers must be concerned with “the way things are, not the way they wish them to be.” Wanted the Italian city- states to un ...
Renaissance - Livingston Public Schools
... The Elizabethan Age Queen Elizabeth I • Renaissance spreads to England in mid-1500s • Period known as the Elizabethan Age, after Queen Elizabeth I • Elizabeth reigns from 1558 to 1603 ...
... The Elizabethan Age Queen Elizabeth I • Renaissance spreads to England in mid-1500s • Period known as the Elizabethan Age, after Queen Elizabeth I • Elizabeth reigns from 1558 to 1603 ...
Renaissance Art Document
... Ages, many people felt as if the world was indeed being born again. The Renaissance witnessed a remaking of nearly all of society’s institutions: political, economic, social, educational, and family. It was also a time when leading thinkers revisited the great or classical ideas of ancient Greece an ...
... Ages, many people felt as if the world was indeed being born again. The Renaissance witnessed a remaking of nearly all of society’s institutions: political, economic, social, educational, and family. It was also a time when leading thinkers revisited the great or classical ideas of ancient Greece an ...
Renaissance
... Humanists favored a liberal arts education which was to include geometry, arithmetic, music, astronomy, literature, and history. Humanists favored the use of the vernacular in education, so more merchants could be educated. Two major universities: U. of Bologna: Law and U. of Paris: Theology ...
... Humanists favored a liberal arts education which was to include geometry, arithmetic, music, astronomy, literature, and history. Humanists favored the use of the vernacular in education, so more merchants could be educated. Two major universities: U. of Bologna: Law and U. of Paris: Theology ...
Student
... 8. One way in which the writers of the Renaissance were influenced by the writers of ancient Greece was that the Renaissance writers: a. Stressed the power of human reason b. Promoted the religious doctrines of the Roman Catholic Church c. Showed little interest in secular affairs d. Produced few ne ...
... 8. One way in which the writers of the Renaissance were influenced by the writers of ancient Greece was that the Renaissance writers: a. Stressed the power of human reason b. Promoted the religious doctrines of the Roman Catholic Church c. Showed little interest in secular affairs d. Produced few ne ...
File
... (7.53) 6. Why were the printing press, literacy (ability to read), and widespread use of Latin some of the most important events during Renaissance Europe? The printing press printed books quickly, making them widely available to people; More people became literate (knew how to read); Latin allowed ...
... (7.53) 6. Why were the printing press, literacy (ability to read), and widespread use of Latin some of the most important events during Renaissance Europe? The printing press printed books quickly, making them widely available to people; More people became literate (knew how to read); Latin allowed ...
The Renaissance
... continuation of Greek and Roman ideas or a new intellectual movement altogether? ...
... continuation of Greek and Roman ideas or a new intellectual movement altogether? ...
Week 10 - Renaissance
... In the center are the central stories (9 stories of Genesis); Sibyls and Prophets are found in between the webs (triangles); the 4 pendentives relate tales of miraculous salvation; the webs (triangles) precise identification is still debated but thought to be ancestors of Christ. Without having seen ...
... In the center are the central stories (9 stories of Genesis); Sibyls and Prophets are found in between the webs (triangles); the 4 pendentives relate tales of miraculous salvation; the webs (triangles) precise identification is still debated but thought to be ancestors of Christ. Without having seen ...
The Renaissance File - Galena Park ISD Moodle
... education, science, art, literature, music, and a better life for people in general. Coming out of the Dark The Middle Ages began with the fall of the Roman Empire. Much of the advances in science, art, and government that had been made by the Greeks and Romans were lost during this time. Part of th ...
... education, science, art, literature, music, and a better life for people in general. Coming out of the Dark The Middle Ages began with the fall of the Roman Empire. Much of the advances in science, art, and government that had been made by the Greeks and Romans were lost during this time. Part of th ...
Notes 09/13/2013 The Renaissance The Renaissance begins in
... Italy is a peninsula and surrounded on three sides by water. Italy escaped many of the horrors of Middle Ages life that other European countries experienced. Art: How did art differ from the Middle Ages to the Renaissance? Middle Ages art: Depiction of knights and bloody wars or religion. Middle Age ...
... Italy is a peninsula and surrounded on three sides by water. Italy escaped many of the horrors of Middle Ages life that other European countries experienced. Art: How did art differ from the Middle Ages to the Renaissance? Middle Ages art: Depiction of knights and bloody wars or religion. Middle Age ...
Renaissance Thinkers and Their Values
... • The Renaissance intensified a new way of thinking. Granted, a small minority of the Italian and European population came into contact with this idea, but it at least began. This new way of thinking held the conviction that humanity was capable of mastering the world where it lived. Man’s fate on ...
... • The Renaissance intensified a new way of thinking. Granted, a small minority of the Italian and European population came into contact with this idea, but it at least began. This new way of thinking held the conviction that humanity was capable of mastering the world where it lived. Man’s fate on ...
The Renaissance
... European cities / The middle class The state system - representative government English common law -concept of liberty Equality and the sacred worth of the individual Universities Corporations, Bookkeeping & Banking Preserved Greco-Roman scholarship Growth of secularism ...
... European cities / The middle class The state system - representative government English common law -concept of liberty Equality and the sacred worth of the individual Universities Corporations, Bookkeeping & Banking Preserved Greco-Roman scholarship Growth of secularism ...
Renaissance in Scotland

The Renaissance in Scotland was a cultural, intellectual and artistic movement in Scotland, from the late fifteenth century to the beginning of the seventeenth century. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late fourteenth century and reaching northern Europe as a Northern Renaissance in the fifteenth century. It involved an attempt to revive the principles of the classical era, including humanism, a spirit of scholarly enquiry, scepticism, and concepts of balance and proportion. Since the twentieth century the uniqueness and unity of the Renaissance has been challenged by historians, but significant changes in Scotland can be seen to have taken place in education, intellectual life, literature, art, architecture, music and politics.The court was central to the patronage and dissemination of Renaissance works and ideas. It was also central to the staging of lavish display that portrayed the political and religious role of the monarchy. The Renaissance led to the adoption of ideas of imperial monarchy, encouraging the Scottish crown to join the new monarchies by asserting imperial jurisdiction and distinction. The growing emphasis on education in the Middle Ages became part of a humanist and then Protestant programme to extend and reform learning. It resulted in the expansion of the school system and the foundation of six university colleges by the end of the sixteenth century. Relatively large numbers of Scottish scholars studied on the continent or in England and some, such as Hector Boece, John Mair, Andrew Melville and George Buchanan, returned to Scotland to play a major part in developing Scottish intellectual life. Vernacular works in Scots began to emerge in the fifteenth century, while Latin remained a major literary language. With the patronage of James V and James VI, writers included William Stewart, John Bellenden, David Lyndsay, William Fowler and Alexander Montgomerie.In the sixteenth century, Scottish kings, particularly James V, built palaces in a Renaissance style, beginning at Linlithgow. The trend soon spread to members of the aristocracy. Painting was strongly influenced by Flemish art, with works commissioned from the continent and Flemings serving as court artists. While church art suffered iconoclasm and a loss of patronage as a result of the Reformation, house decoration and portraiture became significant for the wealthy, with George Jamesone emerging as the first major named artist in the early seventeenth century. Music also incorporated wider European influences although the Reformation caused a move from complex polyphonic church music to the simpler singing of metrical psalms. Combined with the Union of Crowns in 1603, the Reformation also removed the church and the court as sources of patronage, changing the direction of artistic creation and limiting its scope. In the early seventeenth century the major elements of the Renaissance began to give way to Stoicism, Mannerism and the Baroque.