NM Study Guide 2 Lecture #1 10/6/14 I. Normal Upper Extremity
... Eyes move first to locate object followed by head if necessary ...
... Eyes move first to locate object followed by head if necessary ...
Action Potential Riddle Quiz
... Please take out 1 piece of notebook paper & label it “Action Potential Riddle Quiz”. Write your NAME, DATE & PERIOD in the top right! For the 10 questions of the quiz, you will see screens for 30 secs. with “riddles” about Action Potentials. Write JUST THE ANSWER to the riddle next to the number (do ...
... Please take out 1 piece of notebook paper & label it “Action Potential Riddle Quiz”. Write your NAME, DATE & PERIOD in the top right! For the 10 questions of the quiz, you will see screens for 30 secs. with “riddles” about Action Potentials. Write JUST THE ANSWER to the riddle next to the number (do ...
(2006) Changes in visual receptive fields with microstimulation of
... has been described in terms of its effect on the structure of receptive fields (RFs), where multiple stimuli compete to drive neural responses and ultimately behavior. We stimulated the frontal eye field (FEF) of passively fixating monkeys and produced changes in V4 responses similar to known effect ...
... has been described in terms of its effect on the structure of receptive fields (RFs), where multiple stimuli compete to drive neural responses and ultimately behavior. We stimulated the frontal eye field (FEF) of passively fixating monkeys and produced changes in V4 responses similar to known effect ...
Central Topography of Cranial Motor Nuclei Controlled by
... neurons and are located in highly stereotyped positions. Establishment of this CNS topography is critical to neural circuit assembly. However, little is known of either the cellular or molecular mechanisms that drive nucleus formation during development, a process termed nucleogenesis [2–5]. Brainst ...
... neurons and are located in highly stereotyped positions. Establishment of this CNS topography is critical to neural circuit assembly. However, little is known of either the cellular or molecular mechanisms that drive nucleus formation during development, a process termed nucleogenesis [2–5]. Brainst ...
Detecting Action Potentials in Neuronal Populations with Calcium
... action potentials, which can produce generalized calcium accumulations throughout the cell, due to the backpropagation of the spike (24), and (iii) calcium spikes, which can produce generalized calcium influxes that are much larger than those produced by sodium spikes (26). Thus, it is possible to d ...
... action potentials, which can produce generalized calcium accumulations throughout the cell, due to the backpropagation of the spike (24), and (iii) calcium spikes, which can produce generalized calcium influxes that are much larger than those produced by sodium spikes (26). Thus, it is possible to d ...
as a PDF
... facilitates glutamate actions at NMDA receptors [26,27,69,70]. D2 receptor activity attenuates glutamate actions at non-NMDA receptors [26,70]. Since the nonNMDA glutamate activity is necessary before the NMDA receptor can become activated, this selective amplification of the NMDA response should se ...
... facilitates glutamate actions at NMDA receptors [26,27,69,70]. D2 receptor activity attenuates glutamate actions at non-NMDA receptors [26,70]. Since the nonNMDA glutamate activity is necessary before the NMDA receptor can become activated, this selective amplification of the NMDA response should se ...
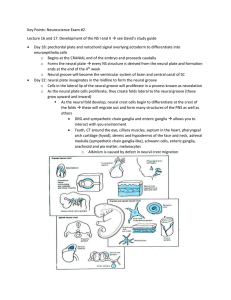
Key Points: Neuroscience Exam #2 Lecture 16 and 17: Development of
... complex sequences of voluntary movements. Receive projections from: Prefrontal cortex (decision making) Parietal association areas (spatial relationships between body & external world) o The brainstem also comes into play through a collective group of tracts that give inputs to body movements ...
... complex sequences of voluntary movements. Receive projections from: Prefrontal cortex (decision making) Parietal association areas (spatial relationships between body & external world) o The brainstem also comes into play through a collective group of tracts that give inputs to body movements ...
PDF file - Izhikevich
... denotes its recovery variable, e.g. the activation of K current. The part 0.04v2 + 5v + 140 was obtained by fitting the spike initiation dynamics of cortical neurons so that units of v correspond to mV and units of time correspond to ms. The variable Isyn denotes the total synaptic current as explai ...
... denotes its recovery variable, e.g. the activation of K current. The part 0.04v2 + 5v + 140 was obtained by fitting the spike initiation dynamics of cortical neurons so that units of v correspond to mV and units of time correspond to ms. The variable Isyn denotes the total synaptic current as explai ...
Roles for miRNAs in Timing Developmental Progression Within
... developmental time for defined classes of neurons in vivo, temporally restricted patterns of expression have been documented for many miRNAs (Kosik and Krichevsky, 2005). Additionally, some miRNAs are enriched in dendrites (Kye et al., 2007); given that axons and dendrites of an individual neuron de ...
... developmental time for defined classes of neurons in vivo, temporally restricted patterns of expression have been documented for many miRNAs (Kosik and Krichevsky, 2005). Additionally, some miRNAs are enriched in dendrites (Kye et al., 2007); given that axons and dendrites of an individual neuron de ...
A Candidate Pathway for a Visual Instructional Signal to the Barn
... Many organisms use multimodal maps to generate coherent neuronal representations that allow adequate responses to stimuli that excite several sensory modalities. During ontogeny of these maps, one modality typically acts as the dominant system the other modalities are aligned to. A well studied mode ...
... Many organisms use multimodal maps to generate coherent neuronal representations that allow adequate responses to stimuli that excite several sensory modalities. During ontogeny of these maps, one modality typically acts as the dominant system the other modalities are aligned to. A well studied mode ...
Hindbrain catecholamine neurons mediate
... Keywords: Norepinephrine; Epinephrine; Anti-dopamine-h-hydroxylase – saporin; Food intake; Glucoprivation; Hypoglycemia; Mercaptoacetate ...
... Keywords: Norepinephrine; Epinephrine; Anti-dopamine-h-hydroxylase – saporin; Food intake; Glucoprivation; Hypoglycemia; Mercaptoacetate ...
Lack of response suppression follows repeated ventral tegmental
... studies showing that cumulative dosing of various cannabinoids excites dopaminergic neurons in the VTA in a dosedependent and CB1-specific manner. 9 The present in vitro study shows that the ability of cannabinoids to excite VTA neurons is not altered by repeated administration. In our preparation, ...
... studies showing that cumulative dosing of various cannabinoids excites dopaminergic neurons in the VTA in a dosedependent and CB1-specific manner. 9 The present in vitro study shows that the ability of cannabinoids to excite VTA neurons is not altered by repeated administration. In our preparation, ...
Function of Peripheral Olfactory Organs
... insect trails such as those produced by termites, ants, and gregarious caterpillars in which the trail follower is never more than a few millimeters from the source - there is no evidence that anything other than the relative difference in concentration, either in time or space (between two antennae ...
... insect trails such as those produced by termites, ants, and gregarious caterpillars in which the trail follower is never more than a few millimeters from the source - there is no evidence that anything other than the relative difference in concentration, either in time or space (between two antennae ...
Mushroom body efferent neurons responsible for aversive olfactory
... to repellent odorants, we propose that MB-V2 neurons recruit the olfactory pathway involved in innate odor avoidance during memory retrieval. Different odors induce innate approach or avoidance behaviors in Drosophila. Innate odor responses can be modulated by experience, such as associative learnin ...
... to repellent odorants, we propose that MB-V2 neurons recruit the olfactory pathway involved in innate odor avoidance during memory retrieval. Different odors induce innate approach or avoidance behaviors in Drosophila. Innate odor responses can be modulated by experience, such as associative learnin ...
disparity detection from stereo
... The work presented here also investigates the more challenging problem of regression with subpixel precision, in contrast with the prior scheme of classification in Solgi and Weng 2008 [28]. For the first time, we present a spatio-temporal regression model of the laminar architecture of the cortex f ...
... The work presented here also investigates the more challenging problem of regression with subpixel precision, in contrast with the prior scheme of classification in Solgi and Weng 2008 [28]. For the first time, we present a spatio-temporal regression model of the laminar architecture of the cortex f ...
Cortical cfos Expression Reveals Broad Receptive Field Excitatory
... layer 2 neurons but also the subthreshold synaptic input that drives spiking. The short latency sensory-evoked synaptic response reflects both direct thalamic and recurrent cortical inputs into the layer 2 network. To isolate this response for comparison between cells, we focused analysis on the ear ...
... layer 2 neurons but also the subthreshold synaptic input that drives spiking. The short latency sensory-evoked synaptic response reflects both direct thalamic and recurrent cortical inputs into the layer 2 network. To isolate this response for comparison between cells, we focused analysis on the ear ...
PDF file
... In the real world, objects do not come into and disappear from the field of view randomly, but rather, they move continuously across the field of view, given their motion is not too fast for the brain to respond. At the pixel level, views are very discontinuous as image patches sweep across the fiel ...
... In the real world, objects do not come into and disappear from the field of view randomly, but rather, they move continuously across the field of view, given their motion is not too fast for the brain to respond. At the pixel level, views are very discontinuous as image patches sweep across the fiel ...
Signals Conveyed in the Pulvinar Pathway from Superior Colliculus
... complete description of our stimulation parameters, including discuscentral spot (0.4°) for 100 –500 ms. A visual stimulus then appeared for sion of the strengths and limitations of this technique, is provided in our 500 –1000 ms and the fixation spot remained on for an additional 250 ms previous pa ...
... complete description of our stimulation parameters, including discuscentral spot (0.4°) for 100 –500 ms. A visual stimulus then appeared for sion of the strengths and limitations of this technique, is provided in our 500 –1000 ms and the fixation spot remained on for an additional 250 ms previous pa ...
Duration Sensitivity to Other Response Properties of the Rat
... sounds. For example, the IC of mice contains a high proportion of long-pass neurons selective for sounds longer than several tens of milliseconds. The few observed bandpass neurons typically have best durations on the order of tens of milliseconds (Brand et al. 2000). Both of these filtering propert ...
... sounds. For example, the IC of mice contains a high proportion of long-pass neurons selective for sounds longer than several tens of milliseconds. The few observed bandpass neurons typically have best durations on the order of tens of milliseconds (Brand et al. 2000). Both of these filtering propert ...
Linköping University Post Print the developmental age of the cells
... number of neurons per chamber was found for P4 cells cultured under glucose-free or glucose-rich conditions (p < 0.001; Table 1). The highest mean number of cells with neuritic processes was also seen for P4 neurons cultured in the absence or presence of glucose (p ≤ 0.01: Table 1). At each particul ...
... number of neurons per chamber was found for P4 cells cultured under glucose-free or glucose-rich conditions (p < 0.001; Table 1). The highest mean number of cells with neuritic processes was also seen for P4 neurons cultured in the absence or presence of glucose (p ≤ 0.01: Table 1). At each particul ...
embryonic development of the leech nervous system
... whole nerve cord. The medial muscle cells are positioned along the ventral midline as early as stage 9(0/4) when there are only ganglionic primordia. The lateral muscle cells appear to migrate from the mesodermal tissue block to a position on either side of the medial muscle cells by stage 9(1/4) (F ...
... whole nerve cord. The medial muscle cells are positioned along the ventral midline as early as stage 9(0/4) when there are only ganglionic primordia. The lateral muscle cells appear to migrate from the mesodermal tissue block to a position on either side of the medial muscle cells by stage 9(1/4) (F ...
D22 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... formula to calculate conduction velocity in motor fibers: motor conduction velocity* = distance between two stimulation sites / time difference in latencies. *velocity is so measured only for fastest conducting fibers. N.B. difference in latencies is used to exclude neuromuscular transmission time ...
... formula to calculate conduction velocity in motor fibers: motor conduction velocity* = distance between two stimulation sites / time difference in latencies. *velocity is so measured only for fastest conducting fibers. N.B. difference in latencies is used to exclude neuromuscular transmission time ...
Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher
... In the first brain relay of the olfactory system, odors are encoded by combinations of glomeruli, but it is not known how glomerular signals are ultimately integrated. In Drosophila melanogaster, the majority of glomerular projections target the lateral horn. Here we show that lateral horn neurons ( ...
... In the first brain relay of the olfactory system, odors are encoded by combinations of glomeruli, but it is not known how glomerular signals are ultimately integrated. In Drosophila melanogaster, the majority of glomerular projections target the lateral horn. Here we show that lateral horn neurons ( ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... procedure used with humans, participants were instructed to watch as a blue square appeared on a computer screen and to be “aware” of the amount of time that passed (either 8,12, or 21sec) before the square changed color (the criterion duration). After several training trials, participants were inst ...
... procedure used with humans, participants were instructed to watch as a blue square appeared on a computer screen and to be “aware” of the amount of time that passed (either 8,12, or 21sec) before the square changed color (the criterion duration). After several training trials, participants were inst ...
A Hebbian learning rule gives rise to mirror neurons and links them
... loop during motor explorations and stabilized by heterosynaptic competition, naturally gives rise to mirror neurons as well as control theoretic inverse models encoded in the synaptic weights from sensory to motor neurons. Crucially, we find that the correlational structure or stereotypy of the neur ...
... loop during motor explorations and stabilized by heterosynaptic competition, naturally gives rise to mirror neurons as well as control theoretic inverse models encoded in the synaptic weights from sensory to motor neurons. Crucially, we find that the correlational structure or stereotypy of the neur ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.