Morphological Studies of Wobbler Mouse Dorsal Root Ganglia
... animal models have been suggested to cause these symptoms, such as oxidative stress due to mitochondrial dysfunction, protein aggregation, neuroinflammation in different parts of the central nervous system and impaired axonal transport [26]. Up till now, none of the cellular defects found have led t ...
... animal models have been suggested to cause these symptoms, such as oxidative stress due to mitochondrial dysfunction, protein aggregation, neuroinflammation in different parts of the central nervous system and impaired axonal transport [26]. Up till now, none of the cellular defects found have led t ...
Stochastic dynamics as a principle of brain function
... factor in a network with a finite (i.e., limited) number of neurons. The spiking noise can be described as introducing statistical fluctuations into the finite-size system. It is important that the outcome that is reached, and not just its time course, is influenced on each trial by these statistical flu ...
... factor in a network with a finite (i.e., limited) number of neurons. The spiking noise can be described as introducing statistical fluctuations into the finite-size system. It is important that the outcome that is reached, and not just its time course, is influenced on each trial by these statistical flu ...
Subcircuit-specific neuromodulation in the prefrontal cortex
... neurons that project back to the PFC, but not with neurons projecting to the accumbens. Conversely, prefrontal inputs synapse onto GABAergic neurons projecting to nucleus accumbens, but not those projecting to the PFC (Carr and Sesack, 2000). Prefrontal inputs to LC synapse onto the dendrites of nor ...
... neurons that project back to the PFC, but not with neurons projecting to the accumbens. Conversely, prefrontal inputs synapse onto GABAergic neurons projecting to nucleus accumbens, but not those projecting to the PFC (Carr and Sesack, 2000). Prefrontal inputs to LC synapse onto the dendrites of nor ...
Striate cortex increases contrast gain of macaque LGN neurons
... contrast–response functions using chromatically opponent gratings of very low spatial frequency modulated along the neuron’s preferred azimuth in the equiluminant plane (Derrington et al., 1984; Lennie et al., 1990). In almost all cases, the contrast gain, which we define as the amplitude of the fir ...
... contrast–response functions using chromatically opponent gratings of very low spatial frequency modulated along the neuron’s preferred azimuth in the equiluminant plane (Derrington et al., 1984; Lennie et al., 1990). In almost all cases, the contrast gain, which we define as the amplitude of the fir ...
Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed
... Myelin sheath is a protective coat around the axon of a neuron and acts as an insulator to the electrical signal that is conducted down the axon as a neuron fires. This increases the conduction speed of action potential and thus is a critical factor in maintaining the proper communication within the ...
... Myelin sheath is a protective coat around the axon of a neuron and acts as an insulator to the electrical signal that is conducted down the axon as a neuron fires. This increases the conduction speed of action potential and thus is a critical factor in maintaining the proper communication within the ...
Structural changes of the human superior cervical
... Since SCG is the main source of sympathetic innervation of the cerebral arteries, we proposed a hypothesis that a stroke damaging the integrity of cerebral arteries and the structure of perivascular nervous plexus may cause distal axonal damage and indirectly contribute to defects in axonal transpor ...
... Since SCG is the main source of sympathetic innervation of the cerebral arteries, we proposed a hypothesis that a stroke damaging the integrity of cerebral arteries and the structure of perivascular nervous plexus may cause distal axonal damage and indirectly contribute to defects in axonal transpor ...
Emotional and Behavioral Correlates of Mediodorsal Thalamic
... bars that had a single steel bar on one end and two bars on the other end. Once the cement had hardened, these bars were removed, leaving a negative impression of the double end on each side of the acrylic block. During subsequent surgery or during the recording session, the double end of these arti ...
... bars that had a single steel bar on one end and two bars on the other end. Once the cement had hardened, these bars were removed, leaving a negative impression of the double end on each side of the acrylic block. During subsequent surgery or during the recording session, the double end of these arti ...
Kandel ch. 42 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Mossy fibers originate from nuclei in the spinal cord and brain stem and carry sensory information from the periphery as well as information from the cerebral cortex. They terminate as excitatory synapses on the dendrites of granule cells in the granular layer (Figure 42-4). The axons of the granule ...
... Mossy fibers originate from nuclei in the spinal cord and brain stem and carry sensory information from the periphery as well as information from the cerebral cortex. They terminate as excitatory synapses on the dendrites of granule cells in the granular layer (Figure 42-4). The axons of the granule ...
Regulation of neuronal survival and death by extracellular signals
... innervation affects the number of innervating neurons that survive led to the idea that neuronal death matches the number of neurons to the size and requirements of their target ®elds (Oppenheim, 1991). A long established idea, the neurotrophic hypothesis, provides an explanation for how target ®eld ...
... innervation affects the number of innervating neurons that survive led to the idea that neuronal death matches the number of neurons to the size and requirements of their target ®elds (Oppenheim, 1991). A long established idea, the neurotrophic hypothesis, provides an explanation for how target ®eld ...
Hypothalamus and Limbic System
... Temperature regulation is an excellent example of a servo-control mechanism operating in the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is sensitive both to hypothalamic and peripheral temperature, and it mediates changes in autonomic, endocrine and behavioral responses in order to maintain homeostasis. Feeding ...
... Temperature regulation is an excellent example of a servo-control mechanism operating in the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is sensitive both to hypothalamic and peripheral temperature, and it mediates changes in autonomic, endocrine and behavioral responses in order to maintain homeostasis. Feeding ...
How the brain uses time to represent and process visual information
... For both D spike and D interval , we examined a wide range of values for q, since neural coincidence-detectors with precisions ranging from milliseconds to seconds have been identified [10], and the range of timescales for which firing rates influence synaptic efficacy is also large. Fortunately, th ...
... For both D spike and D interval , we examined a wide range of values for q, since neural coincidence-detectors with precisions ranging from milliseconds to seconds have been identified [10], and the range of timescales for which firing rates influence synaptic efficacy is also large. Fortunately, th ...
Document
... Age 15-25years Distal leg weaknss followed by shoulder girdle few years later Sparing intrinsic muscle of the foot Sensory abnormalities may developed AD neurogenic scapuloperoneal amyotrophy Congenital absence of some muscles Laryngeal palsy Males > females ...
... Age 15-25years Distal leg weaknss followed by shoulder girdle few years later Sparing intrinsic muscle of the foot Sensory abnormalities may developed AD neurogenic scapuloperoneal amyotrophy Congenital absence of some muscles Laryngeal palsy Males > females ...
Full-Text PDF
... many different in vitro applications, using 64 electrode channels. In a parallel respect, Franke and colleagues [6] used a high-density (HD) electrode array to perform real-time spike sorting for closed-loop experiments that study neural plasticity. These studies exploited the existing electrode arr ...
... many different in vitro applications, using 64 electrode channels. In a parallel respect, Franke and colleagues [6] used a high-density (HD) electrode array to perform real-time spike sorting for closed-loop experiments that study neural plasticity. These studies exploited the existing electrode arr ...
Purves chs. 15, 19 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... An orderly relationship between the location of the motor neuron pools and the muscles they innervate is evident both along the length of the spinal cord and across the mediolateral dimension of the cord, an arrangement that in effect provides a spatial map of the body’s musculature. For example, th ...
... An orderly relationship between the location of the motor neuron pools and the muscles they innervate is evident both along the length of the spinal cord and across the mediolateral dimension of the cord, an arrangement that in effect provides a spatial map of the body’s musculature. For example, th ...
Cortical Motor Organization, Mirror Neurons, and
... this property, can also contribute to provide the observer with the details of the observed act, probably through feedback connections between motor cortex and posterior, higher order, visual areas. This mechanism, which is supported by the presence of reciprocal connections between anterior and pos ...
... this property, can also contribute to provide the observer with the details of the observed act, probably through feedback connections between motor cortex and posterior, higher order, visual areas. This mechanism, which is supported by the presence of reciprocal connections between anterior and pos ...
Efficient Event-Driven Simulation of Large Networks of Spiking
... necessary ordering of events in time. Then we go into detail on the working of the algorithm. 4.1 Main Elements and Data Structures. Each recurrent, instantaneous spike (event) emitted by an IF neuron of the simulated network is represented by the pair (i, t) where i is the emitting neuron and t is ...
... necessary ordering of events in time. Then we go into detail on the working of the algorithm. 4.1 Main Elements and Data Structures. Each recurrent, instantaneous spike (event) emitted by an IF neuron of the simulated network is represented by the pair (i, t) where i is the emitting neuron and t is ...
The Role of Dorsal Columns Pathway in Visceral Pain
... supraspinal sites, as it was not affected by decerebration but it could not be evoked after spinalization (Ness and Gebhart 1988). It was shown previously that responses of spinal neurons to visceral stimuli are under strong descending facilitatory control (Cervero and Wolstencroft 1984, Tattersall ...
... supraspinal sites, as it was not affected by decerebration but it could not be evoked after spinalization (Ness and Gebhart 1988). It was shown previously that responses of spinal neurons to visceral stimuli are under strong descending facilitatory control (Cervero and Wolstencroft 1984, Tattersall ...
Scene perception: inferior temporal cortex neurons encode the
... Inferior temporal cortex (IT) neurons have reduced receptive field sizes in complex natural scenes. This facilitates the read-out of information about individual objects from IT, but raises the question of whether more than the single object present at the fovea is represented by the firing of IT ne ...
... Inferior temporal cortex (IT) neurons have reduced receptive field sizes in complex natural scenes. This facilitates the read-out of information about individual objects from IT, but raises the question of whether more than the single object present at the fovea is represented by the firing of IT ne ...
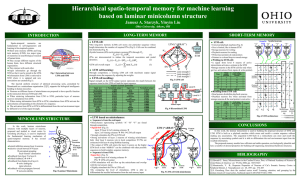
From/To LTM - Ohio University
... They occupy different regions of the human brain, have different structural organization. They interact with each other. Input information go through the STM so that it can be stored in the LTM. Information from LTM is retrieved to STM where it is updated and new associations are created (Fi ...
... They occupy different regions of the human brain, have different structural organization. They interact with each other. Input information go through the STM so that it can be stored in the LTM. Information from LTM is retrieved to STM where it is updated and new associations are created (Fi ...
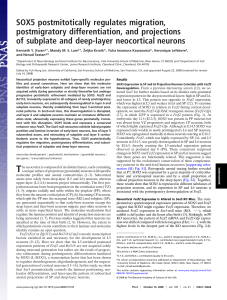
kwanPNAS08
... alterations in neuronal migration. Therefore, we used 5-chloro2-deoxyuridine (CldU) and IdU to birth-date SP and deep-layer neurons at E11.5, E12.5, and E13.5 (n ⫽ 3 per genotype) and upper-layer neurons at E15.5 and E16.5 (n ⫽ 2) and then analyzed their radial distribution at P0 (Fig. S7). In the K ...
... alterations in neuronal migration. Therefore, we used 5-chloro2-deoxyuridine (CldU) and IdU to birth-date SP and deep-layer neurons at E11.5, E12.5, and E13.5 (n ⫽ 3 per genotype) and upper-layer neurons at E15.5 and E16.5 (n ⫽ 2) and then analyzed their radial distribution at P0 (Fig. S7). In the K ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... The nervous system is the master controlling and communicating system of the body. Every thought, action, and emotion reflects its activity. Its cells communicate by electrical and chemical signals, which are rapid and specific, and usually cause almost immediate responses. We begin this chapter wit ...
... The nervous system is the master controlling and communicating system of the body. Every thought, action, and emotion reflects its activity. Its cells communicate by electrical and chemical signals, which are rapid and specific, and usually cause almost immediate responses. We begin this chapter wit ...
Spiking Neurons - Computing Science and Mathematics
... or T = 500 ms are typical , but the duration may also be longer or shorter. This definition of rate has been successfully used in many preparations , particularly in experiments on sensory or motor systems. A classicalexample is the stretch receptor in a muscle spindle [Adrian, 1926] . The number of ...
... or T = 500 ms are typical , but the duration may also be longer or shorter. This definition of rate has been successfully used in many preparations , particularly in experiments on sensory or motor systems. A classicalexample is the stretch receptor in a muscle spindle [Adrian, 1926] . The number of ...
Sten Grillner
... belt, with the belt speed set on low, the two limbs generated alternating locomotor movements. But when the speed was increased, the coordination of the limbs changed to in phase locomotor movements like in a gallop. This thus demonstrated that the two basic modes of coordination could be generated ...
... belt, with the belt speed set on low, the two limbs generated alternating locomotor movements. But when the speed was increased, the coordination of the limbs changed to in phase locomotor movements like in a gallop. This thus demonstrated that the two basic modes of coordination could be generated ...
Heading: Sensory Deprivation in Humans, Mice, and History Caleb B. Carson Running Head: Sensory Deprivation
... pelagic hair, but, like other hairs, the shaft consists of an inert material called keratin, and contains no nerves. Contrastly, if these vibrissae have no nerves, how can they be used for tactile sensory? The answer is that they grow from a special hair follicle, incorporating a capsule of blood ...
... pelagic hair, but, like other hairs, the shaft consists of an inert material called keratin, and contains no nerves. Contrastly, if these vibrissae have no nerves, how can they be used for tactile sensory? The answer is that they grow from a special hair follicle, incorporating a capsule of blood ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.