A quantitative description of the mouse piriform cortex
... piriform cortex. Quantitative descriptions such as these are important because they make it possible to construct realistic models and provide a constraint that theories of the olfactory circuit must fulfil. We show how quantitative descriptions can be useful for modelling by using our data to refin ...
... piriform cortex. Quantitative descriptions such as these are important because they make it possible to construct realistic models and provide a constraint that theories of the olfactory circuit must fulfil. We show how quantitative descriptions can be useful for modelling by using our data to refin ...
neuronal types and their specification dynamics in
... Autonomic neurons regulate organ function via release of neurotransmitters. Virtually every organ (with a few exceptions discussed below) receives both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervations (Figure 1). Because autonomic neurons are tonically active, target tissues receive some input at all ti ...
... Autonomic neurons regulate organ function via release of neurotransmitters. Virtually every organ (with a few exceptions discussed below) receives both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervations (Figure 1). Because autonomic neurons are tonically active, target tissues receive some input at all ti ...
empathize with fictional characters
... Furthermore, research on how language conveys meaning has suggested that linguistic meaning must be grounded in perceptual and motor experiences associated with bodily activity. The abstract symbols of language cannot relate only to other abstract symbols, but must be mapped to the world, if they ar ...
... Furthermore, research on how language conveys meaning has suggested that linguistic meaning must be grounded in perceptual and motor experiences associated with bodily activity. The abstract symbols of language cannot relate only to other abstract symbols, but must be mapped to the world, if they ar ...
Neurons in Anterior Cingulate Cortex Multiplex
... of ACC neurons for specific actions remains almost entirely unknown. To address these questions, we probed the activity of single neurons within dACC while monkeys performed a variably rewarded eight-option decision task. We found that postsaccade responses of most dACC neurons strongly encoded the ...
... of ACC neurons for specific actions remains almost entirely unknown. To address these questions, we probed the activity of single neurons within dACC while monkeys performed a variably rewarded eight-option decision task. We found that postsaccade responses of most dACC neurons strongly encoded the ...
Mechanisms of Plasticity of Inhibition in Chronic Pain Conditions
... The release of GABA/glycine can also be regulated by specific presynaptic receptors. In particular, GABAB and glutamate receptors are expressed on presynaptic inhibitory terminals and their activation can modulate the transmitter release (Chéry and De Koninck 2000; Kerchner et al. 2001; Hugel and Sc ...
... The release of GABA/glycine can also be regulated by specific presynaptic receptors. In particular, GABAB and glutamate receptors are expressed on presynaptic inhibitory terminals and their activation can modulate the transmitter release (Chéry and De Koninck 2000; Kerchner et al. 2001; Hugel and Sc ...
V1 mechanisms underlying chromatic contrast detection
... (Graham 1977; Sachs et al. 1971). We asked whether signals measured in V1 at a psychophysical detection threshold (PT) are consistent with the cardinal mechanisms model. Although V1 neurons are not tuned to the cardinal color directions when tested with high-contrast stimuli (Horwitz et al. 2007; Jo ...
... (Graham 1977; Sachs et al. 1971). We asked whether signals measured in V1 at a psychophysical detection threshold (PT) are consistent with the cardinal mechanisms model. Although V1 neurons are not tuned to the cardinal color directions when tested with high-contrast stimuli (Horwitz et al. 2007; Jo ...
Integration of Perspective and Disparity Cues in Surface
... Single-unit activity was recorded during the performance of the DMTS task under three conditions (D⫹P, P-only, and D-only) in a blocked manner. Each block consisted of 45 trials, in which each of 9 different surface orientations was presented as a sample stimulus for every 9 trials in a random order ...
... Single-unit activity was recorded during the performance of the DMTS task under three conditions (D⫹P, P-only, and D-only) in a blocked manner. Each block consisted of 45 trials, in which each of 9 different surface orientations was presented as a sample stimulus for every 9 trials in a random order ...
Nerve Cells and Insect Behavior—Studies on Crickets1 This report
... adapting wing handedness and tooth impact (for literature see Kutsch and Huber, 1989). In this respect one should never forget that large parts of the body are employed in a single behavioral act. When a male cricket calls it not only moves the forewings periodically, but also suppresses fast walkin ...
... adapting wing handedness and tooth impact (for literature see Kutsch and Huber, 1989). In this respect one should never forget that large parts of the body are employed in a single behavioral act. When a male cricket calls it not only moves the forewings periodically, but also suppresses fast walkin ...
The functional asymmetry of auditory cortex is reflected
... of the map. We filled each neuron with a fluorescent marker (Alexa 594) to confirm that the dendritic tree was mostly contained within the slice, and to establish whether spines were present (Fig. 1b, right). All cells analyzed in this study were excitatory, as based on morphology and the presence o ...
... of the map. We filled each neuron with a fluorescent marker (Alexa 594) to confirm that the dendritic tree was mostly contained within the slice, and to establish whether spines were present (Fig. 1b, right). All cells analyzed in this study were excitatory, as based on morphology and the presence o ...
Activity-dependent editing of neuromuscular synaptic connections
... related experiments suggest that inputs driven by each eye compete for cortical targets, and that more active terminals from the open eye have a competitive advantage over inactive inputs from the closed eye. Activity manipulations during the critical period produced permanent changes in the synapti ...
... related experiments suggest that inputs driven by each eye compete for cortical targets, and that more active terminals from the open eye have a competitive advantage over inactive inputs from the closed eye. Activity manipulations during the critical period produced permanent changes in the synapti ...
“Congruent” and “Opposite” Neurons: Sisters for Multisensory
... the disparity information between the cues is lost, and the brain can no longer discriminate objects clearly when the cues actually come from different objects. To solve this dilemma, here we argue that the brain needs to carry out multisensory integration and segregation concurrently in the early s ...
... the disparity information between the cues is lost, and the brain can no longer discriminate objects clearly when the cues actually come from different objects. To solve this dilemma, here we argue that the brain needs to carry out multisensory integration and segregation concurrently in the early s ...
Recording Electrical Signals from Human Muscle
... Every deliberate movement a person makes involves contractions of various skeletal muscles in the body. Each skeletal muscle is composed of many thousands of muscle fibers and each of these fibers is a multi-nucleated cell. An example of a skeletal muscle is the biceps, which contracts as you reach ...
... Every deliberate movement a person makes involves contractions of various skeletal muscles in the body. Each skeletal muscle is composed of many thousands of muscle fibers and each of these fibers is a multi-nucleated cell. An example of a skeletal muscle is the biceps, which contracts as you reach ...
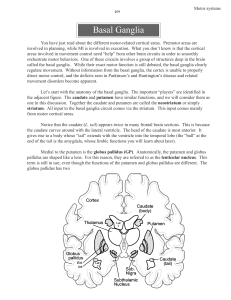
Motor systems Basal ganglia
... that project to VA/VL also use GABA. So, the cortical signal excites striatal neurons, which results in MORE inhibition from striatum to GP(internal). More inhibition of GP(internal) means LESS inhibition of motor thalamus (VA/VL). Since the motor thalamus receives LESS inhibition, the VA/VL cells w ...
... that project to VA/VL also use GABA. So, the cortical signal excites striatal neurons, which results in MORE inhibition from striatum to GP(internal). More inhibition of GP(internal) means LESS inhibition of motor thalamus (VA/VL). Since the motor thalamus receives LESS inhibition, the VA/VL cells w ...
Decision Making in Recurrent Neuronal Circuits
... a fixed decision threshold. In a race model, accumulators representing different choice options build up their activities, and whichever is the first to reach a prescribed threshold produces the choice (Logan and Cowan, 1984). In a drift diffusion model for two-alternative forced choices, an accumul ...
... a fixed decision threshold. In a race model, accumulators representing different choice options build up their activities, and whichever is the first to reach a prescribed threshold produces the choice (Logan and Cowan, 1984). In a drift diffusion model for two-alternative forced choices, an accumul ...
Somatic motor pathways
... • The basal ganglia help program habitual or automatic sequences and set an appropriate level of muscle tone. • They also selectively inhibit other motor neuron circuits that are intrinsically active or excitatory. ...
... • The basal ganglia help program habitual or automatic sequences and set an appropriate level of muscle tone. • They also selectively inhibit other motor neuron circuits that are intrinsically active or excitatory. ...
Cough, Expiration and Aspiration Reflexes following
... network generating the cough reflex were introduced by Shannon et al. (1998, 2000). According to this model neuronal circuitries of the Respiratory Central Pattern Generator can also produce the cough motor pattern. However, the possibility that other brainstem circuits overlapping the main respirat ...
... network generating the cough reflex were introduced by Shannon et al. (1998, 2000). According to this model neuronal circuitries of the Respiratory Central Pattern Generator can also produce the cough motor pattern. However, the possibility that other brainstem circuits overlapping the main respirat ...
Attractor concretion as a mechanism for the formation of context
... number of trials, the CS-reinforcement contingencies were reversed and monkeys had to learn the new contingencies. In the experiments, the CS–US associations were reversed only once. However, in principle, the two contexts defined by the sets of CS–US associations could be alternated multiple times. ...
... number of trials, the CS-reinforcement contingencies were reversed and monkeys had to learn the new contingencies. In the experiments, the CS–US associations were reversed only once. However, in principle, the two contexts defined by the sets of CS–US associations could be alternated multiple times. ...
PDF
... (L5 and L6) and subplate (SP; see Glossary, Box 1) neurons, whereas upper-layer (L2-L4) neurons project within the cortex, either intra-hemispherically or contralaterally, mostly via the corpus callosum (see Glossary, Box 1). In addition to projection neurons, interneurons of distinct lineages and m ...
... (L5 and L6) and subplate (SP; see Glossary, Box 1) neurons, whereas upper-layer (L2-L4) neurons project within the cortex, either intra-hemispherically or contralaterally, mostly via the corpus callosum (see Glossary, Box 1). In addition to projection neurons, interneurons of distinct lineages and m ...
Turtle Dorsal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons Comprise Two Distinct Cell
... O2 and 5% CO2), adjusted to pH 7.4 at room temperature. For diffuse whole-field visual stimulation of the retina, a red light emitting diode (LED) was positioned 2 cm above the eye cup. Timed brief flashes of 10 ms duration were presented with at least thirty seconds between flashes. Approximately 2 ...
... O2 and 5% CO2), adjusted to pH 7.4 at room temperature. For diffuse whole-field visual stimulation of the retina, a red light emitting diode (LED) was positioned 2 cm above the eye cup. Timed brief flashes of 10 ms duration were presented with at least thirty seconds between flashes. Approximately 2 ...
Dorsal spinal cord stimulation obtunds the capacity of intrathoracic
... power 1401 data acquisition system) and analyzed using the Spike 2 software package (Cambridge Electronics Design). Ganglionic loci were identified from which action potentials with signal-to-noise ratios ⬎ 3:1 could be recorded. The activity generated by individual neuronal somata was identified by ...
... power 1401 data acquisition system) and analyzed using the Spike 2 software package (Cambridge Electronics Design). Ganglionic loci were identified from which action potentials with signal-to-noise ratios ⬎ 3:1 could be recorded. The activity generated by individual neuronal somata was identified by ...
Pattern of Motor Coordination Underlying Backward Swimming in
... A representative recording of four EMGs during BS is shown in Fig. 3A. The electrodes were positioned bilaterally in the midbody area at two rostrocaudal levels (Fig. 3D). A clear-cut periodic bursting pattern is seen in each EMG, with cycle duration of about 2 s and a burst proportion of about 40% ...
... A representative recording of four EMGs during BS is shown in Fig. 3A. The electrodes were positioned bilaterally in the midbody area at two rostrocaudal levels (Fig. 3D). A clear-cut periodic bursting pattern is seen in each EMG, with cycle duration of about 2 s and a burst proportion of about 40% ...
Studies of the Role of the Paramedian Pontine Reticular Formation
... SLBNs and 9.9° for long-lead burst neurons. Cullen and Guitton17 reported that the preferred directions in their sample of IBNs varied from 29° upward to 30° downward. The mean preferred direction was −1°, closely aligned with the horizontal plane. Based upon these results and the data presented in ...
... SLBNs and 9.9° for long-lead burst neurons. Cullen and Guitton17 reported that the preferred directions in their sample of IBNs varied from 29° upward to 30° downward. The mean preferred direction was −1°, closely aligned with the horizontal plane. Based upon these results and the data presented in ...
Induction of NADPH diaphoraselnitric oxide synthase in the spinal
... after the blast but were drastically reduced thereafter, so that at 7 days after the blast only a few positive neurons were observed. In rats killed at 2 weeks and in longer surviving intervals, i.e. up to 1 month, NADPH-d/NOS reactivity in the ventral horn motor neurons had diminished. The function ...
... after the blast but were drastically reduced thereafter, so that at 7 days after the blast only a few positive neurons were observed. In rats killed at 2 weeks and in longer surviving intervals, i.e. up to 1 month, NADPH-d/NOS reactivity in the ventral horn motor neurons had diminished. The function ...
Proprioceptive Eye Position Signals Are Still Missing a Sensory
... analysis based on examination of tracerpositive populations. Therefore, it remains unclear whether most axons would be expected to make motor contacts on MIFs, as the summary schema suggests (Zimmermann et al., their Fig. 8), or whether palisade ending innervation should be subdivided into two separ ...
... analysis based on examination of tracerpositive populations. Therefore, it remains unclear whether most axons would be expected to make motor contacts on MIFs, as the summary schema suggests (Zimmermann et al., their Fig. 8), or whether palisade ending innervation should be subdivided into two separ ...
Septins promote dendrite and axon development by negatively
... Neurite growth requires two guanine nucleotide-binding protein polymers of tubulins and septins. However, whether and how those cytoskeletal systems are coordinated was unknown. Here we show that the acute knockdown or knockout of the pivotal septin subunit SEPT7 from cerebrocortical neurons impairs ...
... Neurite growth requires two guanine nucleotide-binding protein polymers of tubulins and septins. However, whether and how those cytoskeletal systems are coordinated was unknown. Here we show that the acute knockdown or knockout of the pivotal septin subunit SEPT7 from cerebrocortical neurons impairs ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.