NK1 receptor-expressing spinoparabrachial neurons trigger diffuse
... DH, Sp5O neurons are indirectly activated by cutaneous C-fiber input [18,58]. Accordingly, there is evidence for ipsilateral connections between the MDH and the Sp5O, emanating from laminae III–V of the MDH and to a lesser degree from lamina I and external II [14,57,58]. Although interneurons located ...
... DH, Sp5O neurons are indirectly activated by cutaneous C-fiber input [18,58]. Accordingly, there is evidence for ipsilateral connections between the MDH and the Sp5O, emanating from laminae III–V of the MDH and to a lesser degree from lamina I and external II [14,57,58]. Although interneurons located ...
Restraining influence of A2 neurons in chronic control of arterial
... cardiovascular responses observed. Rats were supplied with normal rat chow and drinking water ad libitum, and kept on a 12 h light–12 h dark cycle in a sound proofed, temperature and humidity controlled room. Water drunk and urine produced were measured daily. A radio-telemetry system (Data Sciences ...
... cardiovascular responses observed. Rats were supplied with normal rat chow and drinking water ad libitum, and kept on a 12 h light–12 h dark cycle in a sound proofed, temperature and humidity controlled room. Water drunk and urine produced were measured daily. A radio-telemetry system (Data Sciences ...
Espasticidad,!!nuevos!conceptos!fisiológicos!y!patofisiológicos
... In) the) nervous) system,) reflexes) are) transmitted) via) signals) through) action) potentials,% which) are) changes) in) membrane) potential) at) very) high) speeds) that) are) spread) across) the) mem0 brane)of)the)nerve)fiber.)These)begin)with)an)abrupt)change)of) the) resting) potential) from) ...
... In) the) nervous) system,) reflexes) are) transmitted) via) signals) through) action) potentials,% which) are) changes) in) membrane) potential) at) very) high) speeds) that) are) spread) across) the) mem0 brane)of)the)nerve)fiber.)These)begin)with)an)abrupt)change)of) the) resting) potential) from) ...
Prosjektoppgave - Mirror neurons_ver4.2
... movement in the monkey's F5 region, it should also activate the neurons in the F1 region that control them. None of the neurons showed any activity during the observation phase (3). Furthermore, because the monkey would usually be watching its own movements, the behavior the recorded neurons display ...
... movement in the monkey's F5 region, it should also activate the neurons in the F1 region that control them. None of the neurons showed any activity during the observation phase (3). Furthermore, because the monkey would usually be watching its own movements, the behavior the recorded neurons display ...
Cranial Nerves with a Focus on Swallowing and Voice.
... - Touch anterior tongue on both sides - Observe contours of masseter at rest. Observe chewing. “Bite down” and palpate masseter muscles ...
... - Touch anterior tongue on both sides - Observe contours of masseter at rest. Observe chewing. “Bite down” and palpate masseter muscles ...
Neural Coding and Auditory Perception
... onset of a stimulus, we hypothesized that spike rate adaptation may enhance directional coding of reverberant sounds i.e. that units which adapt more rapidly to a sustained stimulus will more faithfully encode the true source ITD. This hypothesis was supported by the finding of a significant correla ...
... onset of a stimulus, we hypothesized that spike rate adaptation may enhance directional coding of reverberant sounds i.e. that units which adapt more rapidly to a sustained stimulus will more faithfully encode the true source ITD. This hypothesis was supported by the finding of a significant correla ...
PDF
... subpopulations were performed in various species (Table 1A). It is curious that only rarely the same group performed a systematic analysis of several species, using the same methodology, making it difficult to conclude about interspecies differences. Most of the studies performed in rat and mouse fou ...
... subpopulations were performed in various species (Table 1A). It is curious that only rarely the same group performed a systematic analysis of several species, using the same methodology, making it difficult to conclude about interspecies differences. Most of the studies performed in rat and mouse fou ...
Action recognition in the premotor cortex
... grip', i.e. opposition of the index finger and thumb. This grip was evoked by small objects, (ii) 'Finger prehension', i.e. opposition of the thumb to the other fingers. The monkeys used finger prehension to pick up middle-size objects from a deep narrow container, (iii) 'Whole hand prehension', i.e ...
... grip', i.e. opposition of the index finger and thumb. This grip was evoked by small objects, (ii) 'Finger prehension', i.e. opposition of the thumb to the other fingers. The monkeys used finger prehension to pick up middle-size objects from a deep narrow container, (iii) 'Whole hand prehension', i.e ...
Dexterous Finger Movements in Primate Without Monosynaptic
... finger (D2) and of digit 5 (D5) viewed from the lateral side at the time of contact with the morsel. When the index finger was flexed during removal of the morsel, there was always parallel flexion of digit 5. This was the case throughout a postoperative observation period of 3 mo in the three monke ...
... finger (D2) and of digit 5 (D5) viewed from the lateral side at the time of contact with the morsel. When the index finger was flexed during removal of the morsel, there was always parallel flexion of digit 5. This was the case throughout a postoperative observation period of 3 mo in the three monke ...
Biomimetic approaches to the control of underwater walking machines
... To approach the behavioural capabilities of the model organism, we base the controller on existing models of the underlying lobster neuronal circuitry which are incomplete (Chrachri & Clarac 1989). The intact walking pattern has three phases with a late swing bringing the limb back into contact with ...
... To approach the behavioural capabilities of the model organism, we base the controller on existing models of the underlying lobster neuronal circuitry which are incomplete (Chrachri & Clarac 1989). The intact walking pattern has three phases with a late swing bringing the limb back into contact with ...
Formation of Neuronal Pathways in the lmaginal Discs of Drosophila
... During the next few hours APF, the disc elongates rapidly. Simultaneous with the elongation, several groups of neurons differentiate and pioneer a secondary branching pattern. Figure 2C shows the pathways in leg discs at 4 hr APF. By this time, the leg disc has already assumed a tubular shape and in ...
... During the next few hours APF, the disc elongates rapidly. Simultaneous with the elongation, several groups of neurons differentiate and pioneer a secondary branching pattern. Figure 2C shows the pathways in leg discs at 4 hr APF. By this time, the leg disc has already assumed a tubular shape and in ...
pdf file. - Harvard Vision Lab
... LETTERS Influence of the thalamus on spatial visual processing in frontal cortex Marc A. Sommer1,2 & Robert H. Wurtz2 ...
... LETTERS Influence of the thalamus on spatial visual processing in frontal cortex Marc A. Sommer1,2 & Robert H. Wurtz2 ...
The fate of Nissl-stained dark neurons following
... using various staining methods, such as hematoxylin and eosin stain, Nissl stain and silver stain [17, 19, 25, 29, 33, 41]. Since dark neurons show massive shrinkage and abnormal basophilia, they can be clearly distinguished from normal neurons. Some studies have shown the following electron microsc ...
... using various staining methods, such as hematoxylin and eosin stain, Nissl stain and silver stain [17, 19, 25, 29, 33, 41]. Since dark neurons show massive shrinkage and abnormal basophilia, they can be clearly distinguished from normal neurons. Some studies have shown the following electron microsc ...
Sample Chapter 8 from the Textbook
... The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a unique subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. The ENS has both sensory and motor neurons contained wholly within the digestive tract. The ENS can function without input from the CNS or other parts of the PNS, although it is normally integrated with the CN ...
... The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a unique subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. The ENS has both sensory and motor neurons contained wholly within the digestive tract. The ENS can function without input from the CNS or other parts of the PNS, although it is normally integrated with the CN ...
Anatomy of Olivocochlear Neurons
... Both groups of OC neurons have fibers that branch extensively in the cochlea (Fig. 2.3). The end result of the branching is that a relatively small number of OC neurons gives rise to numerous synapses in the cochlea. LOC fibers synapse mainly on dendrites of auditory nerve fibers beneath IHCs. In th ...
... Both groups of OC neurons have fibers that branch extensively in the cochlea (Fig. 2.3). The end result of the branching is that a relatively small number of OC neurons gives rise to numerous synapses in the cochlea. LOC fibers synapse mainly on dendrites of auditory nerve fibers beneath IHCs. In th ...
Sodium channel expression in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of
... expression within the thalamus are associated with abnormal sensory processing and chronic neuropathic pain after CCI. The abnormal expression of Nav1.3 in third-order neurons suggests a mechanism whereby injury to a peripheral nerve can propagate pathological molecular changes to sequentially-order ...
... expression within the thalamus are associated with abnormal sensory processing and chronic neuropathic pain after CCI. The abnormal expression of Nav1.3 in third-order neurons suggests a mechanism whereby injury to a peripheral nerve can propagate pathological molecular changes to sequentially-order ...
A Neural Mass Model to Simulate Different Rhythms in a Cortical
... a peak in the γ band. These results together confirm the findings, obtained in previous studies [9], that networks of fast inhibitory interneurons may be responsible for gamma activity in the brain. Another important result is represented by the use of more biologically plausible values for the time ...
... a peak in the γ band. These results together confirm the findings, obtained in previous studies [9], that networks of fast inhibitory interneurons may be responsible for gamma activity in the brain. Another important result is represented by the use of more biologically plausible values for the time ...
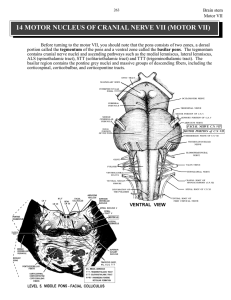
14 MOTOR NUCLEUS OF CRANIAL NERVE VII (MOTOR VII)
... AN INTERESTING CLINICAL OBSERVATION It is known that following a stroke muscles of facial expression of the lower face on the opposite side are weak and the patient cannot voluntarily move these muscles. However, reflex smiling (at a joke) did result in movement of these muscles. This suggests that ...
... AN INTERESTING CLINICAL OBSERVATION It is known that following a stroke muscles of facial expression of the lower face on the opposite side are weak and the patient cannot voluntarily move these muscles. However, reflex smiling (at a joke) did result in movement of these muscles. This suggests that ...
Peripheral and Central Mechanisms of Pain Generation
... mechanical stimuli, thus acting as specific nociceptors that detect potentially or actually damaging mechanical stimuli. At least in the skin many nociceptors respond to noxious heat. The heat threshold may be below the frankly noxious range but the neurons encode different heat intensities by their ...
... mechanical stimuli, thus acting as specific nociceptors that detect potentially or actually damaging mechanical stimuli. At least in the skin many nociceptors respond to noxious heat. The heat threshold may be below the frankly noxious range but the neurons encode different heat intensities by their ...
Early Functional Impairment of Sensory-Motor Connectivity in a Mouse Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy
... excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) due to primary afferent stimulation can be analyzed quantitatively by comparing the peak amplitude of the response 3 ms after its onset (Shneider et al., 2009a). The resulting measurements are similar to other reports (Mears and Frank, 1997; Wang et al., 20 ...
... excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) due to primary afferent stimulation can be analyzed quantitatively by comparing the peak amplitude of the response 3 ms after its onset (Shneider et al., 2009a). The resulting measurements are similar to other reports (Mears and Frank, 1997; Wang et al., 20 ...
Temporal and Spatial Integration in the Rat SI Vibrissa Cortex
... of the vibrissal hairs are innervated by as many as 200 large myelinated axons whose parent cell bodies are located in the trigeminal ganglion (63; see also Ref. 28). Physiological studies have demonstrated that these first-order afferent fibers functionally innervate not more than one whisker (79; ...
... of the vibrissal hairs are innervated by as many as 200 large myelinated axons whose parent cell bodies are located in the trigeminal ganglion (63; see also Ref. 28). Physiological studies have demonstrated that these first-order afferent fibers functionally innervate not more than one whisker (79; ...
Two Types of Neurons in the Primate Globus
... each trial (see below). Experiments were carried out in a darkened booth. Voltages proportional to horizontal and vertical eye position were calibrated before each experiment by having monkeys fixate on a stationary target spot at known visual angles. Thereafter, visual stimuli were presented in indi ...
... each trial (see below). Experiments were carried out in a darkened booth. Voltages proportional to horizontal and vertical eye position were calibrated before each experiment by having monkeys fixate on a stationary target spot at known visual angles. Thereafter, visual stimuli were presented in indi ...
identification of cell types in brain slices of the inferior colliculus
... colliculus suggest that intrinsic electrical properties contribute to discharge patterns, but the intrinsic discharge patterns have not been fully characterized in the central nucleus, the main part of the inferior colliculus. Whether different types of neurons are related to different discharge pat ...
... colliculus suggest that intrinsic electrical properties contribute to discharge patterns, but the intrinsic discharge patterns have not been fully characterized in the central nucleus, the main part of the inferior colliculus. Whether different types of neurons are related to different discharge pat ...
Purves ch. 8 + Kandel ch. 23 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... skin depression. Meissner’s corpuscles are the most common mechanoreceptors of “glabrous” (smooth, hairless) skin (the fingertips, for instance), and their afferent fibers account for about 40% of the sensory innervation of the human hand. These corpuscles are particularly efficient in transducing i ...
... skin depression. Meissner’s corpuscles are the most common mechanoreceptors of “glabrous” (smooth, hairless) skin (the fingertips, for instance), and their afferent fibers account for about 40% of the sensory innervation of the human hand. These corpuscles are particularly efficient in transducing i ...
The Inferior Parietal Lobule Is the Target of Output from the Superior
... ointment was placed in the eyes. A craniotomy was performed over the parietal lobe, and the dura was incised and reflected to expose the region of interest. The cortex was kept moist by the use of warmed (37– 40°C) sterile saline throughout the entire procedure. Injection sites. One monkey received ...
... ointment was placed in the eyes. A craniotomy was performed over the parietal lobe, and the dura was incised and reflected to expose the region of interest. The cortex was kept moist by the use of warmed (37– 40°C) sterile saline throughout the entire procedure. Injection sites. One monkey received ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.