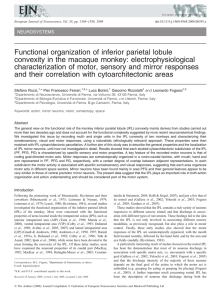
Descending Systems Translate Transient Cortical Commands into a
... 1981; He et al. 1993; Porter and Lemon 1993; Lemon 2008) could be used to extract the muscle command from the integrated cortical representation (Shah et al. 2004). Recently, based on the finding that intrinsic commands emerge first downstream to M1, we hypothesized that spinal interneurons do not ser ...
... 1981; He et al. 1993; Porter and Lemon 1993; Lemon 2008) could be used to extract the muscle command from the integrated cortical representation (Shah et al. 2004). Recently, based on the finding that intrinsic commands emerge first downstream to M1, we hypothesized that spinal interneurons do not ser ...
Chapter 13
... 23. Drinking alcohol causes what change in the body? A.pH of blood declines as it becomes acidic B.Krebs cycle does not operate properly C.fat accumulates in the liver; also, liver cells die D.immune system functioning declines E.All of the choices are correct. 24. Reflex centers for visual, audito ...
... 23. Drinking alcohol causes what change in the body? A.pH of blood declines as it becomes acidic B.Krebs cycle does not operate properly C.fat accumulates in the liver; also, liver cells die D.immune system functioning declines E.All of the choices are correct. 24. Reflex centers for visual, audito ...
The dual nature of time preparation: neural
... follows the MEP in the ongoing electromyogram (EMG) when the response agonists are tonically contracted (Burle et al., 2002). While the initial part of the SP can be a direct consequence of the MEP (refractory period of neurons involved in the MEP, pause in spindle firing, or Renshaw inhibition), the ...
... follows the MEP in the ongoing electromyogram (EMG) when the response agonists are tonically contracted (Burle et al., 2002). While the initial part of the SP can be a direct consequence of the MEP (refractory period of neurons involved in the MEP, pause in spindle firing, or Renshaw inhibition), the ...
Mirror Neurons Responding to Observation of Actions Made with
... food with the stick to the whole holding phase. In contrast, when the experimenter grasped food with the hand (B), during the approaching and grasping phase, there was a complete inhibition of the neuron response. However, the holding phase, similarly to condition A, was excitatory. Thus, the discri ...
... food with the stick to the whole holding phase. In contrast, when the experimenter grasped food with the hand (B), during the approaching and grasping phase, there was a complete inhibition of the neuron response. However, the holding phase, similarly to condition A, was excitatory. Thus, the discri ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Somatic nervous system • A, thick, heavily myelinated somatic motor fiber makes up each pathway from the CNS to the muscle ...
... • Somatic nervous system • A, thick, heavily myelinated somatic motor fiber makes up each pathway from the CNS to the muscle ...
PDF
... eosinophilic cell bodies were remarkably shrunken with condensed and clumped nuclear chromatin at 12 to 48 hours (Figure 1A). These shrunken eosinophilic neurons were observed by EM as disseminated electron-dense dark neurons that were homogeneously condensed and surrounded by remarkably swollen ast ...
... eosinophilic cell bodies were remarkably shrunken with condensed and clumped nuclear chromatin at 12 to 48 hours (Figure 1A). These shrunken eosinophilic neurons were observed by EM as disseminated electron-dense dark neurons that were homogeneously condensed and surrounded by remarkably swollen ast ...
Forward Processing of Long-Term Associative Memory in Monkey
... Figure 2. Stimulus-selective responses to both paired associates of two representative A36 neurons (A and B for one neuron; C and D for the other neuron). A, C, Raster displays and PSTHs in the optimal (optimal, thick black line) and pair ( pair, thick gray line) trials. The trials were aligned at t ...
... Figure 2. Stimulus-selective responses to both paired associates of two representative A36 neurons (A and B for one neuron; C and D for the other neuron). A, C, Raster displays and PSTHs in the optimal (optimal, thick black line) and pair ( pair, thick gray line) trials. The trials were aligned at t ...
Phase synchronization of bursting neurons in clustered small
... subnetwork is a SW network obtained from a regular onedimensional lattice of neurons with periodic boundary conditions. Each neuron is connected to its nearest and next-tonearest neighbors. Then we randomly add new connections among neurons in the lattice with a given intracluster probability pi [17 ...
... subnetwork is a SW network obtained from a regular onedimensional lattice of neurons with periodic boundary conditions. Each neuron is connected to its nearest and next-tonearest neighbors. Then we randomly add new connections among neurons in the lattice with a given intracluster probability pi [17 ...
A dendritic disinhibitory circuit mechanism for pathway
... the disinhibitory motif mediated by VIP and SOM interneurons6,8,12–15. These studies generally found that VIP neurons are activated, and SOM neurons are inactivated, in response to changes in the animals’ behavioural states, such as when mice receive reinforcement14, or start active whisking6,15 or ...
... the disinhibitory motif mediated by VIP and SOM interneurons6,8,12–15. These studies generally found that VIP neurons are activated, and SOM neurons are inactivated, in response to changes in the animals’ behavioural states, such as when mice receive reinforcement14, or start active whisking6,15 or ...
the giant serotonergic neuron of aplysia: a multi
... morphological characteristics of synapses on axonal processes and cell bodies of neurons in the buccal ganglion and, unexpectedly, it forms appositions most often with glial cells which form the lining of intraganglionic hemal sinuses. Thus, GCN, through contacts on a variety of postsynaptic targets ...
... morphological characteristics of synapses on axonal processes and cell bodies of neurons in the buccal ganglion and, unexpectedly, it forms appositions most often with glial cells which form the lining of intraganglionic hemal sinuses. Thus, GCN, through contacts on a variety of postsynaptic targets ...
Decoding Complete Reach and Grasp Actions from Local Primary
... now being evaluated in human pilot clinical trials, could potentially be used to control a realistic robotic arm and hand or even reanimate multiple muscles in a paralyzed limb using extant functional electrical stimulation techniques (Moritz et al., 2008), going far beyond the few dimensions of neu ...
... now being evaluated in human pilot clinical trials, could potentially be used to control a realistic robotic arm and hand or even reanimate multiple muscles in a paralyzed limb using extant functional electrical stimulation techniques (Moritz et al., 2008), going far beyond the few dimensions of neu ...
Functional organization of inferior parietal lobule convexity in the
... out moving the electrode row caudally in steps of 1 mm. During each experimental session each electrode was inserted one after the other inside the dura until the first neuronal activity was detected for each of them. Each electrode was then deepened into the cortex independently one from the other, ...
... out moving the electrode row caudally in steps of 1 mm. During each experimental session each electrode was inserted one after the other inside the dura until the first neuronal activity was detected for each of them. Each electrode was then deepened into the cortex independently one from the other, ...
CN V - Trigeminal
... Cochlear ganglion to CN VIII CN VIII synapses in the cochlear nuclei Cochlear nuclei project to the superior olivary nucleus and inferior colliculus Superior olivary nucleus is also receiving input from contralateral cochlear nuclei Superior olivary nucleus projects to inferior colliculus Inferior c ...
... Cochlear ganglion to CN VIII CN VIII synapses in the cochlear nuclei Cochlear nuclei project to the superior olivary nucleus and inferior colliculus Superior olivary nucleus is also receiving input from contralateral cochlear nuclei Superior olivary nucleus projects to inferior colliculus Inferior c ...
CHAPTER 13- The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... A) is divided into anterior, posterior and lateral columns. B) contains ascending myelinated axons in groups called sensory tracts. C) contains descending myelinated axons in groups called motor tracts. D) A and B are correct. E) A, B and C are correct. 9) A tumor is growing in the left lateral horn ...
... A) is divided into anterior, posterior and lateral columns. B) contains ascending myelinated axons in groups called sensory tracts. C) contains descending myelinated axons in groups called motor tracts. D) A and B are correct. E) A, B and C are correct. 9) A tumor is growing in the left lateral horn ...
angol tézisfüzet0531
... The retrograde tracer cholera toxin β subunit (CTB; List Biological Laboratories) was injected into specific brain regions where the majority of PHAL/pro-TRHcontaining, double-labeled axons were found in the anterograde tract-tracing experiment (0.5% CTB, 6.0 µamps for 11-15 min, pulsed at 7 second ...
... The retrograde tracer cholera toxin β subunit (CTB; List Biological Laboratories) was injected into specific brain regions where the majority of PHAL/pro-TRHcontaining, double-labeled axons were found in the anterograde tract-tracing experiment (0.5% CTB, 6.0 µamps for 11-15 min, pulsed at 7 second ...
Visuomotor development
... sensorimotor pathways in computational neuroethology, Cliff, 1995). The concept of a unitary sensorimotor cycle as a motor primitive for the generation of adaptive behavior in animals (and humans) is not recent. For a long time in biology, the reflex arc was assumed to play a central role in the pro ...
... sensorimotor pathways in computational neuroethology, Cliff, 1995). The concept of a unitary sensorimotor cycle as a motor primitive for the generation of adaptive behavior in animals (and humans) is not recent. For a long time in biology, the reflex arc was assumed to play a central role in the pro ...
Increased responses in trigeminocervical nociceptive neurons to cervical input after
... The receptive ®eld of each neuron was tested systematically using a range of different stimuli. The cutaneous facial and cervical receptive ®eld, including the cornea, was assessed in all three trigeminal innervation territories and upper cervical roots, respectively. Additionally, input from subocc ...
... The receptive ®eld of each neuron was tested systematically using a range of different stimuli. The cutaneous facial and cervical receptive ®eld, including the cornea, was assessed in all three trigeminal innervation territories and upper cervical roots, respectively. Additionally, input from subocc ...
From swimming to walking with a salamander robot
... locomotor region (MLR) located in the midbrain (15). Low levels of stimulation induce the slow walking gait and, at some threshold, higher stimulation induces a rapid switch to the faster swimming mode. In both modes, the frequency of motion is proportional to the stimulation strength. Gait transiti ...
... locomotor region (MLR) located in the midbrain (15). Low levels of stimulation induce the slow walking gait and, at some threshold, higher stimulation induces a rapid switch to the faster swimming mode. In both modes, the frequency of motion is proportional to the stimulation strength. Gait transiti ...
Clarke`s column neurons as the focus of a corticospinal corollary circuit
... and excitatory inputs to Clarke’s column neurons established local spinal circuits with the capacity to mark or modulate incoming proprioceptive input. Together, our genetic, anatomical and physiological results indicate that Clarke’s column spinocerebellar neurons nucleate local spinal corollary ci ...
... and excitatory inputs to Clarke’s column neurons established local spinal circuits with the capacity to mark or modulate incoming proprioceptive input. Together, our genetic, anatomical and physiological results indicate that Clarke’s column spinocerebellar neurons nucleate local spinal corollary ci ...
Cell type-specific pharmacology of NMDA receptors using masked
... engineering can be used to selectively knock out NMDA receptors in certain types of brain cells, but these techniques are too slow, and can take weeks or even a lifetime to work. Now, Yang et al. have developed a clever way to combine an NMDA-blocking drug and genetic engineering to study NMDA recep ...
... engineering can be used to selectively knock out NMDA receptors in certain types of brain cells, but these techniques are too slow, and can take weeks or even a lifetime to work. Now, Yang et al. have developed a clever way to combine an NMDA-blocking drug and genetic engineering to study NMDA recep ...
Embodied Cognition and Mirror Neurons
... that during a control task requiring subjects to evaluate whether a particular motor property was associated with an object (e.g., HAIR = combed). The authors found a greater signal for the color knowledge task than for the control task in a left fusiform area demonstrated to be more active during c ...
... that during a control task requiring subjects to evaluate whether a particular motor property was associated with an object (e.g., HAIR = combed). The authors found a greater signal for the color knowledge task than for the control task in a left fusiform area demonstrated to be more active during c ...
Neurons
... temperature, blood pH, or the position of a joint – Dendrites of neurons in the brain and spinal cord usually respond to chemicals, called neurotransmitters, that are released by other neurons Biology: Life on Earth, 9e ...
... temperature, blood pH, or the position of a joint – Dendrites of neurons in the brain and spinal cord usually respond to chemicals, called neurotransmitters, that are released by other neurons Biology: Life on Earth, 9e ...
Voluntary Nicotine Consumption Triggers Potentiation of Cortical Excitatory Drives to Midbrain
... neurons. Thus, recruitment of these specific excitatory inputs to VTA DA neurons may be a neural correlate for the learned association between active responding and the reward experience. ...
... neurons. Thus, recruitment of these specific excitatory inputs to VTA DA neurons may be a neural correlate for the learned association between active responding and the reward experience. ...
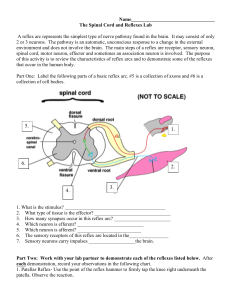
Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord
... A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex are receptor, sensory neuron, spi ...
... A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex are receptor, sensory neuron, spi ...
the brainstem control of saccadic eye movements
... the speed and direction of full-field image motion across the retina initiate optokinetic reflexes that supplement the VOR in the low-frequency range. ...
... the speed and direction of full-field image motion across the retina initiate optokinetic reflexes that supplement the VOR in the low-frequency range. ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.