Spinal Cord Motor Activity
... of extrafusal muscle fibers and spindles, Golgi tendon organs are in series with the muscle fibers. When a muscle is passively stretched, most of the change in length occurs in the muscle fibers, since they are more elastic than the fibrils of the tendon. When a muscle actively contracts, however, t ...
... of extrafusal muscle fibers and spindles, Golgi tendon organs are in series with the muscle fibers. When a muscle is passively stretched, most of the change in length occurs in the muscle fibers, since they are more elastic than the fibrils of the tendon. When a muscle actively contracts, however, t ...
Hypothalamus - aHuman Project
... ¾Firing rate of ADH-releasing neurons depends on central and peripheral inputs (baroreceptors!) as well as their intrinsic osmosensitivity ...
... ¾Firing rate of ADH-releasing neurons depends on central and peripheral inputs (baroreceptors!) as well as their intrinsic osmosensitivity ...
Variation in the area of distribution of the lateral pectoral nerve and a
... nerve supply from the ventral division of brachial plexus. ...
... nerve supply from the ventral division of brachial plexus. ...
MECHANISMS OF CENTRAL TRANSMISSION OF RESPIRATORY
... (1889) "Paradoxical reflex". That means that under certain conditions expiratory, as well as inspiratory activity is depressed by pulmonary inflation. At these higher ranges of lung inflation we could observe also inhibition of unspecific reticular activity (Koepchen 1969, Fig. 8). These findings su ...
... (1889) "Paradoxical reflex". That means that under certain conditions expiratory, as well as inspiratory activity is depressed by pulmonary inflation. At these higher ranges of lung inflation we could observe also inhibition of unspecific reticular activity (Koepchen 1969, Fig. 8). These findings su ...
Direction of action is represented in the ventral premotor cortex
... location of a target, specified in an external coordinate frame, into a set of muscle activation patterns, specified in an intrinsic coordinate frame. Insight into the sensorimotor transformations involved in this process1,2 and how these transformations are implemented in the central nervous system ...
... location of a target, specified in an external coordinate frame, into a set of muscle activation patterns, specified in an intrinsic coordinate frame. Insight into the sensorimotor transformations involved in this process1,2 and how these transformations are implemented in the central nervous system ...
Pyramidal neurons: dendritic structure and synaptic integration
... neurons, their functional significance is not clearly understood. They might increase the dendritic surface area in order to optimize the packing of a large number of synapses onto a given length of dendrite186–188. Alternatively, they might serve as biochemical compartments that restrict the diffus ...
... neurons, their functional significance is not clearly understood. They might increase the dendritic surface area in order to optimize the packing of a large number of synapses onto a given length of dendrite186–188. Alternatively, they might serve as biochemical compartments that restrict the diffus ...
Nervous System - El Camino College
... A. Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. B. When sensory impulses are integrated in the brain as perceptions, this is the integrative function of the nervous system. C. Conscious or subconscious decisions follow, leading to motor fu ...
... A. Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. B. When sensory impulses are integrated in the brain as perceptions, this is the integrative function of the nervous system. C. Conscious or subconscious decisions follow, leading to motor fu ...
Aggregate Input-Output Models of Neuronal Populations
... are biophysical-based models, which characterize the nonlinear dynamics of ionic conductances and synapses between neurons [6], [7]. Although useful in understanding underlying physiology and mechanisms of spike generation, these models become intractable for analysis of populations of neurons. Furt ...
... are biophysical-based models, which characterize the nonlinear dynamics of ionic conductances and synapses between neurons [6], [7]. Although useful in understanding underlying physiology and mechanisms of spike generation, these models become intractable for analysis of populations of neurons. Furt ...
Rules Ventral Prefrontal Cortical Axons Use to Reach Their Targets
... differences in the trajectories of fibers from different vPFC areas. Overall, the medial/lateral vPFC position dictates the route that fibers take to enter major WM tracts, as well as the position within specific tracts: axons from medial vPFC regions travel ventral to those from more lateral areas. ...
... differences in the trajectories of fibers from different vPFC areas. Overall, the medial/lateral vPFC position dictates the route that fibers take to enter major WM tracts, as well as the position within specific tracts: axons from medial vPFC regions travel ventral to those from more lateral areas. ...
~ Pergamon
... We combined data from prefrontal areas with similar laminar definition to determine whether regional differences in the distribution of labelled neurons were related to differences in laminar characteristics noted previously/4 Categories were constructed on the basis of number of layers and laminar ...
... We combined data from prefrontal areas with similar laminar definition to determine whether regional differences in the distribution of labelled neurons were related to differences in laminar characteristics noted previously/4 Categories were constructed on the basis of number of layers and laminar ...
Central Nervous System
... neurons (nerve cells) and glia (specialized connective tissue cells). Neurons conduct impulses Glia (support) cells In other words, neurons are the conducting cells and glial cells are the supportive and connective tissue cells. Copyright (c) 2008, 2005 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier ...
... neurons (nerve cells) and glia (specialized connective tissue cells). Neurons conduct impulses Glia (support) cells In other words, neurons are the conducting cells and glial cells are the supportive and connective tissue cells. Copyright (c) 2008, 2005 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier ...
Grasping the Intentions of Others with One`s Own Mirror Neuron
... Grasping the Intentions of Others with One’s Own Mirror Neuron System ...
... Grasping the Intentions of Others with One’s Own Mirror Neuron System ...
Webb et al 2002 - User Web Areas at the University of York
... trial to trial, and was presented alone, or surrounded by a grating of the same or orthogonal orientation, contained within either a larger annular field, or flanks oriented either horizontally or vertically. V1 was ablated to inactivate cortico-geniculate feedback. The maximum firing rate of LGN ne ...
... trial to trial, and was presented alone, or surrounded by a grating of the same or orthogonal orientation, contained within either a larger annular field, or flanks oriented either horizontally or vertically. V1 was ablated to inactivate cortico-geniculate feedback. The maximum firing rate of LGN ne ...
Spike-Wave Complexes and Fast Components of Cortically
... the action potentials of the intracellularly recorded neuron, demonstrated that the area 4 neuron discharged in close time relation with one, but not the other, neuronal pool before their coalescence (see bottom left panel). Trains of fast stimuli (100 Hz) applied to cortical areas induced seizures ...
... the action potentials of the intracellularly recorded neuron, demonstrated that the area 4 neuron discharged in close time relation with one, but not the other, neuronal pool before their coalescence (see bottom left panel). Trains of fast stimuli (100 Hz) applied to cortical areas induced seizures ...
Sodium channel expression in the ventral posterolateral nucleus of
... ing of the skin, and pinching of the skin. Our new data also document the abnormal expression of the Nav1.3 voltage-gated sodium channel transcripts in the VPL during this time of neuronal hyperresponsiveness and reduced nociceptive thresholds. We observed no changes in the expression of neuronal so ...
... ing of the skin, and pinching of the skin. Our new data also document the abnormal expression of the Nav1.3 voltage-gated sodium channel transcripts in the VPL during this time of neuronal hyperresponsiveness and reduced nociceptive thresholds. We observed no changes in the expression of neuronal so ...
Zoology 242 Anatomy of Nervous systems Lecture 8
... projects towards the region in question, e.g. sensory afferent neuron. • Efferent – originates from the region in question and projects towards a distal point. e.g. motor efferent neuron. • Interneuron – integrating neuron which remains within the central nervous system • Effector – tissue (muscle, ...
... projects towards the region in question, e.g. sensory afferent neuron. • Efferent – originates from the region in question and projects towards a distal point. e.g. motor efferent neuron. • Interneuron – integrating neuron which remains within the central nervous system • Effector – tissue (muscle, ...
Effect of Adrenalectomy on Miniature Inhibitory Postsynaptic
... Verkuyl, J. M. and M. Joëls. Effect of adrenalectomy on miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. J Neurophysiol 89: 237–245, 2003; 10.1152/jn.00401.2002. Within the rat paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus two types of neurons have been d ...
... Verkuyl, J. M. and M. Joëls. Effect of adrenalectomy on miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. J Neurophysiol 89: 237–245, 2003; 10.1152/jn.00401.2002. Within the rat paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus two types of neurons have been d ...
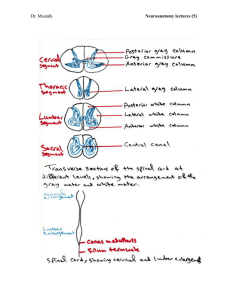
anterior spinothalamic tract.
... White matter of the spinal cord is outside the gray matter and it divides into: dorsal column, anterior column and lateral column. The white matter of the spinal cord contains two major types of nerve fibers: 1- Descending tracts (motor) from high centers of the brain. 2- Ascending tracts (sensory) ...
... White matter of the spinal cord is outside the gray matter and it divides into: dorsal column, anterior column and lateral column. The white matter of the spinal cord contains two major types of nerve fibers: 1- Descending tracts (motor) from high centers of the brain. 2- Ascending tracts (sensory) ...
Chapter 15 The Nervous System
... What are the structures and functions of the central nervous system? What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? What is a reflex? What are two ways in which the nervous system can be injured? ...
... What are the structures and functions of the central nervous system? What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? What is a reflex? What are two ways in which the nervous system can be injured? ...
Turtle Dorsal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons Comprise Two Distinct Cell
... PLOS ONE | DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0144012 December 3, 2015 ...
... PLOS ONE | DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0144012 December 3, 2015 ...
Title - HAL
... For MSNs, scalar values issued from the simulations based on model 1 were in good agreement with the real values, with only one exception, the average branch length, Ln. Simulated trees displayed two remarkable features of MSNs: a weak asymmetry index and an extremely high terminal branch length. In ...
... For MSNs, scalar values issued from the simulations based on model 1 were in good agreement with the real values, with only one exception, the average branch length, Ln. Simulated trees displayed two remarkable features of MSNs: a weak asymmetry index and an extremely high terminal branch length. In ...
Labeled lines meet and talk: population coding of somatic sensations
... sensitivity. In the past century, great progress has been made in understanding the coding of these sensory modalities. From this work, two major features have emerged. First, there are specific neuronal circuits or labeled lines transmitting specific sensory information from the skin to the brain. ...
... sensitivity. In the past century, great progress has been made in understanding the coding of these sensory modalities. From this work, two major features have emerged. First, there are specific neuronal circuits or labeled lines transmitting specific sensory information from the skin to the brain. ...
Module 1 - Doral Academy Preparatory
... CULTURAL DIVERSITY: USE OF PLACEBOS (CONT.) – researchers believe that placebos work by reducing tension and distress and by creating powerful selffulfilling prophecies – individuals think and behave as if the drug, actually a ...
... CULTURAL DIVERSITY: USE OF PLACEBOS (CONT.) – researchers believe that placebos work by reducing tension and distress and by creating powerful selffulfilling prophecies – individuals think and behave as if the drug, actually a ...
Module 3 and 4 Practice Test
... e. thresholds. ____ 11. The chemical messengers released into the spatial junctions between neurons are called a. hormones. b. neurotransmitters. c. synapses. d. sensory neurons. e. motor neurons. ____ 12. When the release of ACh is blocked, the result is a. depression. b. muscular paralysis. c. agg ...
... e. thresholds. ____ 11. The chemical messengers released into the spatial junctions between neurons are called a. hormones. b. neurotransmitters. c. synapses. d. sensory neurons. e. motor neurons. ____ 12. When the release of ACh is blocked, the result is a. depression. b. muscular paralysis. c. agg ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.