Central Dogma.pptx
... DNA’s message (gene) is expressed (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
... DNA’s message (gene) is expressed (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
protein Synthesis
... 1. Protein synthesis is2. The set of instructions in a cell is called? 3. DNA has the information to make what? 4. What do proteins do? What do enzymes do? 5. Where is DNA located? What are genes? 6. What units are proteins made from? Where are proteins synthesized? 7. How does the DNA information g ...
... 1. Protein synthesis is2. The set of instructions in a cell is called? 3. DNA has the information to make what? 4. What do proteins do? What do enzymes do? 5. Where is DNA located? What are genes? 6. What units are proteins made from? Where are proteins synthesized? 7. How does the DNA information g ...
Study Guide
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
... How are the functions of mRNA and tRNA different? Describe the process of transcription and translation. What is a codon? What is an anticodon? How are they related? Why is RNA necessary for expressing the code in DNA? How does an organism’s DNA code for its traits? Summarize the process ...
RNA interference 1. The central dogma 3. The RNAi mechanism
... mRNA is cleaved and destroyed. No protein can be synthesized. ...
... mRNA is cleaved and destroyed. No protein can be synthesized. ...
Slide 1
... Genes defined as regions of the genome that encode RNA that are translated into proteins. Estimated >100,000 proteins from 35,000 genes (only 1.5% of the genome are “genes”) Each gene can encode multiple proteins due to “alternative splicing”. ...
... Genes defined as regions of the genome that encode RNA that are translated into proteins. Estimated >100,000 proteins from 35,000 genes (only 1.5% of the genome are “genes”) Each gene can encode multiple proteins due to “alternative splicing”. ...
DNA Replication - Texas Tech University
... Do not bind directly onto DNA Usually too weak to act on their own ...
... Do not bind directly onto DNA Usually too weak to act on their own ...
Presentation title: Introduction to RNA
... The central dogma of genetics is that the genome, comprised of DNA, encodes many thousands of genes that can be transcribed into RNA. Following this, the RNA may be translated into amino acids giving a functional protein. While the genome of an individual will be identical for each cell througho ...
... The central dogma of genetics is that the genome, comprised of DNA, encodes many thousands of genes that can be transcribed into RNA. Following this, the RNA may be translated into amino acids giving a functional protein. While the genome of an individual will be identical for each cell througho ...
Chapter 10 Protein Synthesis Test Study Guide THERE WILL BE 21
... mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUCG. 15. What would the sequence of DNA be from which the mRNA strand CUCAAGUGCUUC was made? 16. The original DNA sequence below undergoes the following chang ...
... mRNA sequence CUCAAGUGCUUC. 14. Using pg. 207 in your textbook, determine the series of amino acids encoded for by the mRNA sequence AUGGACAAUUCG. 15. What would the sequence of DNA be from which the mRNA strand CUCAAGUGCUUC was made? 16. The original DNA sequence below undergoes the following chang ...
2009 WH Freeman and Company
... Eukaryotic cells contain far more DNA than is required to encode proteins. Nuclear RNAs undergo some type of change before they are exported to the cytoplasm. Regions of DNA might not be transcribed. ...
... Eukaryotic cells contain far more DNA than is required to encode proteins. Nuclear RNAs undergo some type of change before they are exported to the cytoplasm. Regions of DNA might not be transcribed. ...
D7-Transcription and Translation
... redundant, but never ambiguous. It is also (nearly) universal, allowing for DNA from one species to function in another! ...
... redundant, but never ambiguous. It is also (nearly) universal, allowing for DNA from one species to function in another! ...
Chapter 14 – RNA molecules and RNA processing
... • DNA and RNA transcripts within the nucleus are larger than transcripts found in the cytoplasm – Exons are coding regions ...
... • DNA and RNA transcripts within the nucleus are larger than transcripts found in the cytoplasm – Exons are coding regions ...
Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria.
... Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria. 1. Define the three main types of RNA. 2. What are the nucleotides that are used to synthesize RNA? 3. What is the direction of RNA polymerization? 4. What is meant by the statement “RNA polymerization is thermodynamically assisted by PPi hydroly ...
... Chapter 36: RNA Synthesis and Regulation in Bacteria. 1. Define the three main types of RNA. 2. What are the nucleotides that are used to synthesize RNA? 3. What is the direction of RNA polymerization? 4. What is meant by the statement “RNA polymerization is thermodynamically assisted by PPi hydroly ...
second of Chapter 10: RNA processing
... • Introns may play a role in gene evolution. • In some proteins, each exon has its own independent folding characteristics. • Folding domains (=exons) can be grouped together to give new proteins with new functions. • This is called the exon-shuffle model. • Not all genes have domain boundaries that ...
... • Introns may play a role in gene evolution. • In some proteins, each exon has its own independent folding characteristics. • Folding domains (=exons) can be grouped together to give new proteins with new functions. • This is called the exon-shuffle model. • Not all genes have domain boundaries that ...
Improving site-directed RNA editing by screening RNA editing
... Recoding genetic information through RNA editing is a process catalyzed by adenosine deaminases that act on RNA (ADAR). ADARs are an evolutionarily conserved family of enzymes that convert adenosines to inosines within mRNA transcripts. Because inosine is read as guanosine during translation, RNA ed ...
... Recoding genetic information through RNA editing is a process catalyzed by adenosine deaminases that act on RNA (ADAR). ADARs are an evolutionarily conserved family of enzymes that convert adenosines to inosines within mRNA transcripts. Because inosine is read as guanosine during translation, RNA ed ...
P310 Trypanosoma brucei PUF RNA binding proteins Katelyn Fenn
... regulation, with RNA binding proteins proving to be very important in these processes. The mechanic actions of the large number of RNA binding proteins found in the T. brucei genome remain largely unknown. One of the major cellular changes upon differentiation to the procyclic form is the activation ...
... regulation, with RNA binding proteins proving to be very important in these processes. The mechanic actions of the large number of RNA binding proteins found in the T. brucei genome remain largely unknown. One of the major cellular changes upon differentiation to the procyclic form is the activation ...
DNA
... RNA & Protein Synthesis A. Structure 1. Made of a single strand of nucleotides 2. Each nucleotide consists of a. five carbon sugar (ribose) b. phosphate group c. nitrogenous base (adenine, URACIL, guanine, cytosine) B. Transcription (DNA & mRNA) 1. Occurs in the nucleus 2. RNA polymerase a. Binds to ...
... RNA & Protein Synthesis A. Structure 1. Made of a single strand of nucleotides 2. Each nucleotide consists of a. five carbon sugar (ribose) b. phosphate group c. nitrogenous base (adenine, URACIL, guanine, cytosine) B. Transcription (DNA & mRNA) 1. Occurs in the nucleus 2. RNA polymerase a. Binds to ...
Three Types of RNA and Their Functions
... Like rRNA, tRNA is located in the cellular cytoplasm and is involved in protein synthesis. Transfer RNA brings or transfers amino acids to the ribosome that corresponds to each three-nucleotide codon of rRNA. The amino acids then can be joined together and processed to make polypeptides and proteins ...
... Like rRNA, tRNA is located in the cellular cytoplasm and is involved in protein synthesis. Transfer RNA brings or transfers amino acids to the ribosome that corresponds to each three-nucleotide codon of rRNA. The amino acids then can be joined together and processed to make polypeptides and proteins ...
Protein Synthesis - Madison County Schools
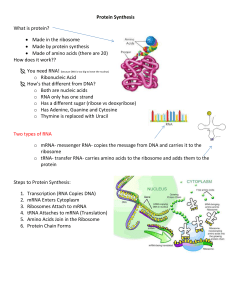
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
Protein Synthesis Review Sheet
... 2. What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair up? a. b. c. d. 3. Name the two types of RNA and the basic function of each. II. Protein Synthesis List the 5 steps of protein synthesis here (use separate notes handout): ...
... 2. What are the 4 bases of RNA and how do they pair up? a. b. c. d. 3. Name the two types of RNA and the basic function of each. II. Protein Synthesis List the 5 steps of protein synthesis here (use separate notes handout): ...
Earth`s Early History 10-2
... New entry “Early Earth History” Review of Biochemistry TEST (spoon) ...
... New entry “Early Earth History” Review of Biochemistry TEST (spoon) ...
Review for Molecular Genetics Quest
... 19. Describe the following mutations: Substitution? Deletion? Insertion? Silent? ...
... 19. Describe the following mutations: Substitution? Deletion? Insertion? Silent? ...
RNA
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
Protein Synthesis Study Guide 1. What is the “central dogma” of
... 5. What are the three types of RNA? What do they do? 6. Explain the process of translation. How do the different types of RNA work together? 7. What is a codon? 8. How does a ribosome know where to start and stop translation? 9. What is an anticodon? Where are anticodons located? 10. What type of bo ...
... 5. What are the three types of RNA? What do they do? 6. Explain the process of translation. How do the different types of RNA work together? 7. What is a codon? 8. How does a ribosome know where to start and stop translation? 9. What is an anticodon? Where are anticodons located? 10. What type of bo ...