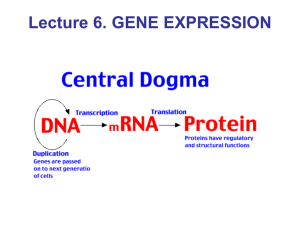
Central dogma: from genome to proteins
... Several important differences between the bacterial and eucaryotic RNA polymerases. • .While bacterial RNA polymerase (with s factor as one of its subunits) is able to initiate transcription on a DNA template in vitro without the help of additional proteins, eucaryotic RNA polymerases cannot. They ...
... Several important differences between the bacterial and eucaryotic RNA polymerases. • .While bacterial RNA polymerase (with s factor as one of its subunits) is able to initiate transcription on a DNA template in vitro without the help of additional proteins, eucaryotic RNA polymerases cannot. They ...
Protein Synthesis
... then carried to the cytoplasm • A ribosome attaches to the mRNA. • The instructions carried by the mRNA will be used to assemble the amino acids in the proper order ...
... then carried to the cytoplasm • A ribosome attaches to the mRNA. • The instructions carried by the mRNA will be used to assemble the amino acids in the proper order ...
Protein Synthesis
... then carried to the cytoplasm • A ribosome attaches to the mRNA. • The instructions carried by the mRNA will be used to assemble the amino acids in the proper order ...
... then carried to the cytoplasm • A ribosome attaches to the mRNA. • The instructions carried by the mRNA will be used to assemble the amino acids in the proper order ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... RNA molecules are complementary to the DNA template. • mRNA is complementary to template strand • mRNA is identical (except for U to T changes) to ...
... RNA molecules are complementary to the DNA template. • mRNA is complementary to template strand • mRNA is identical (except for U to T changes) to ...
Protein Synthesis A gene is a segment of DNA that is located on a
... b. rRNA reads the mRNA strand and assists in the assembly of proteins c. tRNA has a 3 nucleotide anticodon on one end and its corresponding amino acid attached to its other end. It gets the amino acid from the cytosol. d. tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine at one end and the anticodon UAC on th ...
... b. rRNA reads the mRNA strand and assists in the assembly of proteins c. tRNA has a 3 nucleotide anticodon on one end and its corresponding amino acid attached to its other end. It gets the amino acid from the cytosol. d. tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine at one end and the anticodon UAC on th ...
Lecture 15 Biol302 Spring 2011
... How often is this site found in the genome? 1/45 Once every 1000 nucleotides 109 nucleotides or 106 times ...
... How often is this site found in the genome? 1/45 Once every 1000 nucleotides 109 nucleotides or 106 times ...
Standard Deviants RNA Movie
... 1 What is the section of mRNA that is cut out like “garbage”? 2. What section of mRNA is going to be expressed? 3. What is the process by which proteins are created? 4. What 2 shapes do proteins form? 5. Protein shape determines? 6. What is the template that determines the order of the amino acids? ...
... 1 What is the section of mRNA that is cut out like “garbage”? 2. What section of mRNA is going to be expressed? 3. What is the process by which proteins are created? 4. What 2 shapes do proteins form? 5. Protein shape determines? 6. What is the template that determines the order of the amino acids? ...
1, 2, 5, 6, 7 Time: 08:00
... involved in the transcription and translation of genes. -Summarize the role of RNA polymerase in the synthesis of messenger RNA. -Describe how the code of DNA is translated into messenger RNA and is utilized to synthesize a particular protein. ...
... involved in the transcription and translation of genes. -Summarize the role of RNA polymerase in the synthesis of messenger RNA. -Describe how the code of DNA is translated into messenger RNA and is utilized to synthesize a particular protein. ...
Gene Expression
... Transcription is the process of creating RNA from DNA. Transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. RNA polymerase is the protein molecule that reads the DNA and creates the RNA intermediary. Transcription requires: DNA, RNA polymerase, ribonucleotides, and some ATP for energy. Uracil (U) is substitu ...
... Transcription is the process of creating RNA from DNA. Transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. RNA polymerase is the protein molecule that reads the DNA and creates the RNA intermediary. Transcription requires: DNA, RNA polymerase, ribonucleotides, and some ATP for energy. Uracil (U) is substitu ...
dsRNA synthesis RNAi (Howard Clarke)
... Selection and preparation of DNA template: Chose an exon-rich region of genomic DNA 300bp in length (>500 is better, and 3’ UTR sequence is fine). Alternatively, cDNA clones or first-strand cDNA generated by RT-PCR can be used as template (see protocol “Oligo d(T) primed cDNA synthesis”). cDNA templ ...
... Selection and preparation of DNA template: Chose an exon-rich region of genomic DNA 300bp in length (>500 is better, and 3’ UTR sequence is fine). Alternatively, cDNA clones or first-strand cDNA generated by RT-PCR can be used as template (see protocol “Oligo d(T) primed cDNA synthesis”). cDNA templ ...
Chapter 21 (part 1) - Nevada Agricultural Experiment
... site • The a subunit acts as scaffold on which the other subunits assemble. • Also requires s-factor for initiation –forms holo enzyme complex ...
... site • The a subunit acts as scaffold on which the other subunits assemble. • Also requires s-factor for initiation –forms holo enzyme complex ...
“Algorithms for genomes” 2b Central Dogma Transcription start and
... Modular build-up of proteins: visualized ...
... Modular build-up of proteins: visualized ...
Slide 1
... What molecule contains the master instructions for genetic traits & where is it found? What molecule does DNA actually code for the production of? Why do we care about proteins? Where are proteins made? What are they made of? TRAITS!!! How does DNA send the ‘message’ to the ribosomes to make protein ...
... What molecule contains the master instructions for genetic traits & where is it found? What molecule does DNA actually code for the production of? Why do we care about proteins? Where are proteins made? What are they made of? TRAITS!!! How does DNA send the ‘message’ to the ribosomes to make protein ...
Nucleic Acids: Revisiting the Central Dogma
... The molecular hallmarks of lin-4, the founding member of the microRNA family. Sequence complementarity between lin-4 (red) and the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of lin-14 mRNA (blue). lin-4 is partially complementary to 7 sites in the lin-14 3' UTR; its binding to these sites of complementarity bring ...
... The molecular hallmarks of lin-4, the founding member of the microRNA family. Sequence complementarity between lin-4 (red) and the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of lin-14 mRNA (blue). lin-4 is partially complementary to 7 sites in the lin-14 3' UTR; its binding to these sites of complementarity bring ...
Review Game
... WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF RNA? (YOU HAVE TO BE SPECIFIC) Messenger, Transfer, Ribosomal ...
... WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF RNA? (YOU HAVE TO BE SPECIFIC) Messenger, Transfer, Ribosomal ...
Gene Expression
... DNA that makes up the human genome can be subdivided into information bytes called genes. Each gene encodes a unique protein that performs a specialized function in the cell. The human genome contains more than 25,000 genes. ...
... DNA that makes up the human genome can be subdivided into information bytes called genes. Each gene encodes a unique protein that performs a specialized function in the cell. The human genome contains more than 25,000 genes. ...
File - MRS. WILSON Science
... During transcription, a gene is transferred into RNA. Specific DNA sequences and a combination of accessory proteins help RNA polymerase recognize the start of a gene. RNA polymerase is a large enzyme that bonds nucleotides together to make RNA. RNA polymerase, in combination with the other proteins ...
... During transcription, a gene is transferred into RNA. Specific DNA sequences and a combination of accessory proteins help RNA polymerase recognize the start of a gene. RNA polymerase is a large enzyme that bonds nucleotides together to make RNA. RNA polymerase, in combination with the other proteins ...