大腦神經解剖與建置
... and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers for further processing. Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fight-or-flight response. It is also the source of posterior pituitary h ...
... and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers for further processing. Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fight-or-flight response. It is also the source of posterior pituitary h ...
SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
... auditory nerve take signals to cochlear nucleus before thalamus and auditory cortex in the temporal lobe each tone “mapped” to a different area of the cortex some fibers cross over in brainstem • unlike other senses, each cortical lobe receives input from both ears ...
... auditory nerve take signals to cochlear nucleus before thalamus and auditory cortex in the temporal lobe each tone “mapped” to a different area of the cortex some fibers cross over in brainstem • unlike other senses, each cortical lobe receives input from both ears ...
Izabella Battonyai
... (olfactory lobe, PC), which is located in the cerebral ganglion and is a characteristic unit in Stylommatophora (Pulmonata) snails (Van Mol 1974). There are also a number of morphological and physiological data proving that the PC takes part in olfaction processes, it has important role in olfactory ...
... (olfactory lobe, PC), which is located in the cerebral ganglion and is a characteristic unit in Stylommatophora (Pulmonata) snails (Van Mol 1974). There are also a number of morphological and physiological data proving that the PC takes part in olfaction processes, it has important role in olfactory ...
File
... nervous system, myelin, synapse, axon. 1. high alert 2. transmits impulses away from cell body 3. fatty insulating material 4. gap between neurons ...
... nervous system, myelin, synapse, axon. 1. high alert 2. transmits impulses away from cell body 3. fatty insulating material 4. gap between neurons ...
Maximum entropy modeling of multi-neuron firing patterns in V1
... pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of these correlations is controversial. Correlations may reflect genuine interactions between pairs of neurons or driving by a common input. One way to investigate the structure of neuronal correlations i ...
... pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of these correlations is controversial. Correlations may reflect genuine interactions between pairs of neurons or driving by a common input. One way to investigate the structure of neuronal correlations i ...
Control of Movement
... No visual input -> proprioceptive and vestibular sensors only Won’t be able to maintain balance Can be use to test proprioceptive and vestibular damage ...
... No visual input -> proprioceptive and vestibular sensors only Won’t be able to maintain balance Can be use to test proprioceptive and vestibular damage ...
chapter 43 The Nervous System
... plasma membrane spread or propagate frorri one part of-the cell to another. This signaling depends on the properties 'of a variety of specialized membrane transport proteins. First, we examine some of the basic electrical properties common to the membrane of most animal cells that produce a membrane ...
... plasma membrane spread or propagate frorri one part of-the cell to another. This signaling depends on the properties 'of a variety of specialized membrane transport proteins. First, we examine some of the basic electrical properties common to the membrane of most animal cells that produce a membrane ...
Muscular System Rocks!
... is movement. Muscles are the only tissue in the body that has the ability to contract and therefore move the other parts of the body. The muscular systems second function: the maintenance of posture and body position. ...
... is movement. Muscles are the only tissue in the body that has the ability to contract and therefore move the other parts of the body. The muscular systems second function: the maintenance of posture and body position. ...
The Brain and Behaviour
... A specific area in the temporal lobe of the left hemisphere only, next to the primary auditory cortex and connected to Broca’s area by a bundle of nerves is called Wernicke’s area. Wernicke’s area is involved with comprehension of speech; more specifically, with interpreting the sounds of human spee ...
... A specific area in the temporal lobe of the left hemisphere only, next to the primary auditory cortex and connected to Broca’s area by a bundle of nerves is called Wernicke’s area. Wernicke’s area is involved with comprehension of speech; more specifically, with interpreting the sounds of human spee ...
Control and Communication
... 1. Which of the following are the components of the central nervous system (CNS)? a) Brain and neurons b) Neurons and spinal cord c) Brain and spinal cord d) Brain only 2. The list below refers to stages in the response of the nervous system to a stimulus. 1 Central nervous system sorts information ...
... 1. Which of the following are the components of the central nervous system (CNS)? a) Brain and neurons b) Neurons and spinal cord c) Brain and spinal cord d) Brain only 2. The list below refers to stages in the response of the nervous system to a stimulus. 1 Central nervous system sorts information ...
Brain and Cranial Nerves
... 3. many others, including sensory & motor (only 10% of brain’s mass but 50% of its neurons – 100 billion!) IV. Cerebrum Fig. 15.12 A. Structure 1. cerebral cortex - grows rapidly in the fetus, - why is gray matter on outside of cerebral/cerebellar cortex but on inside of spinal cord? 2. some sul ...
... 3. many others, including sensory & motor (only 10% of brain’s mass but 50% of its neurons – 100 billion!) IV. Cerebrum Fig. 15.12 A. Structure 1. cerebral cortex - grows rapidly in the fetus, - why is gray matter on outside of cerebral/cerebellar cortex but on inside of spinal cord? 2. some sul ...
10-21-09
... are activated. Gamma activity has been shown to underlie intact brain communication (Womelsdorf 2007), particularly social communication. Exzperiment used shapes “caressing” and “kissing” (as commonly described by viewers). rSTS and right PTJ were activated, unsurprisingly. The study also looked at ...
... are activated. Gamma activity has been shown to underlie intact brain communication (Womelsdorf 2007), particularly social communication. Exzperiment used shapes “caressing” and “kissing” (as commonly described by viewers). rSTS and right PTJ were activated, unsurprisingly. The study also looked at ...
Synergy between Transplantation of Olig2
... transplanted into injured spinal cord 9 d after injury. The fate of transplanted cells was tracked by GFP fluorescence after transplantation in different time points. After adoptive immunotherapy, the transferred MBP-T cells (CD4-positive) could be detected in injured spinal cord from 3 d to 4 w. Th ...
... transplanted into injured spinal cord 9 d after injury. The fate of transplanted cells was tracked by GFP fluorescence after transplantation in different time points. After adoptive immunotherapy, the transferred MBP-T cells (CD4-positive) could be detected in injured spinal cord from 3 d to 4 w. Th ...
Reverse Engineering the Brain - Biomedical Computation Review
... Computer simulations of the brain already allow experiments impossible to carry out with animals. “As good as modern neuroscience is—and it has been brilliant over the last two decades—we can’t really sample every neuron and every synapse as they are performing a behavior,” notes consciousness resea ...
... Computer simulations of the brain already allow experiments impossible to carry out with animals. “As good as modern neuroscience is—and it has been brilliant over the last two decades—we can’t really sample every neuron and every synapse as they are performing a behavior,” notes consciousness resea ...
PNS Terminology
... -considered part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) -olfactory & optic contain only sensory axons = sensory nerves -remaining are motor or mixed nerves (both motor and sensory axons) ...
... -considered part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) -olfactory & optic contain only sensory axons = sensory nerves -remaining are motor or mixed nerves (both motor and sensory axons) ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s own track to the cerebral cortex • Audition has it own tra ...
... brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s own track to the cerebral cortex • Audition has it own tra ...
reverse engineering of the visual system using networks of spiking
... selectively to the order in which its inputs fire. One obvious possibility would be to use a series of delay lines so that the inputs will arrive synchronously only if the correct delays are used. This strategy is used in a range of sensory systems that use temporal differences between arrival times ...
... selectively to the order in which its inputs fire. One obvious possibility would be to use a series of delay lines so that the inputs will arrive synchronously only if the correct delays are used. This strategy is used in a range of sensory systems that use temporal differences between arrival times ...
1. a) The sagittal plane divides the brain into left and right sides. The
... Affarent refers to information transport towards something. Effarent refers to information transport away from something. Sensory axons for example are affarent as they bring information into the nervous system. Axons that activate muscles on the other hand are efferent as they transport information ...
... Affarent refers to information transport towards something. Effarent refers to information transport away from something. Sensory axons for example are affarent as they bring information into the nervous system. Axons that activate muscles on the other hand are efferent as they transport information ...
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN DAY 1 Includes Part 1 – Part 3
... separates the brain into right and left sides) and carefully remove it from the brain. BE CAREFUL ON THE INFERIOR SIDE NOT TO DAMAGE THE CRANIAL NERVES! 3. Arachnoid- The arachnoid spaces gets compressed during the preservation process. You can see it mostly in the fissures of the brain. It will app ...
... separates the brain into right and left sides) and carefully remove it from the brain. BE CAREFUL ON THE INFERIOR SIDE NOT TO DAMAGE THE CRANIAL NERVES! 3. Arachnoid- The arachnoid spaces gets compressed during the preservation process. You can see it mostly in the fissures of the brain. It will app ...
to get the file
... Thus, neurons in V1 are orientation selective. They are, however, also selective for retinal position and ocular dominance as well as for color and motion. These are called „features“. The neurons are therefore akin to „feature-detectors“. For each of these parameter there exists a topographic map. ...
... Thus, neurons in V1 are orientation selective. They are, however, also selective for retinal position and ocular dominance as well as for color and motion. These are called „features“. The neurons are therefore akin to „feature-detectors“. For each of these parameter there exists a topographic map. ...
THE NeurobiologyOF “We”
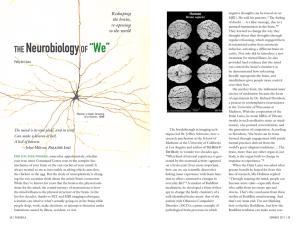
... this little tiny piece of us (the last joint of the two middle fingers) is especially important because it touches all three major parts of our brain: the cortex, limbic area, and brainstem as well as the body-proper. “It’s the middle prefrontal fibers which map out the internal states of others,” h ...
... this little tiny piece of us (the last joint of the two middle fingers) is especially important because it touches all three major parts of our brain: the cortex, limbic area, and brainstem as well as the body-proper. “It’s the middle prefrontal fibers which map out the internal states of others,” h ...
Special Senses
... Olfactory glands secrete a thick mucous, which traps debris and provides a water and lipid soluble medium for odorants (molecules that can be recognized and perceived as scent; typically small organic molecules) ...
... Olfactory glands secrete a thick mucous, which traps debris and provides a water and lipid soluble medium for odorants (molecules that can be recognized and perceived as scent; typically small organic molecules) ...
6-Janata_Natarajan - School of Electronic Engineering and
... • fMRI data showed activity in premotor areas of the brain, which are known to be active in primarily perceptual tasks that have strong and directed anticipatory components to them • This encourages the viewing of music in a perception/action cycle framework. The task demands shape the activity that ...
... • fMRI data showed activity in premotor areas of the brain, which are known to be active in primarily perceptual tasks that have strong and directed anticipatory components to them • This encourages the viewing of music in a perception/action cycle framework. The task demands shape the activity that ...
PDF
... antagonist Lmo4, on the differentiation of motor neurons (MNs) and of V2a interneurons in mice. By combining different mutations that affect Islet expression, the authors demonstrate that reducing Islet protein levels leads to increased V2a interneuron differentiation at the expense of MN formation. ...
... antagonist Lmo4, on the differentiation of motor neurons (MNs) and of V2a interneurons in mice. By combining different mutations that affect Islet expression, the authors demonstrate that reducing Islet protein levels leads to increased V2a interneuron differentiation at the expense of MN formation. ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.