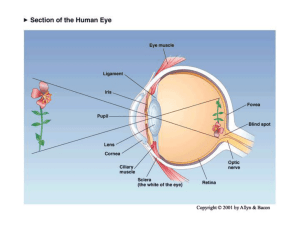
03 Physiology of spinal cord. Physiology of medulla, midbrain and
... The Superior Colliculi receive impulses from the Occipital (Visual) Cortex of the Cerebrum for reflex movements of the Eyes, such as when following objects that are moving across the visual field. The Inferior Colliculi are part of the Auditory Pathway to the Cerebrum. Some fibers pass to the Superi ...
... The Superior Colliculi receive impulses from the Occipital (Visual) Cortex of the Cerebrum for reflex movements of the Eyes, such as when following objects that are moving across the visual field. The Inferior Colliculi are part of the Auditory Pathway to the Cerebrum. Some fibers pass to the Superi ...
Pubertal Influences on Sleep
... “wiring” • By age 6: 95% of brain development completed • YA (10-12 years): 2nd major brain growth spurt • Adolescence (13-20s): Pruning and organizing, especially in frontal cortex ...
... “wiring” • By age 6: 95% of brain development completed • YA (10-12 years): 2nd major brain growth spurt • Adolescence (13-20s): Pruning and organizing, especially in frontal cortex ...
Functional roles of melanocortin-4 receptor in hippocampal synapse
... stimulating hormone (MSH), and adrenocorticotropin hormones. The central melanocortin signaling in the hypothalamus–pituitary-adrenal axis system is critical for regulating various aspects of energy homeostasis and feeding behavior. Although MC4R is highly expressed in other brain regions such as co ...
... stimulating hormone (MSH), and adrenocorticotropin hormones. The central melanocortin signaling in the hypothalamus–pituitary-adrenal axis system is critical for regulating various aspects of energy homeostasis and feeding behavior. Although MC4R is highly expressed in other brain regions such as co ...
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... (thalamus), and then visual association cortex: orienting eyes to things we see and hear – the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then the primary visual cortex (V1, area 17): more to come… ...
... (thalamus), and then visual association cortex: orienting eyes to things we see and hear – the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then the primary visual cortex (V1, area 17): more to come… ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... The autonomic nervous system was described at the beginning of the twentieth century by Langley and coworkers an the term “Autonomic Nervous System was first used by Langley in 1921 As defined, ANS is a motor system “The ANS consists of nerve cells and nerve fibres, by means of which efferent impuls ...
... The autonomic nervous system was described at the beginning of the twentieth century by Langley and coworkers an the term “Autonomic Nervous System was first used by Langley in 1921 As defined, ANS is a motor system “The ANS consists of nerve cells and nerve fibres, by means of which efferent impuls ...
Chapter 1: The Human Body
... plane dividing anterior and posterior portions of the body at right angles to the sagittal plane Horizontal plane dividing the body into superior and inferior portions Midsagittal plane vertically dividing the body into equal right and left portions Sagittal any plane parallel to the midsagittal or ...
... plane dividing anterior and posterior portions of the body at right angles to the sagittal plane Horizontal plane dividing the body into superior and inferior portions Midsagittal plane vertically dividing the body into equal right and left portions Sagittal any plane parallel to the midsagittal or ...
Teaching with the Brain-Based Natural Human Learning FACES
... As a learner goes through the stages of this natural learning process, the learner’s brain constructs its neural networks from the lowest twig up. ...
... As a learner goes through the stages of this natural learning process, the learner’s brain constructs its neural networks from the lowest twig up. ...
nervous system physiology 7
... The ANS coordinates cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, excretory and reproductive systems - visceral afferents as well as from those parts of the CNS that control the viscera and other autonomic functions. - Visceral efferents (general visceral division of the PNS): – Innervates smooth muscle, ...
... The ANS coordinates cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, excretory and reproductive systems - visceral afferents as well as from those parts of the CNS that control the viscera and other autonomic functions. - Visceral efferents (general visceral division of the PNS): – Innervates smooth muscle, ...
7-Physiology of brain stem2016-09-25 05:204.2 MB
... It is involved in the pain desensitization pathway It is involved in the arousal and consciousness systems It contains the locus ceruleus, which is involved in intensive alertness modulation and in autonomic reflexes. ...
... It is involved in the pain desensitization pathway It is involved in the arousal and consciousness systems It contains the locus ceruleus, which is involved in intensive alertness modulation and in autonomic reflexes. ...
Chapter 15 The Nervous System
... What are the structures and functions of the central nervous system? What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? What is a reflex? What are two ways in which the nervous system can be injured? ...
... What are the structures and functions of the central nervous system? What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? What is a reflex? What are two ways in which the nervous system can be injured? ...
Paradigms What is a paradigm? Three to consider The Genetic
... • Loads of new information since the discovery of DNA’s stricture (1953) and the sequencing of the human genome (2003) • Now we know that: 1) virtually all behavior is influenced by genes, and 2) the environment influences how genes are expressed ...
... • Loads of new information since the discovery of DNA’s stricture (1953) and the sequencing of the human genome (2003) • Now we know that: 1) virtually all behavior is influenced by genes, and 2) the environment influences how genes are expressed ...
Genetic analysis of dopaminergic system development in zebrafish
... in zebrafish and compare the positions of DA neurons in fish and mammals using the neuromere model of the vertebrate brain. Based on mutant analysis, we evaluate the role of several signaling pathways in catecholaminergic neuron specification. We further discuss the prospect of identifying novel genes ...
... in zebrafish and compare the positions of DA neurons in fish and mammals using the neuromere model of the vertebrate brain. Based on mutant analysis, we evaluate the role of several signaling pathways in catecholaminergic neuron specification. We further discuss the prospect of identifying novel genes ...
Ch 1 Notes
... • Plant Cells, Animal Cells, Moneran Cells, Fungal Cells, Protist Cell • There are 100 trillion cells in the human body and the majority of these cells are located in the blood. ...
... • Plant Cells, Animal Cells, Moneran Cells, Fungal Cells, Protist Cell • There are 100 trillion cells in the human body and the majority of these cells are located in the blood. ...
29.2 Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... • Pass messages from the central nervous system to the other tissues in the body, such as muscles • Function: Carry nerve impulses out of the brain or spinal cord to effectors •Effectors: muscles and glands • Located in the PNS. ...
... • Pass messages from the central nervous system to the other tissues in the body, such as muscles • Function: Carry nerve impulses out of the brain or spinal cord to effectors •Effectors: muscles and glands • Located in the PNS. ...
what is the brain?? - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... Certain neurological disorders, such as Parkinson's Disease, also affect only specific areas of the brain. The damage caused by these conditions is far less than damage to 90% of the brain. ...
... Certain neurological disorders, such as Parkinson's Disease, also affect only specific areas of the brain. The damage caused by these conditions is far less than damage to 90% of the brain. ...
Sensation and Perception
... • Feature Detectors –nerves cells in the brain that respond to specific features – line, curve, shape color Example: • Supercell clusters – teams of cells that fire in response to complex patterns Example: ...
... • Feature Detectors –nerves cells in the brain that respond to specific features – line, curve, shape color Example: • Supercell clusters – teams of cells that fire in response to complex patterns Example: ...
E4 - Neurotransmitters and Synapses - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... EPSPs depolarize post-synaptic neurons while IPSPs hyper-polarize post-synaptic neurons if the post-synaptic neuron reaches threshold potential at its axon hillock, it will produce an action potential pre-synaptic neurons can vary in the frequency, but not intensity of their input, since act ...
... EPSPs depolarize post-synaptic neurons while IPSPs hyper-polarize post-synaptic neurons if the post-synaptic neuron reaches threshold potential at its axon hillock, it will produce an action potential pre-synaptic neurons can vary in the frequency, but not intensity of their input, since act ...
Completed Notes
... > horns lead to dorsal & ventral roots (outside cord), which is start of PNS. - dorsal root has enlarged ganglion – where cell bodies of sensory neuron cell located. ...
... > horns lead to dorsal & ventral roots (outside cord), which is start of PNS. - dorsal root has enlarged ganglion – where cell bodies of sensory neuron cell located. ...
Message Transmission
... – Yes, even when they are not stimulated (resting) they have an uneven concentration of positive and negative ions on opposite sides of their membranes ...
... – Yes, even when they are not stimulated (resting) they have an uneven concentration of positive and negative ions on opposite sides of their membranes ...
Human Genetics
... associated with autism Two genes in particular may finally explain how autism develops - They encode the cell adhesion proteins neurexins and neuroligins - These proteins strengthen synaptic connections in neurons associated with learning and memory ...
... associated with autism Two genes in particular may finally explain how autism develops - They encode the cell adhesion proteins neurexins and neuroligins - These proteins strengthen synaptic connections in neurons associated with learning and memory ...
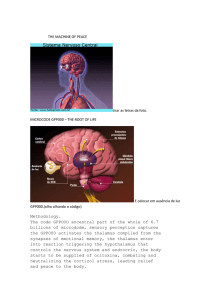
THE MACHINE OF PEACE tirar as letras da foto. MICROCODE
... may influence each other before being redistributed. His connections are more abundant, by far, with the cortex. The main function of the thalamus is to serve as station reorganization of stimuli from the periphery and the brain stem and also some coming from higher centers. There synapse axons of n ...
... may influence each other before being redistributed. His connections are more abundant, by far, with the cortex. The main function of the thalamus is to serve as station reorganization of stimuli from the periphery and the brain stem and also some coming from higher centers. There synapse axons of n ...
Exam - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
PERSPECTIVES
... tracking the location of the rat in the environment. Each place cell discharges only when the animal is in a cell-specific stable region called its “place field.” Place fields occur with about equal density over the entire surface of the environment, hence their ensemble firing can be decoded to det ...
... tracking the location of the rat in the environment. Each place cell discharges only when the animal is in a cell-specific stable region called its “place field.” Place fields occur with about equal density over the entire surface of the environment, hence their ensemble firing can be decoded to det ...
HORMONES AND BEHAVIOR 1. The Neuroendocrine System: Sum
... many of the hormones found in the body. This is usually regulated through “multi-step” signaling mechanisms (_____________) pituitary gland all the way to the various glands in the body that synthesize hormones. In turn, many hormones reach back to the brain and influence various cognitive and behav ...
... many of the hormones found in the body. This is usually regulated through “multi-step” signaling mechanisms (_____________) pituitary gland all the way to the various glands in the body that synthesize hormones. In turn, many hormones reach back to the brain and influence various cognitive and behav ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.