12 - Brazosport College
... • Helps maintain stable environment for brain • Separates neurons from some bloodborne substances • Composition – Continuous endothelium of capillary walls – Thick basal lamina around capillaries – Feet of astrocytes • Provide signal to endothelium for formation of tight junctions MDufilho ...
... • Helps maintain stable environment for brain • Separates neurons from some bloodborne substances • Composition – Continuous endothelium of capillary walls – Thick basal lamina around capillaries – Feet of astrocytes • Provide signal to endothelium for formation of tight junctions MDufilho ...
Unit2-KA3a-NervousSystem
... To pass the message to the CNS. The CNS processes the information from our senses which needs a response Motor neurons enable a response brought about by the CNS to occur. It can be a rapid action from a muscle or a slower response from a gland. A nerve cell which is found between a sensory and a mo ...
... To pass the message to the CNS. The CNS processes the information from our senses which needs a response Motor neurons enable a response brought about by the CNS to occur. It can be a rapid action from a muscle or a slower response from a gland. A nerve cell which is found between a sensory and a mo ...
The Brain of the Planarian as the Ancestor of the Human Brain
... pair of nerve cords in the pianarian is interconnected at regular intervals by commissures. Peripheral nerve fibres extend from the cords to form subepidermal and submuscular plexuses throughout the body, but peripheral ganglia do not develop. The two nerve cords are thus equivalent to the two sides ...
... pair of nerve cords in the pianarian is interconnected at regular intervals by commissures. Peripheral nerve fibres extend from the cords to form subepidermal and submuscular plexuses throughout the body, but peripheral ganglia do not develop. The two nerve cords are thus equivalent to the two sides ...
Chapter 2
... of structural details of the dendritic trees of individual neurons. Filling techniques provide pictures similar to those obtained by the Golgi method but for individual neurons that have been studied physiologically. A histochemically demonstrable ion or enzyme or a fluorescent dye is injected into ...
... of structural details of the dendritic trees of individual neurons. Filling techniques provide pictures similar to those obtained by the Golgi method but for individual neurons that have been studied physiologically. A histochemically demonstrable ion or enzyme or a fluorescent dye is injected into ...
Introduction and Summary - Cyprus Chiropractic Association
... known neurons which are essential to our development as fully functional humans. For further information see the section below on von Economo neurons (VENs), gigantopyramidal cells and Calcium Binding Calretinin cells. The prefrontal lobes are an integral part of what is called the neo-cortex (new b ...
... known neurons which are essential to our development as fully functional humans. For further information see the section below on von Economo neurons (VENs), gigantopyramidal cells and Calcium Binding Calretinin cells. The prefrontal lobes are an integral part of what is called the neo-cortex (new b ...
File
... Dorsal (posterior) Medial Lateral Intermediate Proximal Distal Superficial (external) Deep (internal) ...
... Dorsal (posterior) Medial Lateral Intermediate Proximal Distal Superficial (external) Deep (internal) ...
afaf-el-ansary-king-saud-university-saudi
... glial cells and amidated by GS to the non-toxic amino acid glutamine. Glutamine is then released by glial cells and taken up by neurons, where it is hydrolyzed by glutaminase to form glutamate again, completing the glutamate/glutamine cycle. ...
... glial cells and amidated by GS to the non-toxic amino acid glutamine. Glutamine is then released by glial cells and taken up by neurons, where it is hydrolyzed by glutaminase to form glutamate again, completing the glutamate/glutamine cycle. ...
a study of axonal protein trafficking in neuronal networks via the
... express fluorescent proteins in neurons. Preliminary results show that the neurons can be polarized with their soma and axons being compartmentalized into different fluidically isolated microenvironments. When chemical stimulation was applied to axonal chamber, anterograde migration of expressed flu ...
... express fluorescent proteins in neurons. Preliminary results show that the neurons can be polarized with their soma and axons being compartmentalized into different fluidically isolated microenvironments. When chemical stimulation was applied to axonal chamber, anterograde migration of expressed flu ...
ANS notes filled
... It has a similar function as acetylcholinesterase, but works at a slower rate. As a result some NE tends to diffuse out of the synapse into the surrounding tissues, where it may exert an effect. So the effects of sympathetic stimulation are more wide spread and last longer the parasympathetic stimul ...
... It has a similar function as acetylcholinesterase, but works at a slower rate. As a result some NE tends to diffuse out of the synapse into the surrounding tissues, where it may exert an effect. So the effects of sympathetic stimulation are more wide spread and last longer the parasympathetic stimul ...
Topic A.3 notes
... • 12. optic nerve = transmits visual information from the retina to the brain • 13. blind spot = the specific region of the retina where the optic nerve and blood vessels pass through to connect to the back of the eye • 14. retina = thin layer of neural cells that lines the back of the eyeball ...
... • 12. optic nerve = transmits visual information from the retina to the brain • 13. blind spot = the specific region of the retina where the optic nerve and blood vessels pass through to connect to the back of the eye • 14. retina = thin layer of neural cells that lines the back of the eyeball ...
Perception of stimuli special senses
... • 12. optic nerve = transmits visual information from the retina to the brain • 13. blind spot = the specific region of the retina where the optic nerve and blood vessels pass through to connect to the back of the eye • 14. retina = thin layer of neural cells that lines the back of the eyeball ...
... • 12. optic nerve = transmits visual information from the retina to the brain • 13. blind spot = the specific region of the retina where the optic nerve and blood vessels pass through to connect to the back of the eye • 14. retina = thin layer of neural cells that lines the back of the eyeball ...
thoughts - Budokon MD
... to these patterns of thinking as First-order and Second-order change. First-order change involves solving the problem from within the system of the problem. Second-order change involves getting outside of the problem system in order to find the solution. Dieting is the perfect example of how first-o ...
... to these patterns of thinking as First-order and Second-order change. First-order change involves solving the problem from within the system of the problem. Second-order change involves getting outside of the problem system in order to find the solution. Dieting is the perfect example of how first-o ...
Abstracts - Yale School of Medicine
... neuroanatomy of the brain. Three-dimensional visualization of the trajectories of particular white matter fasciculi has been possible through the Klingler technique of freezing the brain prior to dissection4, while study of the route of particular fibers has been possible through the use of active a ...
... neuroanatomy of the brain. Three-dimensional visualization of the trajectories of particular white matter fasciculi has been possible through the Klingler technique of freezing the brain prior to dissection4, while study of the route of particular fibers has been possible through the use of active a ...
NEUROSCIENCE FOR HUMANITIES HESP SYLLABUS
... select a topic from a list of offered articles, or they may propose their own before week 5. They have to deliver an abstract by week 8, when presentations begin. The activity includes: 1) One page abstract of no more than 550 words (Arial 10) containing the relevant information and three references ...
... select a topic from a list of offered articles, or they may propose their own before week 5. They have to deliver an abstract by week 8, when presentations begin. The activity includes: 1) One page abstract of no more than 550 words (Arial 10) containing the relevant information and three references ...
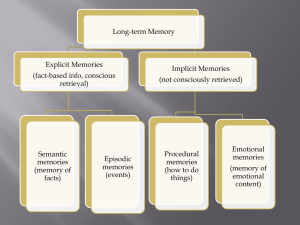
LO: Explain how biological factors may affect one cognitive process.
... in synaptic changes in the neural network. His research showed that learning (forming memories) means growing new connections or strengthening connections between neurons. Kandel went on to study synaptic changes due to memory in the hippocampus. In other words, what changes occur in the hippocampus ...
... in synaptic changes in the neural network. His research showed that learning (forming memories) means growing new connections or strengthening connections between neurons. Kandel went on to study synaptic changes due to memory in the hippocampus. In other words, what changes occur in the hippocampus ...
Autonomic Nervous System ANS - Anderson School District One
... cord: thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves ...
... cord: thoracic and lumbar spinal nerves ...
abstract
... Biology & Neurodegeneration, Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience; Institute for Life Sciences, Center for Neuroscience, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2Swammerdam ...
... Biology & Neurodegeneration, Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience; Institute for Life Sciences, Center for Neuroscience, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands. 2Swammerdam ...
Summary - Publikationsserver UB Marburg
... VTA to the Nucleus accumbens, amygdala and prefrontal cortex are implicated in reward and reinforcing effects of drugs abuse, whereas the nigrostriatal projections are important for habit formation. In animal models, in vivo injections of cocaine lead to changes in glutamatergic and GABAergic signal ...
... VTA to the Nucleus accumbens, amygdala and prefrontal cortex are implicated in reward and reinforcing effects of drugs abuse, whereas the nigrostriatal projections are important for habit formation. In animal models, in vivo injections of cocaine lead to changes in glutamatergic and GABAergic signal ...
SDL 2- CNS Malformations Neural Tube Defects Failure of a portion
... Neurons and glial cells that form the cerebral cortex migrate to cortex guided by adhesion molecules, cortical development entails the generatio of stem cells and their differentiation to neurons and glia, migration to cortex and organization to functional layers. 1. Neurons fail to migrate from the ...
... Neurons and glial cells that form the cerebral cortex migrate to cortex guided by adhesion molecules, cortical development entails the generatio of stem cells and their differentiation to neurons and glia, migration to cortex and organization to functional layers. 1. Neurons fail to migrate from the ...
Ch12 notes Martini 9e
... • Cells that send and receive signals 2. Neuroglia (glial cells) • Cells that support and protect neurons • Organs of the Nervous System • Brain and spinal cord • Sensory receptors of sense organs (eyes, ears, etc.) • Nerves connect nervous system with other systems 12-1 Divisions of the Nervous Sys ...
... • Cells that send and receive signals 2. Neuroglia (glial cells) • Cells that support and protect neurons • Organs of the Nervous System • Brain and spinal cord • Sensory receptors of sense organs (eyes, ears, etc.) • Nerves connect nervous system with other systems 12-1 Divisions of the Nervous Sys ...
a comparative study of the histological changes in cerebral
... Introduction: Lead, a heavy metal is well known for its toxic effects on the central nervous system. Clinically, overall effects of lead on different organ system are called plumbism. Diverse writing can be seen on the subject, but rarely there has been a comparison in any of these writings on diffe ...
... Introduction: Lead, a heavy metal is well known for its toxic effects on the central nervous system. Clinically, overall effects of lead on different organ system are called plumbism. Diverse writing can be seen on the subject, but rarely there has been a comparison in any of these writings on diffe ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... D. Articulations are the connections between bones of the skeleton and determine the type of movement. E. The skeletal system responds to injury and disease. • Describe the functions of the skeletal system • Compare the structures and functions of compact and spongy bones. • Describe remodeling and ...
... D. Articulations are the connections between bones of the skeleton and determine the type of movement. E. The skeletal system responds to injury and disease. • Describe the functions of the skeletal system • Compare the structures and functions of compact and spongy bones. • Describe remodeling and ...
Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity
... dependent on the degree of post-traumatic amnesia (or anterograde amnesia – deficits in new learning) - Pathophysiology of TBI ~ focal damage (coupe & contra-coupe) ~ diffuse damage (shearing & tearing of axons referred to as diffuse axonal injury) ...
... dependent on the degree of post-traumatic amnesia (or anterograde amnesia – deficits in new learning) - Pathophysiology of TBI ~ focal damage (coupe & contra-coupe) ~ diffuse damage (shearing & tearing of axons referred to as diffuse axonal injury) ...
Neuroanatomy

Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and stereotyped organization of nervous systems. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can make much more precise statements about their neuroanatomy. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or ""lesions"" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions.For information about the composition of animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information about the typical structure of the human nervous system, see human brain or peripheral nervous system. This article discusses information pertinent to the study of neuroanatomy.