14. Development and Plasticity
... Learning rules are not biologically realistic Learn entirely from experience Genetic coding would be of minimal importance in the brain development ...
... Learning rules are not biologically realistic Learn entirely from experience Genetic coding would be of minimal importance in the brain development ...
α3β1 integrin modulates neuronal migration and placement during
... towards pial surface deviated by an average of 32±6.6°. By contrast, mean deviation of wild-type dendrites is 7±3.1° [significant at P<0.05 when compared with mutants (Student’s t-test); n=75 for wild type and for mutant]. To assess possible malpositioning of upper layer interneurons, we immunolabel ...
... towards pial surface deviated by an average of 32±6.6°. By contrast, mean deviation of wild-type dendrites is 7±3.1° [significant at P<0.05 when compared with mutants (Student’s t-test); n=75 for wild type and for mutant]. To assess possible malpositioning of upper layer interneurons, we immunolabel ...
Dopamine is produced in the rat spinal cord and regulates
... neurons and the pontine micturition center. Here we show that DA is produced in the rat spinal cord and modulates the bladder reflex. We observed numerous tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the autonomic nuclei and superficial dorsal horn in L6–S3 spinal segments. These neurons are dopamine-β-hydro ...
... neurons and the pontine micturition center. Here we show that DA is produced in the rat spinal cord and modulates the bladder reflex. We observed numerous tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the autonomic nuclei and superficial dorsal horn in L6–S3 spinal segments. These neurons are dopamine-β-hydro ...
Anticipated synchronization in neuronal circuits
... synchronization of the driven circuit with chaotic future states of the driving circuit is insensitive to signal and system perturbations. [13, 14]. Moreover, a transition from AS to DS through zero-lag synchronization with excitatory and inhibitory couplings, as a function of the coupling delay, wa ...
... synchronization of the driven circuit with chaotic future states of the driving circuit is insensitive to signal and system perturbations. [13, 14]. Moreover, a transition from AS to DS through zero-lag synchronization with excitatory and inhibitory couplings, as a function of the coupling delay, wa ...
Striatal Plasticity and Basal Ganglia Circuit Function
... calcium channels, and CB1 receptor activation, but notably, not NMDA receptors or mAChRs (Calabresi et al., 1992a, 1997; Choi and Lovinger, 1997; Gerdeman et al., 2002; Kreitzer and Malenka, 2005; Sung et al., 2001). The basic model that has emerged from these results is that HFS in or near the dors ...
... calcium channels, and CB1 receptor activation, but notably, not NMDA receptors or mAChRs (Calabresi et al., 1992a, 1997; Choi and Lovinger, 1997; Gerdeman et al., 2002; Kreitzer and Malenka, 2005; Sung et al., 2001). The basic model that has emerged from these results is that HFS in or near the dors ...
Excitatory and Inhibitory Vestibular Pathways to the Extraocular
... 1997. Electrophysiological, ultrastructural, and immunohistochemical techniques were utilized to describe the excitatory and inhibitory vestibular innervation of extraocular motor nuclei in the goldfish. In antidromically activated oculomotor motoneurons, electrical stimulation of the intact contral ...
... 1997. Electrophysiological, ultrastructural, and immunohistochemical techniques were utilized to describe the excitatory and inhibitory vestibular innervation of extraocular motor nuclei in the goldfish. In antidromically activated oculomotor motoneurons, electrical stimulation of the intact contral ...
Information processing in the cortex: The relevance of coherent oscillations for neuronal communication
... Another factor: How does addition of fast glutamatergic synapses affect synchronization in interneuron network models? It certainly implies several additional parameters. In a simple two-population network, there are now four types of chemical synapses (I-I, E-I, I-E, E-E, where E stands for excitat ...
... Another factor: How does addition of fast glutamatergic synapses affect synchronization in interneuron network models? It certainly implies several additional parameters. In a simple two-population network, there are now four types of chemical synapses (I-I, E-I, I-E, E-E, where E stands for excitat ...
Layer III Neurons Control Synchronized Waves in the Immature
... anteriorly to the frontal cortex and posteriorly to the medial entorhinal cortex, forming traveling waves that engaged almost the entire cortex. The waves were blocked by ionotropic glutamatergic receptor antagonists but not by GABAergic receptor antagonists. During wave events, glutamatergic and GA ...
... anteriorly to the frontal cortex and posteriorly to the medial entorhinal cortex, forming traveling waves that engaged almost the entire cortex. The waves were blocked by ionotropic glutamatergic receptor antagonists but not by GABAergic receptor antagonists. During wave events, glutamatergic and GA ...
Ping-An Li, Ashfaq Shuaib, Hiro Miyashita, Qing
... above and below which brain damage was exaggerated and postischemic seizures were triggered, supporting the notion of a critical pH range. It has been established that excitatory amino acids (EAAs), notably glutamate, play a pivotal role in neuronal death.8 –10 Recent studies demonstrate that mitoch ...
... above and below which brain damage was exaggerated and postischemic seizures were triggered, supporting the notion of a critical pH range. It has been established that excitatory amino acids (EAAs), notably glutamate, play a pivotal role in neuronal death.8 –10 Recent studies demonstrate that mitoch ...
Memory Maintenance in Synapses with Calcium
... due to the lower extracellular calcium concentration in vivo on the time scale of synaptic decay has not been considered heretofore. In the present paper, we study the persistence of synaptic changes, first in a synapse connecting a pair of independent Poisson neurons, and second in a large network ...
... due to the lower extracellular calcium concentration in vivo on the time scale of synaptic decay has not been considered heretofore. In the present paper, we study the persistence of synaptic changes, first in a synapse connecting a pair of independent Poisson neurons, and second in a large network ...
3-Morpholinylsydnonimine Inhibits Glutamatergic Transmission in
... suggest that SIN-1–induced synaptic depression via a mechanism that is independent of activation of the sGC-cGMP– coupled signaling pathways. Because SIN-1 produces both NO and superoxide anion upon decomposition (Feelisch et al., 1989; Holm et al., 1998) and biological tissues contain oxidants that ...
... suggest that SIN-1–induced synaptic depression via a mechanism that is independent of activation of the sGC-cGMP– coupled signaling pathways. Because SIN-1 produces both NO and superoxide anion upon decomposition (Feelisch et al., 1989; Holm et al., 1998) and biological tissues contain oxidants that ...
Saccades and multisaccadic gaze shifts are gated by different
... We used glass microelectrodes filled with 3.8 M NaCl and bevelled to tip diameters of 1.5–2.0 µm and resistances of 1.5–2.0 M. Only perisomatic extracellular recordings were retained for the study. We identified them by triphasic spikes with a negative main component that could be monitored over a d ...
... We used glass microelectrodes filled with 3.8 M NaCl and bevelled to tip diameters of 1.5–2.0 µm and resistances of 1.5–2.0 M. Only perisomatic extracellular recordings were retained for the study. We identified them by triphasic spikes with a negative main component that could be monitored over a d ...
PDF
... in response to unexpected reward and decreased in response to omission of an expected reward. As seen from unit examples and population responses (Fig. 3a), neural activity increased when a new reward was introduced (start of block 2sh) and decreased when an expected reward was omitted (start of blo ...
... in response to unexpected reward and decreased in response to omission of an expected reward. As seen from unit examples and population responses (Fig. 3a), neural activity increased when a new reward was introduced (start of block 2sh) and decreased when an expected reward was omitted (start of blo ...
CORTICAL PLASTICITY: From Synapses to Maps
... Recordings show EPSPs from two independent pathways elicited in a L-II/III pyramidal cell. One stimulating electrode was placed vertically at the border of L-VI and the white matter (WM); a second electrode was placed horizontally in L-II/III. As is often the case for this LTP preparation, the L-VI/ ...
... Recordings show EPSPs from two independent pathways elicited in a L-II/III pyramidal cell. One stimulating electrode was placed vertically at the border of L-VI and the white matter (WM); a second electrode was placed horizontally in L-II/III. As is often the case for this LTP preparation, the L-VI/ ...
High-frequency stimulation in Parkinson`s disease: more
... spikes and stimuli, or the behavior of spontaneous activity during HFS. Because spikes disappear in the presence of channel blockers, EPSPs and spikes generated during 2 s trains at 100 Hz are proposed to result from the activation of glutamate-mediated transmission. HFS has a dual effect In whole-c ...
... spikes and stimuli, or the behavior of spontaneous activity during HFS. Because spikes disappear in the presence of channel blockers, EPSPs and spikes generated during 2 s trains at 100 Hz are proposed to result from the activation of glutamate-mediated transmission. HFS has a dual effect In whole-c ...
Physiological patterns in the hippocampo
... Stellate neurons have distinct electrophysiological characteristics that could endow them with distinct functional properties (Alonso and Llinás, 1989; Klink and Alonso, 1993a,b). Chiefly, stellate neurons exhibit subthreshold membrane potential oscillations at theta frequency upon depolarization d ...
... Stellate neurons have distinct electrophysiological characteristics that could endow them with distinct functional properties (Alonso and Llinás, 1989; Klink and Alonso, 1993a,b). Chiefly, stellate neurons exhibit subthreshold membrane potential oscillations at theta frequency upon depolarization d ...
Inactivation of Parietal and Prefrontal Cortex Reveals
... contain the same heterogeneity of defined neuronal types while monkeys performed the ODR task (Chafee and GoldmanRakic 1998). The patterns of activation characteristic of each of these subpopulations were matched to a greater extent (Chafee and Goldman-Rakic 1998) than could be gleaned from independ ...
... contain the same heterogeneity of defined neuronal types while monkeys performed the ODR task (Chafee and GoldmanRakic 1998). The patterns of activation characteristic of each of these subpopulations were matched to a greater extent (Chafee and Goldman-Rakic 1998) than could be gleaned from independ ...
Physiological Patterns in the Hippocampo
... Stellate neurons have distinct electrophysiological characteristics that could endow them with distinct functional properties (Alonso and Llinás, 1989; Klink and Alonso, 1993a,b). Chiefly, stellate neurons exhibit subthreshold membrane potential oscillations at theta frequency upon depolarization d ...
... Stellate neurons have distinct electrophysiological characteristics that could endow them with distinct functional properties (Alonso and Llinás, 1989; Klink and Alonso, 1993a,b). Chiefly, stellate neurons exhibit subthreshold membrane potential oscillations at theta frequency upon depolarization d ...
Neuronal Correlates for Preparatory Set Associated with Pro
... during the period 400 –200 msec before stimulus presentation for correct pro-saccade and anti-saccade trials. Gap and overlap trials were combined for this analysis. For comparing the neuronal prestimulus activity, we determined the mean activity in the period 40 –50 msec after stimulus presentation ...
... during the period 400 –200 msec before stimulus presentation for correct pro-saccade and anti-saccade trials. Gap and overlap trials were combined for this analysis. For comparing the neuronal prestimulus activity, we determined the mean activity in the period 40 –50 msec after stimulus presentation ...
Electrolytic lesion of globus pallidus ameliorates the behavioral and
... astrocytes. To quantify the size of the striatal lesion, images of coronal brain sections that contained the core of the lesions were captured for computer assisted image analysis. Striatal lesion size and the size of dorsal striatum on the right and left hemispheres were measured for each rat. The ...
... astrocytes. To quantify the size of the striatal lesion, images of coronal brain sections that contained the core of the lesions were captured for computer assisted image analysis. Striatal lesion size and the size of dorsal striatum on the right and left hemispheres were measured for each rat. The ...
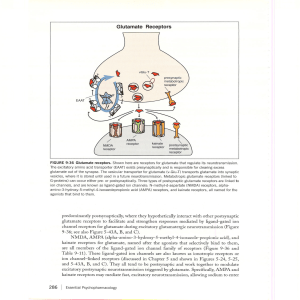
Glutamate Receptors
... dopamine hyperactivity reduces the thalamic filter and permits the escape of excessive sensory information coming into the thalamus, thus allowing it to get into the cortex by means of ascending thalamocortical neurons. If this were not bad enough, there is hypothetical NMDA receptor hypofunction in ...
... dopamine hyperactivity reduces the thalamic filter and permits the escape of excessive sensory information coming into the thalamus, thus allowing it to get into the cortex by means of ascending thalamocortical neurons. If this were not bad enough, there is hypothetical NMDA receptor hypofunction in ...
The GABAergic system in schizophrenia
... further hypofunctioning of the glutamatergic system through feedback mechanisms. Several classes of compounds, including benzodiazepines (BZD), muscurinic receptor antagonist and haloperidol, blocked NMDAinduced neurotoxicity in the posterior cingulate and retrospenial regions of experimental animal ...
... further hypofunctioning of the glutamatergic system through feedback mechanisms. Several classes of compounds, including benzodiazepines (BZD), muscurinic receptor antagonist and haloperidol, blocked NMDAinduced neurotoxicity in the posterior cingulate and retrospenial regions of experimental animal ...
PRESYNAPTIC IONOTROPIC RECEPTORS AND CONTROL OF
... presynaptic membrane determines the shape of presynaptic action potentials, which in turn regulates the time course and amplitude of presynaptic Ca2+ influx. Similarly, the number and arrangement of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs) with respect to presynaptic vesicles also affects the efficacy of ...
... presynaptic membrane determines the shape of presynaptic action potentials, which in turn regulates the time course and amplitude of presynaptic Ca2+ influx. Similarly, the number and arrangement of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels (VGCCs) with respect to presynaptic vesicles also affects the efficacy of ...
Cerebral correlates of delta waves during non
... panel) are in agreement with that preceding work. However, since delta oscillations are more profuse during NREM sleep than during wakefulness in normal human subjects and as this study was aimed at exploring the cerebral correlates of rhythms that characterize NREM sleep, the presence of waking val ...
... panel) are in agreement with that preceding work. However, since delta oscillations are more profuse during NREM sleep than during wakefulness in normal human subjects and as this study was aimed at exploring the cerebral correlates of rhythms that characterize NREM sleep, the presence of waking val ...
Long, intrinsic horizontal axons radiating through and beyond rat
... Current thinking about the structure and function of neocortex is largely shaped by several underlying principles: parcellation of the cortical sheet into distinct regions containing neurons of similar function (Van Essen 2013; Zilles and Amunts 2010), systematic white matter connections between the ...
... Current thinking about the structure and function of neocortex is largely shaped by several underlying principles: parcellation of the cortical sheet into distinct regions containing neurons of similar function (Van Essen 2013; Zilles and Amunts 2010), systematic white matter connections between the ...
Spike-and-wave

Spike-and-wave is the term that describes a particular pattern of the electroencephalogram (EEG) typically observed during epileptic seizures. A spike-and-wave discharge is a regular, symmetrical, generalized EEG pattern seen particularly during absence epilepsy, also known as ‘petit mal’ epilepsy. The basic mechanisms underlying these patterns are complex and involve part of the cerebral cortex, the thalamocortical network, and intrinsic neuronal mechanisms. The first spike-and-wave pattern was recorded in the early twentieth century by Hans Berger. Many aspects of the pattern are still being researched and discovered, and still many aspects are uncertain. The spike-and-wave pattern is most commonly researched in absence epilepsy, but is common in several epilepsies such as Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) and Ohtahara syndrome. Anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) are commonly prescribed to treat epileptic seizures, and new ones are being discovered with less adverse effects. Today, most of the research is focused on the origin of the generalized bilateral spike-and-wave discharge. One proposal suggests that a thalamocortical (TC) loop is involved in the initiation spike-and-wave oscillations. Although there are several theories, the use of animal models has provided new insight on spike-and-wave discharge in humans.