Chapter 17
... generally post ganglionic innervate organs below diaphragm 3 main: celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric ...
... generally post ganglionic innervate organs below diaphragm 3 main: celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric ...
Flash cards
... the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms. ...
... the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms. ...
Navigating The Nervous System
... a. Central Nervous System- Composed of the brain and spinal cord b. Peripheral Nervous System- All motor and sensory neurons leaving the spinal cord. Functions to connect all body’s organs and muscles to the central nervous system. This way all organs and muscles can be controlled by the brain. ...
... a. Central Nervous System- Composed of the brain and spinal cord b. Peripheral Nervous System- All motor and sensory neurons leaving the spinal cord. Functions to connect all body’s organs and muscles to the central nervous system. This way all organs and muscles can be controlled by the brain. ...
The Neuron
... named supporting cells. While the neurons are important for carrying the neural message, the supporting cells are important for insuring that the neurons carry out this process. In fact, without supporting cells communication among neurons would be impossible. There are many types of supporting cell ...
... named supporting cells. While the neurons are important for carrying the neural message, the supporting cells are important for insuring that the neurons carry out this process. In fact, without supporting cells communication among neurons would be impossible. There are many types of supporting cell ...
Payton
... • disorder of CSF circulation, visual- swelling/large head, at birth • Occurs in 2/1000 children. mostly congenital, also as a result of meningitis • tube inserted into the lateral ventricle runs to the abdominal cavity(shunting), value to regulate pressure CSF Summary • produced from blood by the c ...
... • disorder of CSF circulation, visual- swelling/large head, at birth • Occurs in 2/1000 children. mostly congenital, also as a result of meningitis • tube inserted into the lateral ventricle runs to the abdominal cavity(shunting), value to regulate pressure CSF Summary • produced from blood by the c ...
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... Major Function • To control all activities of the body ...
... Major Function • To control all activities of the body ...
Chapter 3 Class Notes / Biological Foundations
... The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the cell body, transmitted along the axon to the terminal buttons found at the end of each a ...
... The synapse or synaptic cleft is the tiny gap found between the axon (terminal buttons) of one neuron and the dendrites of another. When a neural message is received at the dendrites, it is processed through the cell body, transmitted along the axon to the terminal buttons found at the end of each a ...
Essential Questions and Vocabulary
... neurotransmitters, acetylcholine, endorphins, nervous system, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, nerves, sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons, somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system, reflex, neural networks ...
... neurotransmitters, acetylcholine, endorphins, nervous system, central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, nerves, sensory neurons, motor neurons, interneurons, somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, sympathetic nervous system, parasympathetic nervous system, reflex, neural networks ...
Biopsychology revision 2
... – Sympathetic Division of ANS mobilizes fight or flight response (i.e., blood to skeletal muscles; increases respiration) – Somatic NS initiates skeletal muscles to escape – Once escaped, Parasympathetic NS initiates relaxation response ...
... – Sympathetic Division of ANS mobilizes fight or flight response (i.e., blood to skeletal muscles; increases respiration) – Somatic NS initiates skeletal muscles to escape – Once escaped, Parasympathetic NS initiates relaxation response ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Motor neurons convey signals to effector cells (see figure 28.2) 28.2 Neurons are the functional units of nervous systems Neurons are ...
... Motor neurons convey signals to effector cells (see figure 28.2) 28.2 Neurons are the functional units of nervous systems Neurons are ...
Nervous System
... • Constantly interacts with the central nervous system via 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Nerves are the bundles axons and dendrites of many neurons • Each spinal nerve has a dorsal root and a ...
... • Constantly interacts with the central nervous system via 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Nerves are the bundles axons and dendrites of many neurons • Each spinal nerve has a dorsal root and a ...
Mirror Neurons & You
... Is this what makes us HUMAN? Other animals possess mirror neurons. Our highly developed mirror neuron system allows us ...
... Is this what makes us HUMAN? Other animals possess mirror neurons. Our highly developed mirror neuron system allows us ...
The biological Approach
... • Various glands in the body produce hormones. Hormones are secreted into the bloodstream and affect any cell in the body that has a receptor for that particular hormone. • The major endocrine gland is the pituitary gland, located in the brain. It is often called the ‘master gland’ because it contro ...
... • Various glands in the body produce hormones. Hormones are secreted into the bloodstream and affect any cell in the body that has a receptor for that particular hormone. • The major endocrine gland is the pituitary gland, located in the brain. It is often called the ‘master gland’ because it contro ...
Pain - WordPress.com
... spinalthalamic tract). The above three fiber tracts are known also as the paleospinalthalamic tract. ...
... spinalthalamic tract). The above three fiber tracts are known also as the paleospinalthalamic tract. ...
N1 - Kůra mozku HE
... • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vasculature with variable amount of connec ...
... • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vasculature with variable amount of connec ...
Nervous System - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... -blood-brain barrier -buffering of neuroglia (astrocytes) -exchange between CSF and brain ECS Blood-brain barrier limits movement large molecules (proteins) and charged ions from the blood into the brain (Capillary endothelial cells of CNS have tight junctions) ...
... -blood-brain barrier -buffering of neuroglia (astrocytes) -exchange between CSF and brain ECS Blood-brain barrier limits movement large molecules (proteins) and charged ions from the blood into the brain (Capillary endothelial cells of CNS have tight junctions) ...
Nervous System
... There are two types of neurons: Sensory: Gather information from around the body and send it to the brain. Receptors detect change inside and outside the body.(Ex. Eyes) Motor: Send messages from the brain to the rest of the body. They cause a reaction to occur. (Ex. Muscles to contract) ...
... There are two types of neurons: Sensory: Gather information from around the body and send it to the brain. Receptors detect change inside and outside the body.(Ex. Eyes) Motor: Send messages from the brain to the rest of the body. They cause a reaction to occur. (Ex. Muscles to contract) ...
Option H Further Human Physiology
... monitored by osmoreceptors in hypothalamus. The osmoreceptors control the activity of the neurosecretory cells. ...
... monitored by osmoreceptors in hypothalamus. The osmoreceptors control the activity of the neurosecretory cells. ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
Slide ()
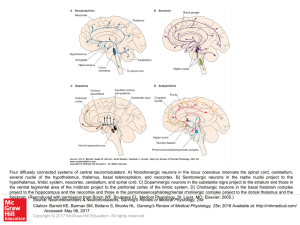
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
peripheral nervous system
... When light enters the eye it first travels through a transparent layer of cells called the cornea. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by muscles of the iris, which is the part of the eye that is colored. Behind the iris is the lens. The lens inverts the image and projects it onto the ...
... When light enters the eye it first travels through a transparent layer of cells called the cornea. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by muscles of the iris, which is the part of the eye that is colored. Behind the iris is the lens. The lens inverts the image and projects it onto the ...
FINAL241NSCC
... C. The dopamine releasing neurons of Parkinson’s patients are damaged and eventually die. If dopamine normally binds to sodium-gated channels on post-synaptic neurons, then explain how AP initiation in the post-synaptic cell will be affected by the death of these cells. ...
... C. The dopamine releasing neurons of Parkinson’s patients are damaged and eventually die. If dopamine normally binds to sodium-gated channels on post-synaptic neurons, then explain how AP initiation in the post-synaptic cell will be affected by the death of these cells. ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam2_180117_final
... The most abundant neurotransmitter in the brain is the _________________________________________ . It is a building block of all proteins, but a high affinity transport system is required to get it through the ____ _____________________________________, thereby its concentration in brain fluids is a ...
... The most abundant neurotransmitter in the brain is the _________________________________________ . It is a building block of all proteins, but a high affinity transport system is required to get it through the ____ _____________________________________, thereby its concentration in brain fluids is a ...
VNS Worksheet - Rice CAAM Department
... waves in the hippocampus. 16. What behavior states are associated with the hippocampal theta rhythm? 17.What is Long Term Potentiation and what does it have to do with memory? 18. Norepinephrine, like all key neurotransmitters and hormones is highly regulated. This control typically comes in two typ ...
... waves in the hippocampus. 16. What behavior states are associated with the hippocampal theta rhythm? 17.What is Long Term Potentiation and what does it have to do with memory? 18. Norepinephrine, like all key neurotransmitters and hormones is highly regulated. This control typically comes in two typ ...