Autonomic Nervous System
... - part of diencephalon (1% of brain volume), located within the walls & floor of 3rd ventricle, constitutes an integrative center essential for survival & reproduction, that regulates and controls the complex interactions between physiology and behavior (temperature regulation, heart rate, blood pre ...
... - part of diencephalon (1% of brain volume), located within the walls & floor of 3rd ventricle, constitutes an integrative center essential for survival & reproduction, that regulates and controls the complex interactions between physiology and behavior (temperature regulation, heart rate, blood pre ...
PowerPoint Chapter 29
... a. Stimulants- increase number of action potentials by increasing amounts of neurotransmitters in synapses b. Depressants- reduce ability of neurons to generate impulses ...
... a. Stimulants- increase number of action potentials by increasing amounts of neurotransmitters in synapses b. Depressants- reduce ability of neurons to generate impulses ...
Central Nervous System Honors Biology Mr. Lee Room 320
... – Lipid layer that covers most axons – Insulates the axon – Speeds up transmission of action potential – Produced by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system – Nodes of Ranvier- gaps in the myelin sheath ...
... – Lipid layer that covers most axons – Insulates the axon – Speeds up transmission of action potential – Produced by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system – Nodes of Ranvier- gaps in the myelin sheath ...
7-6_TheGenOfSpecResp_MajorosMyrtill
... The stretch reflex is a monosynaptic, postural reflex that among the others works against the gravity force. First of all it is important to mention that muscles are attached to tendons which hold them to the bone. At the attachment of the muscles to tendons there is a muscle spindle which is very s ...
... The stretch reflex is a monosynaptic, postural reflex that among the others works against the gravity force. First of all it is important to mention that muscles are attached to tendons which hold them to the bone. At the attachment of the muscles to tendons there is a muscle spindle which is very s ...
Slide 1
... blood pressure in humans. The arrow indicates the plasma AVP concentration at basal plasma osmolality, volume, and blood pressure. Modified with permission from Robertson (1986). Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... blood pressure in humans. The arrow indicates the plasma AVP concentration at basal plasma osmolality, volume, and blood pressure. Modified with permission from Robertson (1986). Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Dendrites- receive messages, impulses, and send them to the cell body. Axons- send messages away from the cell body. ...
... Dendrites- receive messages, impulses, and send them to the cell body. Axons- send messages away from the cell body. ...
48.5, .6, .7
... dementia, characterized by confusion, memory loss, and a variety of other symptoms. It rises from 10% at age 65 and 35% at age 85. • AD is difficult to make while the patient is alive because it is a form of dementia. • Parkinson’s Disease- a motor disorder characterized by difficulty in initiating ...
... dementia, characterized by confusion, memory loss, and a variety of other symptoms. It rises from 10% at age 65 and 35% at age 85. • AD is difficult to make while the patient is alive because it is a form of dementia. • Parkinson’s Disease- a motor disorder characterized by difficulty in initiating ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Most cranial nerves are mixed, but some are sensory. Only the vagus nerve extends to thoracic and abdominal cavities. (Cranial nerves are listed in table 7.1.) Spinal nerves – 31 pairs of mixed nerves are formed by the union of dorsal and ventral roots of spinal cord. The spinal nerves divide into d ...
... Most cranial nerves are mixed, but some are sensory. Only the vagus nerve extends to thoracic and abdominal cavities. (Cranial nerves are listed in table 7.1.) Spinal nerves – 31 pairs of mixed nerves are formed by the union of dorsal and ventral roots of spinal cord. The spinal nerves divide into d ...
Nervous System and Sensory Organs
... • Sensory Neuron ▫ Take nerve impulses from the sensory receptors to the CNS. ...
... • Sensory Neuron ▫ Take nerve impulses from the sensory receptors to the CNS. ...
ORAL SCIENCE I
... brain and spinal cord 2 branches Somatic- nerves that serve skeletal system and sense organs Autonomic- serve smooth muscles and heart ...
... brain and spinal cord 2 branches Somatic- nerves that serve skeletal system and sense organs Autonomic- serve smooth muscles and heart ...
Introduction to the Brain
... • Is continuous with spinal meninges • Protects the brain from cranial trauma ...
... • Is continuous with spinal meninges • Protects the brain from cranial trauma ...
Brain
... • Clusters of capillaries that form tissue fluid filters, which hang from the roof of each ventricle • Have ion pumps that allow them to alter ion concentrations of the CSF • Help cleanse CSF by removing wastes ...
... • Clusters of capillaries that form tissue fluid filters, which hang from the roof of each ventricle • Have ion pumps that allow them to alter ion concentrations of the CSF • Help cleanse CSF by removing wastes ...
Power Point Slides of Interest
... kinase to active form and inhibits an enzyme required for glucagon synthesis. ...
... kinase to active form and inhibits an enzyme required for glucagon synthesis. ...
METABOLIC-REDOX ADAPTATIONS OF NEURONS AND
... pentose-phosphate pathway (PPP) switch, redox status, and survival of neurons. During glutamatergic neurotransmission, (APC/C)-Cdh1 is inhibited leading to PFKFB3 stabilization, glycolysis activation and PPP inhibition in neurons. This unavoidably leads to oxidative stress, since the intrinsic antio ...
... pentose-phosphate pathway (PPP) switch, redox status, and survival of neurons. During glutamatergic neurotransmission, (APC/C)-Cdh1 is inhibited leading to PFKFB3 stabilization, glycolysis activation and PPP inhibition in neurons. This unavoidably leads to oxidative stress, since the intrinsic antio ...
1 NOTES – CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System – LECTURE
... a) passes sensory input from body to cerebral cortex b. epithalamus 1) small area superior and posterior to the thalamus 2) Functions: a) controls emotional & visceral response to odors b) contains pineal body – an endocrine gland i.) influences the onset of puberty c. hypothalamus 1) most inferior ...
... a) passes sensory input from body to cerebral cortex b. epithalamus 1) small area superior and posterior to the thalamus 2) Functions: a) controls emotional & visceral response to odors b) contains pineal body – an endocrine gland i.) influences the onset of puberty c. hypothalamus 1) most inferior ...
Nervous System
... Three features of maintaining homeostasis • Dual innervation – most internal organs receive input from both systems • Antagonistic action – one system stimulates while the other inhibits • Basal tone – Even under resting conditions autonomic neurons produce APs ...
... Three features of maintaining homeostasis • Dual innervation – most internal organs receive input from both systems • Antagonistic action – one system stimulates while the other inhibits • Basal tone – Even under resting conditions autonomic neurons produce APs ...
neurobiological-basis-of-behavior
... neurons in the brain. Nerves – bundles of axons - Often located in the peripheral nervous system - Transmit information to various parts of the body Types of Neurons 1. Sensory neuron (afferent neuron) – carry information from the senses to the spinal cord 2. Interneuron – makes connections to oth ...
... neurons in the brain. Nerves – bundles of axons - Often located in the peripheral nervous system - Transmit information to various parts of the body Types of Neurons 1. Sensory neuron (afferent neuron) – carry information from the senses to the spinal cord 2. Interneuron – makes connections to oth ...
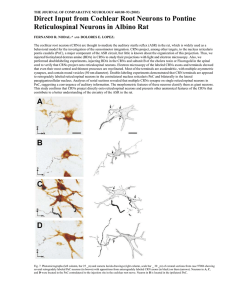
THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 460:80–93 (2003)
... The cochlear root neurons (CRNs) are thought to mediate the auditory startle reflex (ASR) in the rat, which is widely used as a behavioral model for the investigation of the sensorimotor integration. CRNs project, among other targets, to the nucleus reticularis pontis caudalis (PnC), a major compone ...
... The cochlear root neurons (CRNs) are thought to mediate the auditory startle reflex (ASR) in the rat, which is widely used as a behavioral model for the investigation of the sensorimotor integration. CRNs project, among other targets, to the nucleus reticularis pontis caudalis (PnC), a major compone ...
Nervous System - North Mac Schools
... • 3. Axon sends buds into network of Schwann cells and then starts growing along cord of Schwann cells • 4. Axon grows ...
... • 3. Axon sends buds into network of Schwann cells and then starts growing along cord of Schwann cells • 4. Axon grows ...
Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System
... is located in the spine and skull. This is the center of metabolic activity within each neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine and skull). ...
... is located in the spine and skull. This is the center of metabolic activity within each neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine and skull). ...
Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neurons. ...
... communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neurons. ...
Reticular Activating System
... All sensory input that enters brain via the medulla is also sent to neurons of the reticular formation. These neurons may monitor sensory input for importance. May alert higher brain centers when critical input is detected. ...
... All sensory input that enters brain via the medulla is also sent to neurons of the reticular formation. These neurons may monitor sensory input for importance. May alert higher brain centers when critical input is detected. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... skin that a person can control – Sensory neurons which relay info about environment to CNS Reflex Arc – Motor neurons which initiate appropriate response ...
... skin that a person can control – Sensory neurons which relay info about environment to CNS Reflex Arc – Motor neurons which initiate appropriate response ...