The Journal of Neuroscience Journal Club SYMPOSIUM
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
... Persons interested in becoming members of the Society for Neuroscience should contact the Membership Department, Society for Neuroscience, 1121 14th St., NW, Suite 1010, Washington, DC 20005, phone 202-962-4000. Instructions for Authors are available at http://www.jneurosci.org/misc/itoa.shtml. Auth ...
Anat 1: Ch 17 (SS99)
... D. Prepares for emergency action, excitatory to many organs, inhibitory to others ( digestive for example) E. Effects very widespread and somewhat persistent ...
... D. Prepares for emergency action, excitatory to many organs, inhibitory to others ( digestive for example) E. Effects very widespread and somewhat persistent ...
Ch 3 lec 1
... Section parallel to neuraxis and perpendicular to the ground. Midsagittal Plane – special type of sagittal section through the corpus callosum separating the hemispheres. ...
... Section parallel to neuraxis and perpendicular to the ground. Midsagittal Plane – special type of sagittal section through the corpus callosum separating the hemispheres. ...
Biological roots of Behavioral Sciences
... Composed of three parts: the forebrain, midbrain and • hindbrain, the major structures within hindbrain include the medulla which monitor and control vital body functions , the pons which contains important groups of sensory and motor neurons ,and the cerebellum ,which is concerned with motor co-ord ...
... Composed of three parts: the forebrain, midbrain and • hindbrain, the major structures within hindbrain include the medulla which monitor and control vital body functions , the pons which contains important groups of sensory and motor neurons ,and the cerebellum ,which is concerned with motor co-ord ...
Division of Brain Sciences Department of Medicine PhD studentship
... Payment of Home/EU Fees and a stipend of £17,500 per annum for 3 years The pathological hallmark Parkinson’s disease is the gradual loss of the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain. The root causes for degeneration of this inherently vulnerable neuronal populati ...
... Payment of Home/EU Fees and a stipend of £17,500 per annum for 3 years The pathological hallmark Parkinson’s disease is the gradual loss of the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain. The root causes for degeneration of this inherently vulnerable neuronal populati ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
3-1-neuron _1
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... B. Neurons- excitable little cells that make use of their potential! C. Functional Properties of Neurons 1. Irritability- neurons have the ability to respond to a stimulus 2. Conductivity- the ability to transmit an impulse 3. The plasma membrane at rest is polarized, this is called the Resting pot ...
... B. Neurons- excitable little cells that make use of their potential! C. Functional Properties of Neurons 1. Irritability- neurons have the ability to respond to a stimulus 2. Conductivity- the ability to transmit an impulse 3. The plasma membrane at rest is polarized, this is called the Resting pot ...
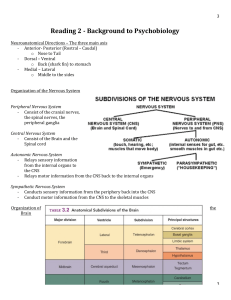
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Contains Primary motor cortex (area 4), premotor cortex (area 6), Broca’s area (area 44) and the prefrontal cortex. - Receives information from: 1. Thalamic nuclei 2. Hypothalamus 3. Limbic system 4. Other lobes - Functions 1. Working memory 2. Higher order cognitive behaviors – Pla ...
... - Contains Primary motor cortex (area 4), premotor cortex (area 6), Broca’s area (area 44) and the prefrontal cortex. - Receives information from: 1. Thalamic nuclei 2. Hypothalamus 3. Limbic system 4. Other lobes - Functions 1. Working memory 2. Higher order cognitive behaviors – Pla ...
Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Hypothalamus – below thalamus; maintains homeostasis by regulating a variety of visceral activities and by linking the nervous and endocrine systems; regulates: ...
... Hypothalamus – below thalamus; maintains homeostasis by regulating a variety of visceral activities and by linking the nervous and endocrine systems; regulates: ...
Unit 3ABC Reading and Study Guide
... What are neurons, and how do they transmit information? How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? How do neurotransmitters influence behavior, and how do drugs and other chemicals affect neurotransmitters? What are the functions of the nervous system’s main divisions? How does the endoc ...
... What are neurons, and how do they transmit information? How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? How do neurotransmitters influence behavior, and how do drugs and other chemicals affect neurotransmitters? What are the functions of the nervous system’s main divisions? How does the endoc ...
Q1 (from chapter 1)
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
Section: Nervous system
... THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM 7. Nerve cells specialized to receive and conduct electrical impulses are called _______________. 8. Electrical messages, called __________________--, may travel as fast as 150 m/s or as slow as 0.2 m/s. Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the let ...
... THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM 7. Nerve cells specialized to receive and conduct electrical impulses are called _______________. 8. Electrical messages, called __________________--, may travel as fast as 150 m/s or as slow as 0.2 m/s. Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the let ...
The body`s information system is built from billions of interconnected
... The Hypothalamus lies below (hypo) the thalamus. It directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. It helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The Cerebral Cortex The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that cove ...
... The Hypothalamus lies below (hypo) the thalamus. It directs several maintenance activities like eating, drinking, body temperature, and control of emotions. It helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The Cerebral Cortex The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that cove ...
nervous system worksheet
... 6. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. ...
... 6. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. ...
Nervous System Test Review After you accidentally touch a hot pan
... 2. In order for a nerve impulse to pass from an axon tip to the next structure, it must cross a space called a _________________. a. synapse 3. The type of neuron known as a(n) _______________ neuron picks up stimuli from the external or internal environment and converts those stimuli to nerve impul ...
... 2. In order for a nerve impulse to pass from an axon tip to the next structure, it must cross a space called a _________________. a. synapse 3. The type of neuron known as a(n) _______________ neuron picks up stimuli from the external or internal environment and converts those stimuli to nerve impul ...
PR_161115_Inaktive_Gehirnzellen_E
... Many things we think we know about the world have their origin in popular culture, not science. The most well-known false ‘fact’ about the brain is the misconception that we only use ten percent of the brain’s overall capacity. This so-called ’ten percent myth’, while accepted as such by neuroscient ...
... Many things we think we know about the world have their origin in popular culture, not science. The most well-known false ‘fact’ about the brain is the misconception that we only use ten percent of the brain’s overall capacity. This so-called ’ten percent myth’, while accepted as such by neuroscient ...
PowerPoint Slides
... time period. • Synapses vary in strength – Good connections allowing a large signal – Slight connections allow only a weak signal. – Synapses can be either excitatory or inhibitory. ...
... time period. • Synapses vary in strength – Good connections allowing a large signal – Slight connections allow only a weak signal. – Synapses can be either excitatory or inhibitory. ...
File
... body's biggest organs, consisting of some 100 billion nerve cells that not only put together thoughts and highly coordinated physical actions but regulate our unconscious body processes, such as digestion and breathing. • The brain's nerve cells are known as neurons, which make up the organ's so-cal ...
... body's biggest organs, consisting of some 100 billion nerve cells that not only put together thoughts and highly coordinated physical actions but regulate our unconscious body processes, such as digestion and breathing. • The brain's nerve cells are known as neurons, which make up the organ's so-cal ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... human stress response Gonads—hormones regulate sexual characteristics and reproductive processes; testes in males, ovaries in ...
... human stress response Gonads—hormones regulate sexual characteristics and reproductive processes; testes in males, ovaries in ...
Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior
... nervous system)-neuron loss after stroke Endorphin-modulates sensory system, including relief of pain and feeling of well being-addictions ...
... nervous system)-neuron loss after stroke Endorphin-modulates sensory system, including relief of pain and feeling of well being-addictions ...
Brain and Behaviour
... For a neural impulse to “FIRE” the combined impulses that reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing response to neurons either reaching the threshold or they don’t . If the Threshold is reached then the neuron transmits an electrical impu ...
... For a neural impulse to “FIRE” the combined impulses that reach the dendrite must reach a certain level of intensity or THRESHOLD – this is an all of nothing response to neurons either reaching the threshold or they don’t . If the Threshold is reached then the neuron transmits an electrical impu ...
The Nervous System
... Important Combining Forms • Brain -------- encephal/o • Spinal cord -------- myel/o ...
... Important Combining Forms • Brain -------- encephal/o • Spinal cord -------- myel/o ...