B) Nervous System Introduction NtG Spring
... Similar to astrocytes Schwann cells Surround and form ______________________ _____________________ in the PNS Help with regeneration of damaged peripheral nerve fibers Nervous Tissue: Neurons Structural unit of the nervous system Highly specialized cells that conduct messages in the form ...
... Similar to astrocytes Schwann cells Surround and form ______________________ _____________________ in the PNS Help with regeneration of damaged peripheral nerve fibers Nervous Tissue: Neurons Structural unit of the nervous system Highly specialized cells that conduct messages in the form ...
Endocrine System
... functions into one harmonious whole. This is called homeostasis. The maintenance of homeostasis involves the growth, maturation, reproduction, and metabolism. The body system responsible for this coordination is the endocrine system. ...
... functions into one harmonious whole. This is called homeostasis. The maintenance of homeostasis involves the growth, maturation, reproduction, and metabolism. The body system responsible for this coordination is the endocrine system. ...
nervous system study guide
... SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM What does each do? Which is involuntary? ...
... SOMATIC VS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM What does each do? Which is involuntary? ...
The Nervous System
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
Nervous System
... bone to 1st or 2nd lumbar vertebrae ~ thickness of thumb Primary reflex center Carries impulses to and from the brain via a 2-way conduction system (ascending and descending tracts) Spinal nerves are named by vertebrae type and number ...
... bone to 1st or 2nd lumbar vertebrae ~ thickness of thumb Primary reflex center Carries impulses to and from the brain via a 2-way conduction system (ascending and descending tracts) Spinal nerves are named by vertebrae type and number ...
Chapter 4 - SCHOOLinSITES
... Parietal Lobe of the Cerebrum - the middle lobe of each cerebral hemisphere between the frontal and occipital lobes; it contains important sensory centers (located at the upper rear of the head). Pituitary Gland - a gland attached to the base of the brain (located between the Pons and the Corpus Ca ...
... Parietal Lobe of the Cerebrum - the middle lobe of each cerebral hemisphere between the frontal and occipital lobes; it contains important sensory centers (located at the upper rear of the head). Pituitary Gland - a gland attached to the base of the brain (located between the Pons and the Corpus Ca ...
NOB Ch 6 Answers - MCC Year 12 Biology
... the arterial walls is conveyed to the central nervous system (CNS). The response is an increase in autonomic nerve impulses from the CNS that lead to the contraction of involuntary muscle tissue in the arterioles and an increase in the rate and force of the pumping action of the heart. This nerve ac ...
... the arterial walls is conveyed to the central nervous system (CNS). The response is an increase in autonomic nerve impulses from the CNS that lead to the contraction of involuntary muscle tissue in the arterioles and an increase in the rate and force of the pumping action of the heart. This nerve ac ...
PowerPoint for 9/29
... Just as “the wave” can flow to the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
... Just as “the wave” can flow to the right in a stadium even though the people only move up and down, a wave moves down an axon although it is only made up of ion exchanges moving in and out. ...
big
... – Soma, the cell body. – Axon, which sends signals on to the next cell. Each neuron has one axon; it can be very long. – Dendrites, tree-like structure which receives signals from the axons of other cells. Often very highly branched, but doesn't go far from soma ...
... – Soma, the cell body. – Axon, which sends signals on to the next cell. Each neuron has one axon; it can be very long. – Dendrites, tree-like structure which receives signals from the axons of other cells. Often very highly branched, but doesn't go far from soma ...
Biology 2121 – Lecture Sheet – ANS 1. The autonomic nervous sy
... 28. The nerves that leave the sacral area via the ventral rami are called the __________________ nerves and join to form the __________________ plexus. 29. The cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons can be found in this portion of the spinal cord: _____________. They exit via the _____ ...
... 28. The nerves that leave the sacral area via the ventral rami are called the __________________ nerves and join to form the __________________ plexus. 29. The cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons can be found in this portion of the spinal cord: _____________. They exit via the _____ ...
The Nervous System
... – Only small branches at the end of peripheral fibers are dendrites, the rest function as axons and therefore carry impulese both toward and away from cell body ...
... – Only small branches at the end of peripheral fibers are dendrites, the rest function as axons and therefore carry impulese both toward and away from cell body ...
Chapter 2 - davis.k12.ut.us
... B) negative C) active D) depolarized E) antagonistic 7. The minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse is called the A) reflex. B) threshold. C) synapse. D) action potential. E) refractory period. 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will ...
... B) negative C) active D) depolarized E) antagonistic 7. The minimum level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse is called the A) reflex. B) threshold. C) synapse. D) action potential. E) refractory period. 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will ...
Lecture_31_2014_noquiz
... Some are myelinated, some are not. Smaller nerves branch off of the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve responsible for innervating muscles, skin, etc. in the leg. It contains both motor neurons and sensory neurons (i.e. messages go both way). There are some neurons that originate at the top and have a ...
... Some are myelinated, some are not. Smaller nerves branch off of the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve responsible for innervating muscles, skin, etc. in the leg. It contains both motor neurons and sensory neurons (i.e. messages go both way). There are some neurons that originate at the top and have a ...
HBNervous
... Dendrites are plasmamembrane extentions; this is the sensing end Cell body contains all organelles including nucleus with genetic information that directs synthesis. Dendritic end surrounds cell body. Axon is elongated region terminates at the axon terminus; the location of the synapse. Action poten ...
... Dendrites are plasmamembrane extentions; this is the sensing end Cell body contains all organelles including nucleus with genetic information that directs synthesis. Dendritic end surrounds cell body. Axon is elongated region terminates at the axon terminus; the location of the synapse. Action poten ...
Slide 1
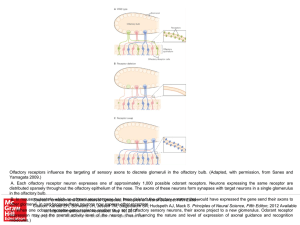
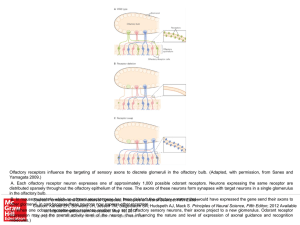
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Notes Intro to Nervous System and Neurons
... – monitor changes inside and outside the body – changes = stimuli – sensory receptors responsible for input ...
... – monitor changes inside and outside the body – changes = stimuli – sensory receptors responsible for input ...
Biological Bases Of Behaviour Central Nervous System
... The network of neurons connecting the CNS to our internal muscles and organs. Controls non-skeletal muscles such as the heart, kidneys, glands, etc. The majority of functions occur without our control, but we can gain control of some functions through biofeedback. This is a process whereby an indivi ...
... The network of neurons connecting the CNS to our internal muscles and organs. Controls non-skeletal muscles such as the heart, kidneys, glands, etc. The majority of functions occur without our control, but we can gain control of some functions through biofeedback. This is a process whereby an indivi ...
Circulatory System Directs blood from the heart to the rest of the
... and sodium rushes into the cell. This rush of positive ions causes the cell’s charge to rise and spike (from -65mv to +40mv). This process is called depolarization. 4. After the initial rush, the sodium gates close (stopping sodium movement) and potassium gates open. Potassium then rushes out of the ...
... and sodium rushes into the cell. This rush of positive ions causes the cell’s charge to rise and spike (from -65mv to +40mv). This process is called depolarization. 4. After the initial rush, the sodium gates close (stopping sodium movement) and potassium gates open. Potassium then rushes out of the ...
cms/lib/NY01001456/Centricity/Domain/535/nervous system tea
... Phrase given to instinctive response to danger where our heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and oxygen intake from lungs increase to give one more energy for a response. Controlled by the sympathetic division. 39. What is Cerebral Palsy? Birth defect often due to a temporary lack of o ...
... Phrase given to instinctive response to danger where our heart rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and oxygen intake from lungs increase to give one more energy for a response. Controlled by the sympathetic division. 39. What is Cerebral Palsy? Birth defect often due to a temporary lack of o ...
Slide ()
... The muscle spindle detects changes in muscle length. A. The main components of the muscle spindle are intrafusal muscle fibers, afferent sensory endings, and efferent motor endings. The intrafusal fibers are specialized muscle fibers with central regions that are not contractile. Gamma motor neurons ...
... The muscle spindle detects changes in muscle length. A. The main components of the muscle spindle are intrafusal muscle fibers, afferent sensory endings, and efferent motor endings. The intrafusal fibers are specialized muscle fibers with central regions that are not contractile. Gamma motor neurons ...