CHAPTER 28 Nervous Systems
... interconnected functions – Sensory input: receptors-structures specialized to detect certain stimuli – Integration: through the spinal cord & brain – Motor output: effectors-respond to a stimulus such as muscles or glands ...
... interconnected functions – Sensory input: receptors-structures specialized to detect certain stimuli – Integration: through the spinal cord & brain – Motor output: effectors-respond to a stimulus such as muscles or glands ...
Lecture 12
... i. type Ia sensory fiber - in center ii. type II sensory fiber - at ends iii. gamma motor neurons - from ventral horn b. extrafusal fibers - outer muscle fibers i. alpha motor neurons - form ventral horn 3. Golgi (tendon) organs a. at junction of tendon and muscle 4. Joint Kinesthetic receptors a. w ...
... i. type Ia sensory fiber - in center ii. type II sensory fiber - at ends iii. gamma motor neurons - from ventral horn b. extrafusal fibers - outer muscle fibers i. alpha motor neurons - form ventral horn 3. Golgi (tendon) organs a. at junction of tendon and muscle 4. Joint Kinesthetic receptors a. w ...
Summary of Chapter 7
... THE HUMAN ORGANISM AND THE EXTERNAL WORLD • The central nervous system coordinates a major part of the activities of the nervous system. It is made up of the brain and the spinal cord (p. 206). ...
... THE HUMAN ORGANISM AND THE EXTERNAL WORLD • The central nervous system coordinates a major part of the activities of the nervous system. It is made up of the brain and the spinal cord (p. 206). ...
SNS—brain and spinal cord
... Brain—control center of the nervous system surrounded by the skull which provides protection and support. Two hemispheres and four major regions. Left and right hemisphere. Four regions: Cerebrum, diencephalons, brain stem, cerebellum. Pg 1470 fig. Tables Each hemisphere: temporal, front ...
... Brain—control center of the nervous system surrounded by the skull which provides protection and support. Two hemispheres and four major regions. Left and right hemisphere. Four regions: Cerebrum, diencephalons, brain stem, cerebellum. Pg 1470 fig. Tables Each hemisphere: temporal, front ...
psych mod 4 terms
... functions include processing sensory info. from body parts, which includes touching, locating positions of limbs, and feeling temperature and pain, and carrying out several cognitive functions, such as attending to and perceiving objects. 29. Somatosensory Cortex- a narrow strip of cortex that is lo ...
... functions include processing sensory info. from body parts, which includes touching, locating positions of limbs, and feeling temperature and pain, and carrying out several cognitive functions, such as attending to and perceiving objects. 29. Somatosensory Cortex- a narrow strip of cortex that is lo ...
ppt
... maggots eat the dead skin cells and bacteria. maggot therapy (also known as maggot debridement therapy (mdt), larval therapy, larva therapy, or larvae therapy) is the intentional introduction of live, disinfected maggots or fly larvae into non-healing skin or soft tissue wounds of a human or other a ...
... maggots eat the dead skin cells and bacteria. maggot therapy (also known as maggot debridement therapy (mdt), larval therapy, larva therapy, or larvae therapy) is the intentional introduction of live, disinfected maggots or fly larvae into non-healing skin or soft tissue wounds of a human or other a ...
Reading_Nervous_System
... The relationship between sensory and motor neurons can be seen in a reflex (rapid motor response to a stimulus). Reflexes are quick because they involve few neurons. Reflexes are either somatic (resulting in contraction of skeletal muscle) or autonomic (activation of smooth and cardiac muscle). All ...
... The relationship between sensory and motor neurons can be seen in a reflex (rapid motor response to a stimulus). Reflexes are quick because they involve few neurons. Reflexes are either somatic (resulting in contraction of skeletal muscle) or autonomic (activation of smooth and cardiac muscle). All ...
Meart: 1000 word catalogue essay:
... creativity. Meart is the ultimate Cartesian dualism —a machine body completely removed from its brain and to complicate matters even further the brain has been reconstituted in vitro from its cellular components. To view Meart is to witness a collage of contradictions. It offers us the actual biolog ...
... creativity. Meart is the ultimate Cartesian dualism —a machine body completely removed from its brain and to complicate matters even further the brain has been reconstituted in vitro from its cellular components. To view Meart is to witness a collage of contradictions. It offers us the actual biolog ...
Spinal Cord - Northside Middle School
... you can’t change, build, and reconstruct your brain. If you communicate indirectly you can practice communicating directly with a direct speaker. If you are a direct speaker you can work with an indirect speaker to build up your ability to speak indirectly. ...
... you can’t change, build, and reconstruct your brain. If you communicate indirectly you can practice communicating directly with a direct speaker. If you are a direct speaker you can work with an indirect speaker to build up your ability to speak indirectly. ...
PPT
... motor neuron; can also describe CNS neurons whose axons do not leave the structure in which they reside ...
... motor neuron; can also describe CNS neurons whose axons do not leave the structure in which they reside ...
Nervous System
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
... Impulses jump from the axon Across the synapse To the dendrite of the next neuron ...
Test 4 Study Guide
... 1. The Nervous System a. Includes all neural tissue in the body; Neural tissue contains two kinds of cells i. Neurons: Cells that send and receive signals ii. Neuroglia (glial cells):Cells that support and protect neurons b. Organs of the Nervous System i. Brain and spinal cord ii. Sensory receptors ...
... 1. The Nervous System a. Includes all neural tissue in the body; Neural tissue contains two kinds of cells i. Neurons: Cells that send and receive signals ii. Neuroglia (glial cells):Cells that support and protect neurons b. Organs of the Nervous System i. Brain and spinal cord ii. Sensory receptors ...
Functions and Anatomy of Human Body - GK Notes in PDF
... Consists of two identical lobes located in front of the heart. ...
... Consists of two identical lobes located in front of the heart. ...
The Nervous System
... • It is a semi-permeable capillary membrane; that is, it allows some materials to cross, but prevents others from crossing. In most parts of the body the capillaries, are lined with endothelial cells. The endothelial tissue has small spaces between each individual cell so substances can move readily ...
... • It is a semi-permeable capillary membrane; that is, it allows some materials to cross, but prevents others from crossing. In most parts of the body the capillaries, are lined with endothelial cells. The endothelial tissue has small spaces between each individual cell so substances can move readily ...
Anatomy of Brain Functions
... CSF helps to maintain chemical homeostasis within the central nervous system. It contains ions, nutrients, oxygen, and albumins that support the chemical and osmotic balance of nervous tissue. CSF also removes waste products that form as byproducts of cellular metabolism within nervous tissue. ...
... CSF helps to maintain chemical homeostasis within the central nervous system. It contains ions, nutrients, oxygen, and albumins that support the chemical and osmotic balance of nervous tissue. CSF also removes waste products that form as byproducts of cellular metabolism within nervous tissue. ...
AP Ch. 2 vocab
... system the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response ...
... system the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response ...
PNS Study Guide
... 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called in between neurons where chemicals are exchanged? What are these special chemicals called? 13. *** Describe the 3 functional classifications and the ...
... 11. Which part of the neuron RECEIVES information and which part of the neuron SENDS information away from the cell body? 12. What is the space called in between neurons where chemicals are exchanged? What are these special chemicals called? 13. *** Describe the 3 functional classifications and the ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... Neurons are specialized cells for the reception, conduction, and transmission of electrochemical signals Many sizes and shapes ~100 billion neurons ...
... Neurons are specialized cells for the reception, conduction, and transmission of electrochemical signals Many sizes and shapes ~100 billion neurons ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... Sensory receptors collect information about the world outside the body as well as processes inside the body. Ex. The rods and cones of the eye; pressure receptors in the skin. Sensory neurons transmit information from the eyes and other sensors that detect stimuli to the brain or spinal cord ...
... Sensory receptors collect information about the world outside the body as well as processes inside the body. Ex. The rods and cones of the eye; pressure receptors in the skin. Sensory neurons transmit information from the eyes and other sensors that detect stimuli to the brain or spinal cord ...
THE MACHINE OF PEACE tirar as letras da foto. MICROCODE
... Almost all pituitary secretion is controlled by the hypothalamus, which receives information from the periphery (ranging from pain to depressive thoughts), and depending on current needs of inhibiting or stimulating the secretion of pituitary hormones, by neural and hormonal signals. The hypothalam ...
... Almost all pituitary secretion is controlled by the hypothalamus, which receives information from the periphery (ranging from pain to depressive thoughts), and depending on current needs of inhibiting or stimulating the secretion of pituitary hormones, by neural and hormonal signals. The hypothalam ...
The fertile brain - Health Research Council
... With infertility becoming more prevalent in Western societies, a new HRCfunded programme at the University of Otago’s Centre for Neuroendocrinology is focusing on how the brain controls fertility. Professor Allan Herbison from the Department of Physiology, Associate Professor Dave Grattan and Dr Gre ...
... With infertility becoming more prevalent in Western societies, a new HRCfunded programme at the University of Otago’s Centre for Neuroendocrinology is focusing on how the brain controls fertility. Professor Allan Herbison from the Department of Physiology, Associate Professor Dave Grattan and Dr Gre ...
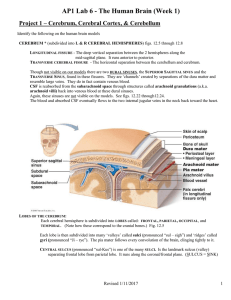
Lab Activity Sheets
... Ventricles are cavities within the brain filled with about 140-150 ml. of cerebrospinal fluid. On our models these cavities are depicted only in the right hemisphere. LATERAL VENTRICLES (There are two… one in each cerebral hemisphere.) The deep cavity visible between the corpus callosum and the forn ...
... Ventricles are cavities within the brain filled with about 140-150 ml. of cerebrospinal fluid. On our models these cavities are depicted only in the right hemisphere. LATERAL VENTRICLES (There are two… one in each cerebral hemisphere.) The deep cavity visible between the corpus callosum and the forn ...
Myers Module Four
... The autonomic nervous system controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, bloo ...
... The autonomic nervous system controls our glands and the muscles of our internal organs, influencing such functions as glandular activity, heartbeat, and digestion. It may be consciously overridden. The sympathetic nervous system arouses and expends energy. Heartrate, blood pressure, digestion, bloo ...