The Nervous System
... • The human brain is not only larger, but heavier than a sheep’s brain, ▫ Sheep brain is roughly 140 grams compared to the human brain, and is only about one third as long. ...
... • The human brain is not only larger, but heavier than a sheep’s brain, ▫ Sheep brain is roughly 140 grams compared to the human brain, and is only about one third as long. ...
Synaptic receptors, neurotransmitters and brain modulators
... Many of the activities of the ANS are involuntary. (However, breathing, for example, can be in part consciously controlled.) ...
... Many of the activities of the ANS are involuntary. (However, breathing, for example, can be in part consciously controlled.) ...
Nervous System
... FLUID – acts as a liquid shock absorber and source of nutrients for the brain. Ventricles of the Brain Brain contains four cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid called CEREBRAL VENTRICLES. ...
... FLUID – acts as a liquid shock absorber and source of nutrients for the brain. Ventricles of the Brain Brain contains four cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid called CEREBRAL VENTRICLES. ...
A.1 Neural Development
... The neural tube of embryonic chordates is formed by in-folding of ectoderm followed by elongation of the tube. Neurons are initially produced by differentiation in the neural tube Immature neurons migrate to a final location ...
... The neural tube of embryonic chordates is formed by in-folding of ectoderm followed by elongation of the tube. Neurons are initially produced by differentiation in the neural tube Immature neurons migrate to a final location ...
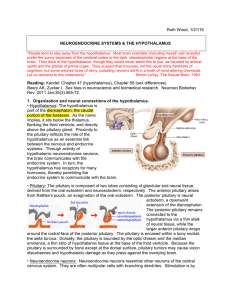
5211: Session 1 Hypothalamus and its regulation of anterior and
... thyroid stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone. Infundibulum contains axons from hypothalamic neurons that project into the posterior pituitary where they terminate near capillaries. These terminals contain hormones oxytocin and vasopressin. ...
... thyroid stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone. Infundibulum contains axons from hypothalamic neurons that project into the posterior pituitary where they terminate near capillaries. These terminals contain hormones oxytocin and vasopressin. ...
The Nervous System
... the other systems in the body. Through this regulation the body can maintain homeostasis. Movement, digestion, circulation, breathing and many other body functions are all controlled by the responses of the nervous system. ...
... the other systems in the body. Through this regulation the body can maintain homeostasis. Movement, digestion, circulation, breathing and many other body functions are all controlled by the responses of the nervous system. ...
12-nervoussystemintro - Alexmac
... • Sensory receptors are structures in the skin and other tissues that detect changes in the internal or external environment. These receptors consist of specialized neuron endings or specialized cells in close contact with neurons that convert the energy of the stimulus (sound, color, odor, etc.) to ...
... • Sensory receptors are structures in the skin and other tissues that detect changes in the internal or external environment. These receptors consist of specialized neuron endings or specialized cells in close contact with neurons that convert the energy of the stimulus (sound, color, odor, etc.) to ...
The Nervous System
... The brain stem (an extension of the spinal cord), the forebrain (Primarily consists of the Cerebrium), and the Cerebellum. Forebrain and Cerebellum are divided into two hemispheres, which are linked by a thick band of nerve fibers and these hemispheres have areas, called "lobes," which perform spe ...
... The brain stem (an extension of the spinal cord), the forebrain (Primarily consists of the Cerebrium), and the Cerebellum. Forebrain and Cerebellum are divided into two hemispheres, which are linked by a thick band of nerve fibers and these hemispheres have areas, called "lobes," which perform spe ...
m5zn_363798b57fd4c88
... Function of the spinal cord The main functions of the spinal cord are: 1. The spinal cord communicates through nerve fibers, its nervous pathways, with various parts of the brain and through spinal nerves with organs. The spinal cord contains two kinds of nervous pathway: ascending (sensory) and d ...
... Function of the spinal cord The main functions of the spinal cord are: 1. The spinal cord communicates through nerve fibers, its nervous pathways, with various parts of the brain and through spinal nerves with organs. The spinal cord contains two kinds of nervous pathway: ascending (sensory) and d ...
Reflexes and Homeostasis
... stimulus (touch, pain, muscle stretch, etc.); an interneuron, which receives a signal if the sensory neuron is stimulated su ciently; and a motor neuron, which is stimulated by the interneuron and then carries out the action required for the stimulus which initiated the response. The sensory neurons ...
... stimulus (touch, pain, muscle stretch, etc.); an interneuron, which receives a signal if the sensory neuron is stimulated su ciently; and a motor neuron, which is stimulated by the interneuron and then carries out the action required for the stimulus which initiated the response. The sensory neurons ...
Nervous System
... Explain and discuss what the nervous system Discuss the functions and diseases/problems the nervous system can bring Show and explain a model of the system Questions for us from the class quiz/worksheet ...
... Explain and discuss what the nervous system Discuss the functions and diseases/problems the nervous system can bring Show and explain a model of the system Questions for us from the class quiz/worksheet ...
chapter 7 the nervous system
... the diencephalons and pons Serves as a reflex center Responsible for moving the eyes to view something as the head is turned It contains the auditory reflex centers that operate when a person needs to move his/her head in order to hear sounds more distinctly ...
... the diencephalons and pons Serves as a reflex center Responsible for moving the eyes to view something as the head is turned It contains the auditory reflex centers that operate when a person needs to move his/her head in order to hear sounds more distinctly ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Parasympathetic Division • Preganglionic cell bodies in nuclei of brainstem or lateral parts of spinal cord gray matter from S2-S4 – Preganglionic axons from brain pass to ganglia through cranial nerves – Preganglionic axons from sacral region pass through pelvic nerves to ganglia ...
... Parasympathetic Division • Preganglionic cell bodies in nuclei of brainstem or lateral parts of spinal cord gray matter from S2-S4 – Preganglionic axons from brain pass to ganglia through cranial nerves – Preganglionic axons from sacral region pass through pelvic nerves to ganglia ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... d. ____________________________– cover the fibers of the __________________ neurons with __________________ __________________. E. Neuron Structure 1. __________________ - cell body a. contains all organelles except centrioles (thus neurons are not able to reproduce) b. __________________ _________ ...
... d. ____________________________– cover the fibers of the __________________ neurons with __________________ __________________. E. Neuron Structure 1. __________________ - cell body a. contains all organelles except centrioles (thus neurons are not able to reproduce) b. __________________ _________ ...
NSCI 525 RWood 1-22-15
... magnocellular neurons, with cell bodies in the paraventricular (PVN) and supraoptic (SON) nuclei of the hypothalamus. Oxytocin is made primarily in the paraventricular nucleus, while the supraoptic nucleus synthesizes mostly vasopressin. These magnocellular neurons project caudally to the posterior ...
... magnocellular neurons, with cell bodies in the paraventricular (PVN) and supraoptic (SON) nuclei of the hypothalamus. Oxytocin is made primarily in the paraventricular nucleus, while the supraoptic nucleus synthesizes mostly vasopressin. These magnocellular neurons project caudally to the posterior ...
CS 256: Neural Computation Lecture Notes
... and desribed the dynamics mathematically. Awarded the Nobel Prize in 1963 for this work. • Two types of electric potentials – Synaptic/receptor potentials are graded, sustained and local. They are usually stimulated by neurotransmitters. (The stronger the stimulus, the larger the potential.) They ad ...
... and desribed the dynamics mathematically. Awarded the Nobel Prize in 1963 for this work. • Two types of electric potentials – Synaptic/receptor potentials are graded, sustained and local. They are usually stimulated by neurotransmitters. (The stronger the stimulus, the larger the potential.) They ad ...
The Endocrine System
... or pituitary gland Weighs about 0.5 g It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone—the sella turcica—an important radiological landmark During embryogenesis, the hypophysis develops partly from oral ectoderm and partly from nerve tissue ...
... or pituitary gland Weighs about 0.5 g It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone—the sella turcica—an important radiological landmark During embryogenesis, the hypophysis develops partly from oral ectoderm and partly from nerve tissue ...
Lecture 11a Nervous System
... • Masses of neuron cell bodies – Called ganglia in the PNS and are surrounded by satellite cells – Called nuclei in the CNS ...
... • Masses of neuron cell bodies – Called ganglia in the PNS and are surrounded by satellite cells – Called nuclei in the CNS ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... • Ganglia – collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system ...
... • Ganglia – collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system ...
Nervous system - Effingham County Schools
... • Vital centers - cardiac, dilates blood vessels (drops and increases blood pressure), respiratory ...
... • Vital centers - cardiac, dilates blood vessels (drops and increases blood pressure), respiratory ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... • The motor division has 2 main parts:(1) Somatic nervous system (voluntary/involuntary);(2) Autonomic nervous system (visceral motor)— functional subdivisions are sympathetic/ parasympathetic (opposite effects on viscera-stimulaton/inhibition) ...
... • The motor division has 2 main parts:(1) Somatic nervous system (voluntary/involuntary);(2) Autonomic nervous system (visceral motor)— functional subdivisions are sympathetic/ parasympathetic (opposite effects on viscera-stimulaton/inhibition) ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Integumentary and Nervous Systems
... Axon – extension off cell body which impulse travels down Terminal branches – contains synaptic knobs Synaptic knobs – impulse is released here across the synapse to another neuron Myelin sheath – layer of fat that insulates the axon to prevent losing impulses Synapse – space between two neurons whe ...
... Axon – extension off cell body which impulse travels down Terminal branches – contains synaptic knobs Synaptic knobs – impulse is released here across the synapse to another neuron Myelin sheath – layer of fat that insulates the axon to prevent losing impulses Synapse – space between two neurons whe ...