Introduction to the Nervous System
... a- Sensory neurons that convey information to the CNS from sense receptors b- Motor neurons that conduct impulses to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands c- For this reason the ANS is generally considered involuntary. d- The ANS is divided into three sections i. Sympathetic nervous system, paras ...
... a- Sensory neurons that convey information to the CNS from sense receptors b- Motor neurons that conduct impulses to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands c- For this reason the ANS is generally considered involuntary. d- The ANS is divided into three sections i. Sympathetic nervous system, paras ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... Arrays, maps and hierarchies support spatial coding in neurons. For example the visual thalamus and area V1 (the first visual projection area) can be seen as maps of the retina. Maps represent spatial arrangements in the world. But the brain makes use of temporal coding as well. Figure 3.23 shows an ...
... Arrays, maps and hierarchies support spatial coding in neurons. For example the visual thalamus and area V1 (the first visual projection area) can be seen as maps of the retina. Maps represent spatial arrangements in the world. But the brain makes use of temporal coding as well. Figure 3.23 shows an ...
nervous system divisions cns, pns 1
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
CNS neurotransmitters
... is involved in the regulation of several aspects of behavior, including sleep, pain perception, depression, sexual activity, and aggressiveness. Some of the most important antidepressant agents are believed to prevent the reuptake of serotonin. Serotonin also may be involved in temperature regulatio ...
... is involved in the regulation of several aspects of behavior, including sleep, pain perception, depression, sexual activity, and aggressiveness. Some of the most important antidepressant agents are believed to prevent the reuptake of serotonin. Serotonin also may be involved in temperature regulatio ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Astrocytes: star shaped cells found between neurons and blood vessels. They are the most abundant glial cells. Function: structural support transport of substance between blood vessels and neurons, mop up excess ions (k) and neurotransmitters. 2. Microglial cells: small ovoid cells. Function: str ...
... 1. Astrocytes: star shaped cells found between neurons and blood vessels. They are the most abundant glial cells. Function: structural support transport of substance between blood vessels and neurons, mop up excess ions (k) and neurotransmitters. 2. Microglial cells: small ovoid cells. Function: str ...
Reflex Arc - Point Loma High School
... Reflex Arc • Monosynaptic- When a reflex arc consists of only two ...
... Reflex Arc • Monosynaptic- When a reflex arc consists of only two ...
Ch. 7: The Nervous System
... 7. If 2 or more nerves converge onto one, the addition of their impulses may be enough to trigger the larger nerve to continue the impulse on toward the CNS. 8. The CNS receives the signal and interprets the information, then it makes a decision. 9. The CNS sends an impulse out through a motor nerve ...
... 7. If 2 or more nerves converge onto one, the addition of their impulses may be enough to trigger the larger nerve to continue the impulse on toward the CNS. 8. The CNS receives the signal and interprets the information, then it makes a decision. 9. The CNS sends an impulse out through a motor nerve ...
File - Mrs. Walston Science
... The Nervous System The nervous system is a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is essentially the body’s electrical wiring. ...
... The Nervous System The nervous system is a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is essentially the body’s electrical wiring. ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Nerves: bundled axons that form neural “cables” connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons: neurons that carry outgoing information from ...
... Nerves: bundled axons that form neural “cables” connecting the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs. Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons: neurons that carry outgoing information from ...
File - Lucinda Supernavage
... • Motor Nerves – carry impulses to muscles or glands; cause a response; EFFERENT nerves • Interneurons – connect sensory and motor nerves NEUROPATHY – damage to nerves in the PNS usually from underlying medical conditions (ie. Diabetes) • symptoms include burning/tingling sensation and loss of sensa ...
... • Motor Nerves – carry impulses to muscles or glands; cause a response; EFFERENT nerves • Interneurons – connect sensory and motor nerves NEUROPATHY – damage to nerves in the PNS usually from underlying medical conditions (ie. Diabetes) • symptoms include burning/tingling sensation and loss of sensa ...
BRAIN
... Connects fore and hind brains. Mainly responsible for movements such as head and eyes focussing on an object. ...
... Connects fore and hind brains. Mainly responsible for movements such as head and eyes focussing on an object. ...
Nervous System Period 3 - Mercer Island School District
... • Receptors are in sense organs; effectors are muscles or glands that coordinate a response • Impulses are passes from one cell to another through SYNAPSES (gap between axon of one neuron and dendrite or cell body of another neuron) • Chemicals, or neurotransmitters, bridge this gap to transfer info ...
... • Receptors are in sense organs; effectors are muscles or glands that coordinate a response • Impulses are passes from one cell to another through SYNAPSES (gap between axon of one neuron and dendrite or cell body of another neuron) • Chemicals, or neurotransmitters, bridge this gap to transfer info ...
Nervous System Nervous system
... Maintain body’s functions in balance Depending on the situation, the autonomic nervous system can speed up or slow down these functions The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system ...
... Maintain body’s functions in balance Depending on the situation, the autonomic nervous system can speed up or slow down these functions The autonomic nervous system has two divisions: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system ...
My Big List Thing
... o Interventricular foramina (foramina of Monro): channels that connect paired lateral ventricles to third ventricle at midline of brain; located at medial and inferior aspect of lateral ventricles, bound by fornix and thalamus; allow CSF produced in lateral ventricles to reach third ventricle and th ...
... o Interventricular foramina (foramina of Monro): channels that connect paired lateral ventricles to third ventricle at midline of brain; located at medial and inferior aspect of lateral ventricles, bound by fornix and thalamus; allow CSF produced in lateral ventricles to reach third ventricle and th ...
Nervous System Bookwork—KEY
... to enter the neuron through sodium gates. This causes local depolarization and generates the action potential, which is then self-propagating. This event is quickly followed by a second permeability change that restricts Na + entry but allows K+ to leave the neuron, causing repolarization. One way c ...
... to enter the neuron through sodium gates. This causes local depolarization and generates the action potential, which is then self-propagating. This event is quickly followed by a second permeability change that restricts Na + entry but allows K+ to leave the neuron, causing repolarization. One way c ...
Describe how action potentials are generated
... • Neuron Classification function: – Sensory (afferent): transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs toward or into the CNS • All are unipolar • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long periphe ...
... • Neuron Classification function: – Sensory (afferent): transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs toward or into the CNS • All are unipolar • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long periphe ...
Describe how action potentials are generated and
... • Neuron Classification function: – Sensory (afferent): transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs toward or into the CNS • All are unipolar • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long periphe ...
... • Neuron Classification function: – Sensory (afferent): transmit impulses from sensory receptors in the skin or internal organs toward or into the CNS • All are unipolar • Cell bodies are located in sensory ganglia outside of the CNS • Only most distal parts act as receptor sites, with long periphe ...
Neurophysiology-Organization of central nervous system
... When they convert these energy into electrical energy, they transmit action potential through afferent neuron bcoz what reach cerebral cortex only nerve impulse (action potential) wither the sensation was touch, pressure,……….. etc. BUT how can I discriminate this kind of sensation as touch or tempe ...
... When they convert these energy into electrical energy, they transmit action potential through afferent neuron bcoz what reach cerebral cortex only nerve impulse (action potential) wither the sensation was touch, pressure,……….. etc. BUT how can I discriminate this kind of sensation as touch or tempe ...
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling
... the cell membrane. Transport 3 Na+ ions out for every 2 K+ ions in. In addition to the SodiumPotassium pump, ions diffuse across the concentration gradient. Many K+ channels are open, allowing for a large amount of K+ to move out of the cell, few Na+ channels are open allowing little flow inside, ...
... the cell membrane. Transport 3 Na+ ions out for every 2 K+ ions in. In addition to the SodiumPotassium pump, ions diffuse across the concentration gradient. Many K+ channels are open, allowing for a large amount of K+ to move out of the cell, few Na+ channels are open allowing little flow inside, ...
nervous system
... Nerves of the body that are under voluntary control, and use skeletal muscles are part of the somatic nervous system. The somatic nervous system relays information from the sensory receptors to the CNS. Somatic motor nerves relay information from the CNS to the skeletal muscles. A reflex arc is also ...
... Nerves of the body that are under voluntary control, and use skeletal muscles are part of the somatic nervous system. The somatic nervous system relays information from the sensory receptors to the CNS. Somatic motor nerves relay information from the CNS to the skeletal muscles. A reflex arc is also ...
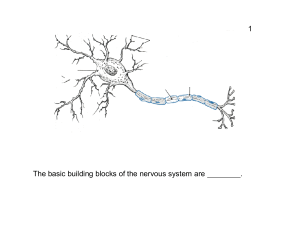
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temp), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, & is linked to emotion ...
... directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temp), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, & is linked to emotion ...