Neuroscience - HuskiesScience
... • When the cell is at rest (i.e., not doing anything), it has a charge of -70 mV. This is called the resting potential. • Because of the cell properties, many forces are acting on the cell. • 1. Diffusion - substances tend to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. • 2. ...
... • When the cell is at rest (i.e., not doing anything), it has a charge of -70 mV. This is called the resting potential. • Because of the cell properties, many forces are acting on the cell. • 1. Diffusion - substances tend to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. • 2. ...
The Brain
... spinal cord. Those structures close to the spinal cord function in reflexes (close to nerves) and RELAYING or CONNECTING peripheral nerves to the brain. Since the midbrain is close to this area, it receives information and... Midbrain: ...
... spinal cord. Those structures close to the spinal cord function in reflexes (close to nerves) and RELAYING or CONNECTING peripheral nerves to the brain. Since the midbrain is close to this area, it receives information and... Midbrain: ...
Cell Structure: From an Information Processing View
... Efferent or motor neuron: conduct impulses from the central nervous system to the effector organs (such as muscles and glands) are called motor (or efferent) neurons ...
... Efferent or motor neuron: conduct impulses from the central nervous system to the effector organs (such as muscles and glands) are called motor (or efferent) neurons ...
The Nervous System
... touch a warm surface, the neurons send a message straight to the brain. This action of getting information from the surrounding environment is called sensory input because things are being sent to the brain by way of the senses. ...
... touch a warm surface, the neurons send a message straight to the brain. This action of getting information from the surrounding environment is called sensory input because things are being sent to the brain by way of the senses. ...
Slide ()
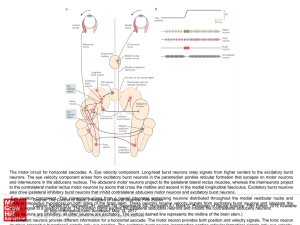
... nucleus prepositus hypoglossi on both sides of the brain stem. These neurons receive velocity signals from excitatory burst neurons and integrate this Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available velocity ...
... nucleus prepositus hypoglossi on both sides of the brain stem. These neurons receive velocity signals from excitatory burst neurons and integrate this Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available velocity ...
The Nervous System funtions and neuron
... Long, thin processes with uniform diameter carry impulses away from cell body Many fine extensions at end called collaterals Axon ending= at ends of collaterals contain synaptic knob (comes in contact with receptive surface of another cell) ...
... Long, thin processes with uniform diameter carry impulses away from cell body Many fine extensions at end called collaterals Axon ending= at ends of collaterals contain synaptic knob (comes in contact with receptive surface of another cell) ...
Neuron encyclopaedia fires up to reveal brain secrets
... or the tens of billions in the human one. “There are too many neurons in the brain, and we have only sampled a very, very small set,” says the Allen Institute’s Hanchuan Peng, who is leading the BigNeuron project. A major bottleneck in cataloguing more neurons has been extracting the three-dimension ...
... or the tens of billions in the human one. “There are too many neurons in the brain, and we have only sampled a very, very small set,” says the Allen Institute’s Hanchuan Peng, who is leading the BigNeuron project. A major bottleneck in cataloguing more neurons has been extracting the three-dimension ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... Split brain operation—procedure used to reduces recurrent seizures of severe epilepsy Corpus callosum—thick band of axons that connects the two ...
... Split brain operation—procedure used to reduces recurrent seizures of severe epilepsy Corpus callosum—thick band of axons that connects the two ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM: NEURAL TISSUE
... – Inters88al environment – Blood‐brain barrier – Structural support – Repairing damaged nervous 8ssue – Neuron development ...
... – Inters88al environment – Blood‐brain barrier – Structural support – Repairing damaged nervous 8ssue – Neuron development ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology, Nervous System and Special
... 9. Rationalize the structures of pain, deep pressure, and stretch receptors. ________: branched, uncovered near the surface for sensitivity Deep pressure = ________________________________: layered for reduced sensitivity _______________: branched and attached along tendon to sense changes in length ...
... 9. Rationalize the structures of pain, deep pressure, and stretch receptors. ________: branched, uncovered near the surface for sensitivity Deep pressure = ________________________________: layered for reduced sensitivity _______________: branched and attached along tendon to sense changes in length ...
Central Nervous System - tvhs2011
... and interrupt messages throughout the body. It allows us to react to stimuli, sends chemicals that give us feelings, and enables our body to function. The nervous system consists mainly of two parts. These parts being the brain and the vertebrae also known as the spinal cord. Another major com ...
... and interrupt messages throughout the body. It allows us to react to stimuli, sends chemicals that give us feelings, and enables our body to function. The nervous system consists mainly of two parts. These parts being the brain and the vertebrae also known as the spinal cord. Another major com ...
Chapter 48 p. 1040-1053
... hormones and hormones acting on anterior pituitary; has body thermostat hypothalamic nuclei: sexual and mating behaviors, fight-or-flight response, pleasure The Hypothalamus and Circadian Rhythms o biological clock: component of circadian rhythms o suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN): in mammal’s hypot ...
... hormones and hormones acting on anterior pituitary; has body thermostat hypothalamic nuclei: sexual and mating behaviors, fight-or-flight response, pleasure The Hypothalamus and Circadian Rhythms o biological clock: component of circadian rhythms o suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN): in mammal’s hypot ...
Biology 4 Study Guide
... ______________ environment of the brain. They form a _____________ between the ________________ & the ___________. 2. _______________ are ____________-like __________________ that dispose of ______________. 3. __________________ cells line the _______________ of the brain & the spinal cord. They hel ...
... ______________ environment of the brain. They form a _____________ between the ________________ & the ___________. 2. _______________ are ____________-like __________________ that dispose of ______________. 3. __________________ cells line the _______________ of the brain & the spinal cord. They hel ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... body is called the axon which carries information away from the cell body. • Axons are highly variable in length and may divide into several branches or collaterals through which information can be distributed to a number of different destinations ...
... body is called the axon which carries information away from the cell body. • Axons are highly variable in length and may divide into several branches or collaterals through which information can be distributed to a number of different destinations ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... body is called the axon which carries information away from the cell body. • Axons are highly variable in length and may divide into several branches or collaterals through which information can be distributed to a number of different destinations ...
... body is called the axon which carries information away from the cell body. • Axons are highly variable in length and may divide into several branches or collaterals through which information can be distributed to a number of different destinations ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... The Nervous and Endocrine Systems The nervous system is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gath ...
... The Nervous and Endocrine Systems The nervous system is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gath ...
PNS/Reflexes
... pain receptors are tonic and do not exhibit peripheral adaptation; but central adaptation can reduce the perception of pain (see below). IV. Adaptation - when you are exposed to a constant stimulus (ex, a scent), your perception of that stimulus can sometimes diminish over time. One of two things ca ...
... pain receptors are tonic and do not exhibit peripheral adaptation; but central adaptation can reduce the perception of pain (see below). IV. Adaptation - when you are exposed to a constant stimulus (ex, a scent), your perception of that stimulus can sometimes diminish over time. One of two things ca ...
Chapter 7 Part 1 Nervous Tissue
... cerebellum, the white matter consists of structures at the core of the brain such as the thalamus and hypothalamus • Certain nuclei within the white matter are involved in the expression of emotions, the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, and in the regulation of food and water intake ...
... cerebellum, the white matter consists of structures at the core of the brain such as the thalamus and hypothalamus • Certain nuclei within the white matter are involved in the expression of emotions, the release of hormones from the pituitary gland, and in the regulation of food and water intake ...
The Nervous System
... Hypothalamus gland: hunger, thirst, sleep, and sexual response, regulates body temperature, blood pressure, emotions, and secretion of hormones Pituitary gland: known as the “master gland,” it controls other endocrine glands in the body; produces many hormones Pineal gland: regulates the body’ ...
... Hypothalamus gland: hunger, thirst, sleep, and sexual response, regulates body temperature, blood pressure, emotions, and secretion of hormones Pituitary gland: known as the “master gland,” it controls other endocrine glands in the body; produces many hormones Pineal gland: regulates the body’ ...
HYPOPHYSIS CEREBRI ( PITUITARY GLAND )
... → Hypophyseal portal Veins (or venules) → 2ry capillary plexus of capillaries in adenohypophysis [ Hypophyseal Portal System ] It carries neurohormones from median eminence to adenohypophysis. ...
... → Hypophyseal portal Veins (or venules) → 2ry capillary plexus of capillaries in adenohypophysis [ Hypophyseal Portal System ] It carries neurohormones from median eminence to adenohypophysis. ...
Nerves and Digestion
... 4. Cerebrum – controls vision, touch, and other senses. 5. Cerebellum – helps control balance and coordination. 6. Brain Stem – Controls digestion, breathing, heartbeat. Links the brain and spinal cord. ...
... 4. Cerebrum – controls vision, touch, and other senses. 5. Cerebellum – helps control balance and coordination. 6. Brain Stem – Controls digestion, breathing, heartbeat. Links the brain and spinal cord. ...
nervous system 2012 - Junction Hill C
... From the cell body, information is transmitted to other cells by a fiber called an axon. Axons can be very short or quite long. You have some really long axons that extend almost 1 meter from your lower back to your ...
... From the cell body, information is transmitted to other cells by a fiber called an axon. Axons can be very short or quite long. You have some really long axons that extend almost 1 meter from your lower back to your ...