Organization and Development of the Nervous System
... Isn’t cancer when mitosis has gone wild??!! ...
... Isn’t cancer when mitosis has gone wild??!! ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... • B) the right hemisphere • C) Both hemispheres control these functions equally. • D) There is no research stating that either hemisphere dominates ...
... • B) the right hemisphere • C) Both hemispheres control these functions equally. • D) There is no research stating that either hemisphere dominates ...
Basics of Anatomy.pub
... the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas that aid in the process. The program then looks at the synthesis of vitamins by bacteria in the large intes ne and then goes on to explore the complex structures in the kidney that allow them to filter wastes out of the blood while returning water and nutrients ...
... the liver, gall bladder, and pancreas that aid in the process. The program then looks at the synthesis of vitamins by bacteria in the large intes ne and then goes on to explore the complex structures in the kidney that allow them to filter wastes out of the blood while returning water and nutrients ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • The functional and structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specializ ...
... • The functional and structural unit of the nervous system • Specialized to conduct information from one part of the body to another • There are many, many different types of neurons but most have certain structural and functional characteristics in common: - Cell body (soma) - One or more specializ ...
Neuroscience and Behavior Notes 2-2 (obj 7-10)
... Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Sympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
... Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Sympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Division of the ANS that calms the body, conserving its ...
SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
... each tone “mapped” to a different area of the cortex some fibers cross over in brainstem • unlike other senses, each cortical lobe receives input from both ears ...
... each tone “mapped” to a different area of the cortex some fibers cross over in brainstem • unlike other senses, each cortical lobe receives input from both ears ...
unit 5: the nervous and endocrine systems
... THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.It is a collection of endocrine glands. They are called endocrine because they secrete internally. The substances they produce (hormones) are secreted directly into the bloodstream. Hormones travel through the bloodstream to the cells. Although all hormones reach all tissues, ea ...
... THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.It is a collection of endocrine glands. They are called endocrine because they secrete internally. The substances they produce (hormones) are secreted directly into the bloodstream. Hormones travel through the bloodstream to the cells. Although all hormones reach all tissues, ea ...
chapter 15 sensory, motor, and integrative systems
... d. head and neck 20. The final common path to the skeletal muscles from both the pyramidal and extrapyramidal pathways is the a. lower motor neurons b. upper motor neurons c. association neurons d. decussation neurons ...
... d. head and neck 20. The final common path to the skeletal muscles from both the pyramidal and extrapyramidal pathways is the a. lower motor neurons b. upper motor neurons c. association neurons d. decussation neurons ...
The Nervous System
... plexuses. It circulates through the brain ventricles and returns to the blood, constantly draining as new CSF forms, keeping the overall volume and pressure relatively constant ...
... plexuses. It circulates through the brain ventricles and returns to the blood, constantly draining as new CSF forms, keeping the overall volume and pressure relatively constant ...
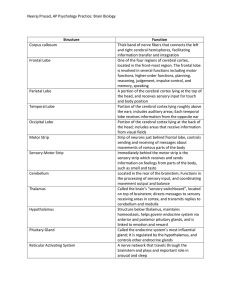
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
... Structure below thalamus, maintains homeostasis, helps govern endocrine system via anterior and posterior pituitary glands, and is linked to emotion and reward Called the endocrine system’s most influential gland; It is regulated by the hypothalamus, and controls other endrocrine glands A nerve netw ...
... Structure below thalamus, maintains homeostasis, helps govern endocrine system via anterior and posterior pituitary glands, and is linked to emotion and reward Called the endocrine system’s most influential gland; It is regulated by the hypothalamus, and controls other endrocrine glands A nerve netw ...
MBBC Junior Neuroscience E-Book v1
... from the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. The brainstem controls, among other things, respiration and the regulation of heart rhythms. CATECHOLAMINES - The neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine, which are active in both the brain and the peripheral sympathetic nervous system. ...
... from the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. The brainstem controls, among other things, respiration and the regulation of heart rhythms. CATECHOLAMINES - The neurotransmitters dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine, which are active in both the brain and the peripheral sympathetic nervous system. ...
The Nervous System - Ridgewood High School
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
... Monitors changes/events occurring in and outside the body. Such changes are known as stimuli and the cells that monitor them are receptors. ...
Dopamine axons of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons and
... Although mutated genes, protein aggregates, environmental toxins and other factors associated with PD are widely distributed in the nervous system and affect many classes of neurons, dopamine (DA) neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) show exceptional and selective vulnerability. One f ...
... Although mutated genes, protein aggregates, environmental toxins and other factors associated with PD are widely distributed in the nervous system and affect many classes of neurons, dopamine (DA) neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) show exceptional and selective vulnerability. One f ...
A neuron receives input from other neurons
... The best mapped (and largest) system in the human brain is the visual system, where the first 10 or 11 processing stages have been identified. ...
... The best mapped (and largest) system in the human brain is the visual system, where the first 10 or 11 processing stages have been identified. ...
Nervous System
... opportunity for scientists to study the frontal lobe and limbic system connection. Limbic system is the emotional region and frontal keeps the limbic region in control. ...
... opportunity for scientists to study the frontal lobe and limbic system connection. Limbic system is the emotional region and frontal keeps the limbic region in control. ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Chapter 12 - FacultyWeb
... Astrocytes and satellite cells/forming scar tissue and engulfing cellular debris Ependymal cells and Schwann cells/forming cerebrospinal fluid and forming myelin sheath Schwann cells and satellite cells/forming myelin sheath and regulating environment around neurons Microglia and ependymal cells/reg ...
... Astrocytes and satellite cells/forming scar tissue and engulfing cellular debris Ependymal cells and Schwann cells/forming cerebrospinal fluid and forming myelin sheath Schwann cells and satellite cells/forming myelin sheath and regulating environment around neurons Microglia and ependymal cells/reg ...
3 Types of nervous systems
... • They do not have a central nervous system. They just have a network of interconnected neurons running along the walls of their bodies. Network of neurons ...
... • They do not have a central nervous system. They just have a network of interconnected neurons running along the walls of their bodies. Network of neurons ...