The Effect of Slow Electrical Stimuli to Achieve Learning in Cultured
... Learning, or more generally, plasticity may be studied using cultured networks of rat cortical neurons on multi electrode arrays. Several protocols have been proposed to affect connectivity in such networks. One of these protocols, proposed by Shahaf and Marom, aimed to train the input-output relati ...
... Learning, or more generally, plasticity may be studied using cultured networks of rat cortical neurons on multi electrode arrays. Several protocols have been proposed to affect connectivity in such networks. One of these protocols, proposed by Shahaf and Marom, aimed to train the input-output relati ...
Information Processing in the Rostral Solitary Nucleus: Modulation
... result from a low concentration of an effective stimulus or a high concentration of a less effective stimulus. If the brain encodes taste using a labeled line code, this ambiguity results in taste quality being confounded with concentration- for example, a high concentration of salt might activate a ...
... result from a low concentration of an effective stimulus or a high concentration of a less effective stimulus. If the brain encodes taste using a labeled line code, this ambiguity results in taste quality being confounded with concentration- for example, a high concentration of salt might activate a ...
Transcripts/2_18 2
... input. So there is a representation of the auditory, somatosensory, vestibular, all within those granule cells. Granule cells send out axons that synapse onto the purkinje cells. f. Coursing up through this pathway and climbing up to the purkinje cell is the input from the inferior olive. That makes ...
... input. So there is a representation of the auditory, somatosensory, vestibular, all within those granule cells. Granule cells send out axons that synapse onto the purkinje cells. f. Coursing up through this pathway and climbing up to the purkinje cell is the input from the inferior olive. That makes ...
Stereoscopic Mechanisms in Monkey Visual Cortex: Binocular
... The brain utilizes the signalsfrom the 2 eyes to recover the relative depth of objects.Wheatstone (1838) first demonstrated that a difference, or disparity, in the relative horizontal position of the object’s imagesin the 2 eyescan generatean impression of depth and solidity. Julesz(1960, 1971)later ...
... The brain utilizes the signalsfrom the 2 eyes to recover the relative depth of objects.Wheatstone (1838) first demonstrated that a difference, or disparity, in the relative horizontal position of the object’s imagesin the 2 eyescan generatean impression of depth and solidity. Julesz(1960, 1971)later ...
Projections From the Ventral Cochlear Nucleus to the Dorsal
... frequencies. In contrast, radiate neurons were infrequent, found scattered throughout the ventral cochlear nucleus, and had long dendrites oriented perpendicular to the isofrequency contours. This dendritic orientation suggests that radiate neurons are sensitive to a broad range of frequencies. Thes ...
... frequencies. In contrast, radiate neurons were infrequent, found scattered throughout the ventral cochlear nucleus, and had long dendrites oriented perpendicular to the isofrequency contours. This dendritic orientation suggests that radiate neurons are sensitive to a broad range of frequencies. Thes ...
Olfactory Learning in Drosophila: Learning from Models
... express receptors in the antennae. Olfactory receptor neurons project via the antennal nerve (green) to the antennal lobes where they form synapses with projection neurons in anatomical clusters called glomeruli (red sphere-like structures). Projection neurons (yellow fibers) carry odor information ...
... express receptors in the antennae. Olfactory receptor neurons project via the antennal nerve (green) to the antennal lobes where they form synapses with projection neurons in anatomical clusters called glomeruli (red sphere-like structures). Projection neurons (yellow fibers) carry odor information ...
On the Biological Plausibility of Grandmother Cells
... columns code for line segments that vary by approximately 10° in rotation). These columns are in turn organized into hypercolumns, such that all simple cells within a given hypercolumn code for lines at the same retinal location (albeit varying in orientation preference), with adjacent hypercolumns ...
... columns code for line segments that vary by approximately 10° in rotation). These columns are in turn organized into hypercolumns, such that all simple cells within a given hypercolumn code for lines at the same retinal location (albeit varying in orientation preference), with adjacent hypercolumns ...
Gating of Sensory Input by Spontaneous Cortical Activity
... (Luczak et al., 2009). Briefly, head post was implanted on the skull of each of four male Sprague Dawley rats (300 –500 g) under ketamine–xylazine anesthesia, and a well drilled above the auditory cortex and covered with wax and dental acrylic. After recovery, each animal was trained for 6 – 8 d to ...
... (Luczak et al., 2009). Briefly, head post was implanted on the skull of each of four male Sprague Dawley rats (300 –500 g) under ketamine–xylazine anesthesia, and a well drilled above the auditory cortex and covered with wax and dental acrylic. After recovery, each animal was trained for 6 – 8 d to ...
(addl. 3)
... connectivity between neurons is not necessary for an accurate emulation. Instead, they assume communication is necessary only when a neuron fires, generating an action potential. The emulated neurons are networked together, generally with a topology of many nested networks, as on the Internet, to al ...
... connectivity between neurons is not necessary for an accurate emulation. Instead, they assume communication is necessary only when a neuron fires, generating an action potential. The emulated neurons are networked together, generally with a topology of many nested networks, as on the Internet, to al ...
Full version (PDF file)
... the neocortex of rodents and primates, including humans. The possible neuroprotective role of calretinin and the presumed “resistance” of calretinin-expressing interneurons to various pathological processes are also discussed. Key words Calcium-binding ...
... the neocortex of rodents and primates, including humans. The possible neuroprotective role of calretinin and the presumed “resistance” of calretinin-expressing interneurons to various pathological processes are also discussed. Key words Calcium-binding ...
Challenges for Brain Emulation
... connectivity between neurons is not necessary for an accurate emulation. Instead, they assume communication is necessary only when a neuron fires, generating an action potential. The emulated neurons are networked together, generally with a topology of many nested networks, as on the Internet, to al ...
... connectivity between neurons is not necessary for an accurate emulation. Instead, they assume communication is necessary only when a neuron fires, generating an action potential. The emulated neurons are networked together, generally with a topology of many nested networks, as on the Internet, to al ...
Continuous attractor network models of grid cell firing based on
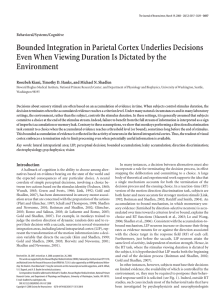
... A, In single bump models grid firing of excitatory cells can be generated by synaptic profiles that produce either surround excitation or surround inhibition. The surround connectivity is strongest for connections to neurons at a distance of about one-half the width of the sheet. Each neuron makes d ...
... A, In single bump models grid firing of excitatory cells can be generated by synaptic profiles that produce either surround excitation or surround inhibition. The surround connectivity is strongest for connections to neurons at a distance of about one-half the width of the sheet. Each neuron makes d ...
TOPIC: progesterone exert neuroprotective and myelinating effects
... Progesterone (PROG) is synthesized in the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Its direct precursor pregnenolone is either derived from the circulation or from local de novo synthesis as cytochrome P450scc, which converts cholesterol to pregnenolone, is expressed in the nervous system. Pregneno ...
... Progesterone (PROG) is synthesized in the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. Its direct precursor pregnenolone is either derived from the circulation or from local de novo synthesis as cytochrome P450scc, which converts cholesterol to pregnenolone, is expressed in the nervous system. Pregneno ...
Bounded Integration in Parietal Cortex Underlies
... at each point in the image as a function of time. These local motion energies were summated across space to calculate the motion energy over the stimulus as a function of time. Finally, motion energies for opponent directions were subtracted from each other to measure the net motion energy in one di ...
... at each point in the image as a function of time. These local motion energies were summated across space to calculate the motion energy over the stimulus as a function of time. Finally, motion energies for opponent directions were subtracted from each other to measure the net motion energy in one di ...
Goal-direction and top-down control
... decision tree: at each state one can choose between one of many different responses, each of which lead to a new state (with its own stimuli and response alternatives, figure 2). And so, behaviour can be modelled as starting at the topmost ‘node’ in the tree, choosing a response ‘branch’, entering a ...
... decision tree: at each state one can choose between one of many different responses, each of which lead to a new state (with its own stimuli and response alternatives, figure 2). And so, behaviour can be modelled as starting at the topmost ‘node’ in the tree, choosing a response ‘branch’, entering a ...
RAAS Basic physiology and Pathophysiolgy
... Physiologic levels of ACTH regulate the minute-to-minute fluctuations of plasma aldosterone. Potassium depletion decreased and potassium repletion ...
... Physiologic levels of ACTH regulate the minute-to-minute fluctuations of plasma aldosterone. Potassium depletion decreased and potassium repletion ...
Spinal Cord - Sydney University Medical Society
... The different types of sensory information are Tactile (i.e. touch / vibration), Proprioception (i.e. position) and Pain / Temperature The sensory receptors / fibres associated with each sensory modality are: o Proprioception Muscle Spindles (also known as Neuromuscular Spindles) – these are locat ...
... The different types of sensory information are Tactile (i.e. touch / vibration), Proprioception (i.e. position) and Pain / Temperature The sensory receptors / fibres associated with each sensory modality are: o Proprioception Muscle Spindles (also known as Neuromuscular Spindles) – these are locat ...
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... II. The white matter tracts are highways for nerve impulse conduction to & from the brain. A. Sensory & motor tracts: Sensory tracts are: spinothalamic tract. Posterior (dorsal) column tract. Motor tracts are the pyramidal tract. The extra-pyramidal tract. The axons of various nerves & CNS tract ...
... II. The white matter tracts are highways for nerve impulse conduction to & from the brain. A. Sensory & motor tracts: Sensory tracts are: spinothalamic tract. Posterior (dorsal) column tract. Motor tracts are the pyramidal tract. The extra-pyramidal tract. The axons of various nerves & CNS tract ...
The Spinal Nerve
... 13-8 The Brain Can Alter Spinal Reflexes Integration and Control of Spinal Reflexes Reflex behaviors are automatic But processing centers in brain can facilitate or inhibit reflex motor patterns based in spinal cord Voluntary Movements and Reflex Motor Patterns Higher centers of brain incorporate l ...
... 13-8 The Brain Can Alter Spinal Reflexes Integration and Control of Spinal Reflexes Reflex behaviors are automatic But processing centers in brain can facilitate or inhibit reflex motor patterns based in spinal cord Voluntary Movements and Reflex Motor Patterns Higher centers of brain incorporate l ...
Current advances and pressing problems in studies of stopping
... already been canceled. Neurons that initiate or inhibit eye movements in FEF and SC modulate early enough to control movements directly (Figure 2A). These neurons project to brainstem structures that house ocular motor neurons, enabling them to influence response production directly [26,27]. After t ...
... already been canceled. Neurons that initiate or inhibit eye movements in FEF and SC modulate early enough to control movements directly (Figure 2A). These neurons project to brainstem structures that house ocular motor neurons, enabling them to influence response production directly [26,27]. After t ...
Human medial frontal cortex mediates unconscious inhibition of
... (Jaskowski, in press; Jaskowski and Przekoracka-Krawczyk, 2005; Lleras and Enns, 2006). While this debate is also tangential to our main purpose of simply studying whether SEF and SMA are associated with automatic inhibition (however it is triggered), the debate’s resolution will have interesting im ...
... (Jaskowski, in press; Jaskowski and Przekoracka-Krawczyk, 2005; Lleras and Enns, 2006). While this debate is also tangential to our main purpose of simply studying whether SEF and SMA are associated with automatic inhibition (however it is triggered), the debate’s resolution will have interesting im ...
physiological reviews
... also, but it now seems (45, 152, 219, 218) that endolymph contains no more protein than cerebrospinal fluid, and that perilymph may contain twice as much. The perilymphatic space communicates with the cerebrospinal space by the cochlear aqueduct and by perineural and perivascular spaces in the inter ...
... also, but it now seems (45, 152, 219, 218) that endolymph contains no more protein than cerebrospinal fluid, and that perilymph may contain twice as much. The perilymphatic space communicates with the cerebrospinal space by the cochlear aqueduct and by perineural and perivascular spaces in the inter ...
Neuronal circuitries involved in thermoregulation
... Cooling the PO increased the BAT temperature (Banet et al., 1978; Imai-Matsumura and Nakayama, 1987), which is the result of the inhibition of warm-sensitive neurons (Chen et al., 1998). The efferent signals from the PO must pass through the lateral part of the hypothalamus, since bilateral knife cu ...
... Cooling the PO increased the BAT temperature (Banet et al., 1978; Imai-Matsumura and Nakayama, 1987), which is the result of the inhibition of warm-sensitive neurons (Chen et al., 1998). The efferent signals from the PO must pass through the lateral part of the hypothalamus, since bilateral knife cu ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.