Looking for the roots of cortical sensory computation in three
... computational properties of turtle primary visual cortex are more similar in essence to those of high-order cortices (e.g. parahippocampal, retrosplenial or infero-temporal), and that the true response properties of DCx neurons have yet to be discovered. Until recently, functional experiments in PCx ...
... computational properties of turtle primary visual cortex are more similar in essence to those of high-order cortices (e.g. parahippocampal, retrosplenial or infero-temporal), and that the true response properties of DCx neurons have yet to be discovered. Until recently, functional experiments in PCx ...
Tasks for inhibitory interneurons in intact brain circuits
... connections (Buzsaki and Wang, 2012). Self-organized circuits with delicate excitatory-inhibitory balance appear to be maximally sensitive to external perturbations, yet they are capable of absorbing large external perturbations without undergoing functional breakdown. However, alterations of these ...
... connections (Buzsaki and Wang, 2012). Self-organized circuits with delicate excitatory-inhibitory balance appear to be maximally sensitive to external perturbations, yet they are capable of absorbing large external perturbations without undergoing functional breakdown. However, alterations of these ...
Hypothalamus and Limbic System
... results from lesion studies may have been due to damage of fibers of passage rather than due to loss of cell bodies in distinct parts of the hypothalamus. • In particular, hypothalamus lesions may damage fibers of: – the trigeminal system which affect sensory processing important for feeding – Dopam ...
... results from lesion studies may have been due to damage of fibers of passage rather than due to loss of cell bodies in distinct parts of the hypothalamus. • In particular, hypothalamus lesions may damage fibers of: – the trigeminal system which affect sensory processing important for feeding – Dopam ...
Computational Constraints that may have Favoured the Lamination
... receives Cff feedforward connections from a further array of N × N “thalamic” units, and Crc recurrent connections from other units in the patch. Both sets of connections are assigned to each receiving unit at random, with a Gaussian probability in register with the unit itself, and of width Sff and ...
... receives Cff feedforward connections from a further array of N × N “thalamic” units, and Crc recurrent connections from other units in the patch. Both sets of connections are assigned to each receiving unit at random, with a Gaussian probability in register with the unit itself, and of width Sff and ...
ANALYSIS OF THE ACTIVITY OF THE CHAINS
... which in weak responses fired upon arrival of late internuncial volleys, in response to strong shocks fired when stimulated either by the impulses of the initial (f) volley or by the early internuncial volleys, and they could not fire again for the remainder of the response. The late internuncial vo ...
... which in weak responses fired upon arrival of late internuncial volleys, in response to strong shocks fired when stimulated either by the impulses of the initial (f) volley or by the early internuncial volleys, and they could not fire again for the remainder of the response. The late internuncial vo ...
Erection - abuad lms
... A penis which is partly, but not fully, erect is sometimes known as a semi-erection (clinically: partial tumescence); a penis which is not erect is typically referred to as being flaccid, or soft. Physiolgy An erection occurs when two tubular structures, called the corpora cavernosa, that run the l ...
... A penis which is partly, but not fully, erect is sometimes known as a semi-erection (clinically: partial tumescence); a penis which is not erect is typically referred to as being flaccid, or soft. Physiolgy An erection occurs when two tubular structures, called the corpora cavernosa, that run the l ...
Activity Regulates the Synaptic Localization of the NMDA Receptor
... antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) and assessed the patterns of NR1 and synaptophysin immunostaining (Figure 3). Chronic treatment with TTX had a similar effect to that of APV, causing a 320% increase in NR1 cluster number and a shift toward more synaptic clusters. CNQX caused a ...
... antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) and assessed the patterns of NR1 and synaptophysin immunostaining (Figure 3). Chronic treatment with TTX had a similar effect to that of APV, causing a 320% increase in NR1 cluster number and a shift toward more synaptic clusters. CNQX caused a ...
Copy of the full paper
... type of model is necessary to emulate the dynamics of individual neurons within a network. Conductance-based models reduced to 2 dimensions are also very popular, as they can be entirely characterized using phase plane analysis. The well-known FitzHugh–Nagumo (FN) (FitzHugh, 1961) and Morris–Lecar m ...
... type of model is necessary to emulate the dynamics of individual neurons within a network. Conductance-based models reduced to 2 dimensions are also very popular, as they can be entirely characterized using phase plane analysis. The well-known FitzHugh–Nagumo (FN) (FitzHugh, 1961) and Morris–Lecar m ...
PDF - Center for Neural Science
... three compartments (soma, proximate, and distal dendrites) and a number of voltage-gated ion channels. Right: spatiotemporal network activity (top) and membrane potential of a single cell (bottom) in a simulation of the delayed oculomotor experiment. Middle: a network simulation of the delayed oculo ...
... three compartments (soma, proximate, and distal dendrites) and a number of voltage-gated ion channels. Right: spatiotemporal network activity (top) and membrane potential of a single cell (bottom) in a simulation of the delayed oculomotor experiment. Middle: a network simulation of the delayed oculo ...
New perspectives on the evolution of protochordate sensory and
... Figure 1. A comparison of structures and cell types in the anterior CNS of amphioxus with that of ascidian larvae. (a) The anterior nerve cord of a young amphioxus larva in dorsal view, based on serial EM reconstruction data (Lacalli et al. 1994; Lacalli 1996; Lacalli & Kelly 1999, 2000). Shows the ...
... Figure 1. A comparison of structures and cell types in the anterior CNS of amphioxus with that of ascidian larvae. (a) The anterior nerve cord of a young amphioxus larva in dorsal view, based on serial EM reconstruction data (Lacalli et al. 1994; Lacalli 1996; Lacalli & Kelly 1999, 2000). Shows the ...
Neuronal-Derived Nitric Oxide and Somatodendritically Released
... The classical model of neurovascular coupling (NVC) implies that activity-dependent axonal glutamate release at synapses evokes the production and release of vasoactive signals from both neurons and astrocytes, which dilate arterioles, increasing in turn cerebral blood flow (CBF) to areas with incre ...
... The classical model of neurovascular coupling (NVC) implies that activity-dependent axonal glutamate release at synapses evokes the production and release of vasoactive signals from both neurons and astrocytes, which dilate arterioles, increasing in turn cerebral blood flow (CBF) to areas with incre ...
Effects of the Abused Inhalant Toluene on the
... Electrophysiological studies reveal that most midbrain DA neurons display low tonic rates of firing (1–5 Hz) interspersed with bursts of firing (20–80 Hz) that are associated with novel or rewarding stimuli [31]. The mechanisms that underlie the transition between tonic and burst modes of VTA DA neu ...
... Electrophysiological studies reveal that most midbrain DA neurons display low tonic rates of firing (1–5 Hz) interspersed with bursts of firing (20–80 Hz) that are associated with novel or rewarding stimuli [31]. The mechanisms that underlie the transition between tonic and burst modes of VTA DA neu ...
The Nervous System
... 1 Resting membrane is polarized. In the resting state, the external face of the membrane is slightly positive; its internal face is slightly negative. The chief extracellular ion is sodium (Na+), whereas the chief intracellular ion is potassium (K+). The membrane is relatively impermeable to both io ...
... 1 Resting membrane is polarized. In the resting state, the external face of the membrane is slightly positive; its internal face is slightly negative. The chief extracellular ion is sodium (Na+), whereas the chief intracellular ion is potassium (K+). The membrane is relatively impermeable to both io ...
Neuron Production, Neuron Number, and Structure Size Are
... Insight Color video camera and SPOT Advanced imaging software (Diagnostic Instruments, Version 2.4.5 for Windows): (a) the hyperstriatum accessorium (HA), (b) the hyperstriatum ventrale and hyperstriatum dorsale together (HV/HD), (c) the neostriatum and ectostriatum together (Neo/Ecto), and (d) the ...
... Insight Color video camera and SPOT Advanced imaging software (Diagnostic Instruments, Version 2.4.5 for Windows): (a) the hyperstriatum accessorium (HA), (b) the hyperstriatum ventrale and hyperstriatum dorsale together (HV/HD), (c) the neostriatum and ectostriatum together (Neo/Ecto), and (d) the ...
Unit 7 Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
CHAPTER 13- The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... B) have posterior sensory roots. C) have anterior root ganglia containing cell bodies of motor neurons. D) have posterior motor roots. E) exit the vertebral column anteriorly between the intervertebral discs and the vertebral bodies. 11) Spinal nerves are A) identified based on the region and level ...
... B) have posterior sensory roots. C) have anterior root ganglia containing cell bodies of motor neurons. D) have posterior motor roots. E) exit the vertebral column anteriorly between the intervertebral discs and the vertebral bodies. 11) Spinal nerves are A) identified based on the region and level ...
Lin J, 2013 - Tsien lab Website - University of California San Diego
... We used ReaChR expressed in the vibrissa motor cortex to drive spiking and vibrissa motion in awake mice when excited with red light through intact skull. Precise vibrissa movements were evoked by expressing ReaChR in the facial motor nucleus in the brainstem and illumination with red light through ...
... We used ReaChR expressed in the vibrissa motor cortex to drive spiking and vibrissa motion in awake mice when excited with red light through intact skull. Precise vibrissa movements were evoked by expressing ReaChR in the facial motor nucleus in the brainstem and illumination with red light through ...
Comparative analysis of the baseline spike activity of
... were determined, along with the mean neuron spike frequency and the coefficient of variation of interspike intervals. The results showed that the most significant changes in neuron activity in fastigial nucleus cells were formed during the first ten days of vibration. On day 15, there was a tendency ...
... were determined, along with the mean neuron spike frequency and the coefficient of variation of interspike intervals. The results showed that the most significant changes in neuron activity in fastigial nucleus cells were formed during the first ten days of vibration. On day 15, there was a tendency ...
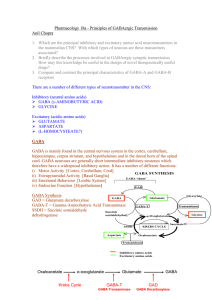
Pharmacology 18a – Priciples of GABAergic Transmission
... GABA Storage and Release GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions T ...
... GABA Storage and Release GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions T ...
Antagonists and agonists at the glycine site of the NMDA receptor for
... studies GV196771A reduced the hyperalgesic response in CCI-treated rats but did not induce a change in normal rats. In comparison, the open-channel blocker MK-801 is very unselective because it also interferes with the activity (firing rates) of non-nociceptive neurons in normal animals. The antihyp ...
... studies GV196771A reduced the hyperalgesic response in CCI-treated rats but did not induce a change in normal rats. In comparison, the open-channel blocker MK-801 is very unselective because it also interferes with the activity (firing rates) of non-nociceptive neurons in normal animals. The antihyp ...
A Neural Circuit Basis for Spatial Working Memory
... location (Sawaguchi and Yamane 1999). In all cases, discharge of the majority of dorsolateral prefrontal neurons was found to encode the location of the remembered stimulus, although a minority of neurons did represent the actual motor response. A signal-detection theory analysis of prefrontal corti ...
... location (Sawaguchi and Yamane 1999). In all cases, discharge of the majority of dorsolateral prefrontal neurons was found to encode the location of the remembered stimulus, although a minority of neurons did represent the actual motor response. A signal-detection theory analysis of prefrontal corti ...
Distribution of phosphorylated cyclic AMP response element binding
... The intensive staining of p-CREB-1 in the GCL suggested positive phosphorylation of CREB-1 in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). The retinal neurons were labeled with microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP-2) or THY1.1, the specific cellular makers for neurons and retinal ganglion cells, respectively. As ...
... The intensive staining of p-CREB-1 in the GCL suggested positive phosphorylation of CREB-1 in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). The retinal neurons were labeled with microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP-2) or THY1.1, the specific cellular makers for neurons and retinal ganglion cells, respectively. As ...
Dopaminergic Transmission and Wake
... midline thalamus and the sleep-active VLPO neurons (Lu et al. 2006). Recent in vitro electrophysiological recordings from these neurons showed that they have similar intrinsic membrane properties as VTA dopamine neurons, including broad action potentials and hyperpolarization-activated cation curren ...
... midline thalamus and the sleep-active VLPO neurons (Lu et al. 2006). Recent in vitro electrophysiological recordings from these neurons showed that they have similar intrinsic membrane properties as VTA dopamine neurons, including broad action potentials and hyperpolarization-activated cation curren ...
Dual inhibition of the dactyl opener muscle in lobster
... Values are means ± s.d. The membrane potential at which the IJP reversed polarity was measured intracellularly as temperature was increased from 2 to 22°C. In five of the experiments, CI and OI were monitored in the same muscle fiber. ...
... Values are means ± s.d. The membrane potential at which the IJP reversed polarity was measured intracellularly as temperature was increased from 2 to 22°C. In five of the experiments, CI and OI were monitored in the same muscle fiber. ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.