The spinothalamic tract: An examination of the cells of origin of the
... cord lesion served to identify the lumbar and cervical cells of origin of the total spinothalamic tract (VSW and DSTT). WGA-HRP was used in three experiments (Controls 1, 2, and 31, whereas HRP-Sigma VI was used in two experiments (Controls 4 and 5). The distribution of label was examined in the cer ...
... cord lesion served to identify the lumbar and cervical cells of origin of the total spinothalamic tract (VSW and DSTT). WGA-HRP was used in three experiments (Controls 1, 2, and 31, whereas HRP-Sigma VI was used in two experiments (Controls 4 and 5). The distribution of label was examined in the cer ...
Massive Loss of Mid- and Hindbrain Neurons during Embryonic
... animals, was intriguing because axons from this nucleus comprise the V cranial nerve, which controls the muscles required for mastication and suckling. Because this nucleus is required at birth, these cells undergo synaptogenesis and terminal differentiation during embryonic life. To determine wheth ...
... animals, was intriguing because axons from this nucleus comprise the V cranial nerve, which controls the muscles required for mastication and suckling. Because this nucleus is required at birth, these cells undergo synaptogenesis and terminal differentiation during embryonic life. To determine wheth ...
Chapter 13
... 2. Sensory information from receptors travels up the spinal cord to the brain along two main routes on each side of the cord: the spinothalamic tracts and the posterior column tract. 3. Motor information travels from the brain down the spinal cord to effectors (muscles and glands) along two types of ...
... 2. Sensory information from receptors travels up the spinal cord to the brain along two main routes on each side of the cord: the spinothalamic tracts and the posterior column tract. 3. Motor information travels from the brain down the spinal cord to effectors (muscles and glands) along two types of ...
PRIMARY VISUAL CORTEX NEURONS THAT CONTRIBUTE TO
... example), the neurons did not receive any direct CRF stimulation, although the global directional cues were clearly presented by the bar ends outside the CRF. For this pattern of masking, the responses of two neurons were not significant different from their spontaneous activities (1-ANOVA, P⬎0.05; ...
... example), the neurons did not receive any direct CRF stimulation, although the global directional cues were clearly presented by the bar ends outside the CRF. For this pattern of masking, the responses of two neurons were not significant different from their spontaneous activities (1-ANOVA, P⬎0.05; ...
Neuronal Control of Mucus Secretion by Leeches: Toward a General
... motility induced by the 5-HT without altering its secretory effects. This implies, of course, that the serotonin is activating either other neurons or different receptor sites which in turn control the gut musculature. Thus, the mammalian gut is rich in serotonin which induces its epithelium to secr ...
... motility induced by the 5-HT without altering its secretory effects. This implies, of course, that the serotonin is activating either other neurons or different receptor sites which in turn control the gut musculature. Thus, the mammalian gut is rich in serotonin which induces its epithelium to secr ...
Chronic Pain
... • Multiple areas of the brain are involved. There is no one location where perception occurs, although major defining components of pain are attributed to processes that take place in specific areas of the brain. • For example, the sensory-discriminative component is the result of activity in the so ...
... • Multiple areas of the brain are involved. There is no one location where perception occurs, although major defining components of pain are attributed to processes that take place in specific areas of the brain. • For example, the sensory-discriminative component is the result of activity in the so ...
Fibroblast growth factor modulates HIV coreceptor - SGF-5000
... 1997; Wirth et al., 1996; Yang and Cui, 1998). While the mechanism(s) by which FGF is neuroprotective have not been fully elucidated, it has been demonstrated that FGF binds to a tyrosine kinase receptor and thus may activate a number of intracellular signaling pathways. FGF has also been shown to b ...
... 1997; Wirth et al., 1996; Yang and Cui, 1998). While the mechanism(s) by which FGF is neuroprotective have not been fully elucidated, it has been demonstrated that FGF binds to a tyrosine kinase receptor and thus may activate a number of intracellular signaling pathways. FGF has also been shown to b ...
Expression of Cux-1 and Cux-2 in the Subventricular Zone and
... a wide range of transcription activities, it functions both as a transcriptional repressor and as an activator, and its transcriptional activity is regulated by posttranslational mechanisms involving phosphorylation, acetylation, and proteolysis (for review see Nepveu, 2001). Notably, several report ...
... a wide range of transcription activities, it functions both as a transcriptional repressor and as an activator, and its transcriptional activity is regulated by posttranslational mechanisms involving phosphorylation, acetylation, and proteolysis (for review see Nepveu, 2001). Notably, several report ...
Immunohistochemical description of the endogenous cannabinoid
... from the inferior olive or GABAergic interneuron. Additionally, we describe the presence of CB2 receptors in fibers related to Purkinje somata (Pinceau formations) and dendrites (parallel fibers), suggesting a potential role of this receptor in the retrograde cannabinoid signaling. A remarkable finding ...
... from the inferior olive or GABAergic interneuron. Additionally, we describe the presence of CB2 receptors in fibers related to Purkinje somata (Pinceau formations) and dendrites (parallel fibers), suggesting a potential role of this receptor in the retrograde cannabinoid signaling. A remarkable finding ...
Estradiol, Substance P, and the PI3K-Akt
... injection of carrageenan leads to C-fiber, A-fiber, and central sensitization, as well as increased sensitivity to thermal and mechanical stimuli (Lisi et al., 2015). Glutamate is the primary signaling molecule in this system, but there are many others involved. Substance P is a tachykinin neuropept ...
... injection of carrageenan leads to C-fiber, A-fiber, and central sensitization, as well as increased sensitivity to thermal and mechanical stimuli (Lisi et al., 2015). Glutamate is the primary signaling molecule in this system, but there are many others involved. Substance P is a tachykinin neuropept ...
theta oscillation in the hippocampus
... synaptic potentials that entrain the discharge of neuronal populations within the D100–200 ms range. The cellular-synaptic generation of theta activity in the hippocampus was investigated by intracellular recordings from the somata and dendrites of CA1 pyramidal cells in urethaneanesthetized rats. T ...
... synaptic potentials that entrain the discharge of neuronal populations within the D100–200 ms range. The cellular-synaptic generation of theta activity in the hippocampus was investigated by intracellular recordings from the somata and dendrites of CA1 pyramidal cells in urethaneanesthetized rats. T ...
The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons 15
... A third component of visceral innervation, the enteric nervous system, also innervates smooth muscle and glands, specifically those within the digestive tract. The enteric nervous system regulates the activity of the digestive tract and functions completely independently of the CNS. Autonomic neuron ...
... A third component of visceral innervation, the enteric nervous system, also innervates smooth muscle and glands, specifically those within the digestive tract. The enteric nervous system regulates the activity of the digestive tract and functions completely independently of the CNS. Autonomic neuron ...
Xavier Nadal i Roura PARTICIPATION OF THE ENDOGENOUS OPIOID AND CANNABINOID SYSTEMS
... significant tissue injury. By contrast, inflammatory pain is the consequence of tissue damage due to the action of trauma events (surgery), physical (sun, heat) or chemical (acids, alkalis) agents. The injury that follows triggers mechanisms of repair that produces pain. It should be remembered tha ...
... significant tissue injury. By contrast, inflammatory pain is the consequence of tissue damage due to the action of trauma events (surgery), physical (sun, heat) or chemical (acids, alkalis) agents. The injury that follows triggers mechanisms of repair that produces pain. It should be remembered tha ...
Optophysiological analysis of associational circuits in the olfactory
... areas associated with the amygdala (Luskin and Price, 1983b; Haberly, 1998). Sensory information from the OB reaches the primary olfactory cortical areas through the lateral olfactory tract (LOT), made up of mitral/tufted cell axons. In addition to direct sensory input, olfactory cortical neurons al ...
... areas associated with the amygdala (Luskin and Price, 1983b; Haberly, 1998). Sensory information from the OB reaches the primary olfactory cortical areas through the lateral olfactory tract (LOT), made up of mitral/tufted cell axons. In addition to direct sensory input, olfactory cortical neurons al ...
A Curious Commentary on a Book on Mirror Neurons and Other
... 2011) or by comparing functional motor deficits with functional action understanding deficits (Hickok et al., 2008) (and see many other examples discussed in the book ranging from apraxia to ALS to cerebral palsy), one fails to find the effects one expects given how fundamental the system is propos ...
... 2011) or by comparing functional motor deficits with functional action understanding deficits (Hickok et al., 2008) (and see many other examples discussed in the book ranging from apraxia to ALS to cerebral palsy), one fails to find the effects one expects given how fundamental the system is propos ...
Hybrid Scheme for Modeling Local Field Potentials from Point
... models and the biophysical principles underlying LFP generation captured by multicompartment neuron models with anatomically reconstructed morphologies. The scheme allows for arbitrary numbers of LFP-contributing populations, and directly incorporates spatial cancellation effects. Furthermore, the s ...
... models and the biophysical principles underlying LFP generation captured by multicompartment neuron models with anatomically reconstructed morphologies. The scheme allows for arbitrary numbers of LFP-contributing populations, and directly incorporates spatial cancellation effects. Furthermore, the s ...
A Self-Organizing Neural Network for Contour Integration through Synchronized Firing
... only if focused (i.e. patchy) lateral connections exist linking collinear neurons with similar orientation preferences. If peripheral areas and the upper visual field do not receive dense enough visual input for such connections to form during development, the connections become diffuse, resulting i ...
... only if focused (i.e. patchy) lateral connections exist linking collinear neurons with similar orientation preferences. If peripheral areas and the upper visual field do not receive dense enough visual input for such connections to form during development, the connections become diffuse, resulting i ...
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST
... Why the difference? The intracellular compartment is separated from the extracellular compartment by cell membranes. This barrier is selectively permeable, and contains active sodiumpotassium pumps which maintain the concentration differences. Plasma and interstitial fluid compartments are separate ...
... Why the difference? The intracellular compartment is separated from the extracellular compartment by cell membranes. This barrier is selectively permeable, and contains active sodiumpotassium pumps which maintain the concentration differences. Plasma and interstitial fluid compartments are separate ...
Print
... At each penetration site, responses from 675 frequency-level stimulus conditions determine the frequency response area (Sutter and Schreiner 1991, 1995), including the excitatory tuning curve. Tone burst frequencies are spaced logarithmically with the range of test frequencies chosen according to th ...
... At each penetration site, responses from 675 frequency-level stimulus conditions determine the frequency response area (Sutter and Schreiner 1991, 1995), including the excitatory tuning curve. Tone burst frequencies are spaced logarithmically with the range of test frequencies chosen according to th ...
“Attention for Action” and “Response Selection” in Primate Anterior
... pressed the key for ⬎0.5 sec and fixated on a small fixation square (0.5 ⫻ 0.5° in visual angle) on the CRT monitor. In the spatial discrimination task, location-related visual cues using a 0.5°-sized gray square were randomly displayed 5° on either the left or right side of the fixation square for ...
... pressed the key for ⬎0.5 sec and fixated on a small fixation square (0.5 ⫻ 0.5° in visual angle) on the CRT monitor. In the spatial discrimination task, location-related visual cues using a 0.5°-sized gray square were randomly displayed 5° on either the left or right side of the fixation square for ...
Motor Threshold - McCausland Center For Brain Imaging
... When performing Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) the relative intensity or strength of stimulation is often referred to as % of Motor Threshold (MT). MT is a patient specific value for each subject or patient which is demined before the TMS session. When a magnetic coil is discharged over the ...
... When performing Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) the relative intensity or strength of stimulation is often referred to as % of Motor Threshold (MT). MT is a patient specific value for each subject or patient which is demined before the TMS session. When a magnetic coil is discharged over the ...
Motor Threshold - McCausland Center | Brain Imaging
... When performing Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) the relative intensity or strength of stimulation is often referred to as % of Motor Threshold (MT). MT is a patient specific value for each subject or patient which is demined before the TMS session. When a magnetic coil is discharged over the ...
... When performing Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) the relative intensity or strength of stimulation is often referred to as % of Motor Threshold (MT). MT is a patient specific value for each subject or patient which is demined before the TMS session. When a magnetic coil is discharged over the ...
Ultrastructural Characterization of Gerbil Olivocochlear Neurons
... neurons labeled by retrograde transport of tritiated D-ASP from the cochlea (Ryan et al., 1987). It is still unresolved whether the small neurons compose the entire population of “intraLSO” OC neurons, as suggested by Ryan et al. (1987) or whether class 5 neurons also contribute to this population. ...
... neurons labeled by retrograde transport of tritiated D-ASP from the cochlea (Ryan et al., 1987). It is still unresolved whether the small neurons compose the entire population of “intraLSO” OC neurons, as suggested by Ryan et al. (1987) or whether class 5 neurons also contribute to this population. ...
Control of Appetite and Food Preference by NMDA Receptor and Its
... melanocortin system is capable of regulating mesocorticolimbic activity and food seeking behavior [29]. In summary, internal metabolic and physiological signals can affect both aspects of appetite, and the homeostatic system do communicate with the reward system to control the feeding behavior. Obes ...
... melanocortin system is capable of regulating mesocorticolimbic activity and food seeking behavior [29]. In summary, internal metabolic and physiological signals can affect both aspects of appetite, and the homeostatic system do communicate with the reward system to control the feeding behavior. Obes ...
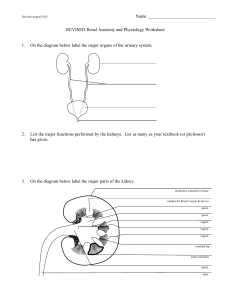
Renal Anatomy and Physiology Worksheet
... out of the tubular fluid to represent reabsorption or going into tubular fluid to represent secretion. The line representing the nephron’s wall is a composite of BOTH the luminal (apical) and basolateral (basal) membranes. If a substance is actively reabsorbed or secreted across either membrane, use ...
... out of the tubular fluid to represent reabsorption or going into tubular fluid to represent secretion. The line representing the nephron’s wall is a composite of BOTH the luminal (apical) and basolateral (basal) membranes. If a substance is actively reabsorbed or secreted across either membrane, use ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.