Synaptic Inputs to Stellate Cells in the Ventral Cochlear Nucleus
... SYNAPTIC INPUTS TO VCN MULTIPOLAR CELLS ...
... SYNAPTIC INPUTS TO VCN MULTIPOLAR CELLS ...
Human nasal olfactory epithelium as a dynamic marker for CNS
... express specific markers of CNS cell types including astrocytic marker GFAP, as well as neuronal markers such as glutamate receptor subtypes, nerve growth factor receptors and neurotransmitters GABA and glutamate (Au and Roskams, 2002; Au and Roskams, 2003; Priest and Puche, 2004; Thukral et al., 199 ...
... express specific markers of CNS cell types including astrocytic marker GFAP, as well as neuronal markers such as glutamate receptor subtypes, nerve growth factor receptors and neurotransmitters GABA and glutamate (Au and Roskams, 2002; Au and Roskams, 2003; Priest and Puche, 2004; Thukral et al., 199 ...
Cortex-inspired Developmental Learning for Vision-based Navigation, Attention and Recognition
... variance of relevant subspace in the neuronal input, resulting in more neurons being recruited along relevant information. The bottom-up input samples contain two classes, indicated by samples “+” and “◦” respectively. The regions of the two classes should not overlap if the input information in X i ...
... variance of relevant subspace in the neuronal input, resulting in more neurons being recruited along relevant information. The bottom-up input samples contain two classes, indicated by samples “+” and “◦” respectively. The regions of the two classes should not overlap if the input information in X i ...
BRAINSTEM
... plexiform layer, w/ ganglion cells in inner plexiform layer. 2 types: ROD – synapses from many rod cells = less acuity, greater sensitivity. CONE – synapses from few cone cells = high acuity. Function: Link photoreceptors directly to retinal projection neurons (ganglion cells) (Ref: NA 167,169) Loca ...
... plexiform layer, w/ ganglion cells in inner plexiform layer. 2 types: ROD – synapses from many rod cells = less acuity, greater sensitivity. CONE – synapses from few cone cells = high acuity. Function: Link photoreceptors directly to retinal projection neurons (ganglion cells) (Ref: NA 167,169) Loca ...
The World: Psychology
... – Damage to either the cochlea or the auditory nerve – Presbycusis is the loss of hearing to high frequencies in part due to less blood flow to the inner ear which destroys some of the critical neural elements in this structure. Copyright © Horizon Textbook Publishing 2007 ...
... – Damage to either the cochlea or the auditory nerve – Presbycusis is the loss of hearing to high frequencies in part due to less blood flow to the inner ear which destroys some of the critical neural elements in this structure. Copyright © Horizon Textbook Publishing 2007 ...
Chapter 2
... microscopic level nor have the local axons from IC GABAergic neurons (see Section 4.2). Although the inputs to ICC have been identified at the electron microscopic level, their synaptic role in processing auditory information remains an area of intense interest. For example, it is unclear whether th ...
... microscopic level nor have the local axons from IC GABAergic neurons (see Section 4.2). Although the inputs to ICC have been identified at the electron microscopic level, their synaptic role in processing auditory information remains an area of intense interest. For example, it is unclear whether th ...
Saladin 5e Extended Outline
... into an anterior ramus, and posterior ramus, and a small meningeal branch. i. Each spinal nerve branches on both ends: anterior and posterior roots approach the spinal cord, and anterior and posterior rami lead away from the vertebral column. b. The meningeal branch reenters the vertebral canal and ...
... into an anterior ramus, and posterior ramus, and a small meningeal branch. i. Each spinal nerve branches on both ends: anterior and posterior roots approach the spinal cord, and anterior and posterior rami lead away from the vertebral column. b. The meningeal branch reenters the vertebral canal and ...
Chapter 2 - Monsignor Farrell High School
... LO 2.5 How Hormones Interact with the Nervous System and Affect Behavior ...
... LO 2.5 How Hormones Interact with the Nervous System and Affect Behavior ...
Full text article
... dynamic interactions between regulatory signals from the brain, pituitary and gonads, all of them leading to the attainment of reproductive capacity, where a coordinated and timely activation of GnRH neurons must occur. The GnRH neurons extend their neurosecretory axons to the hypothalamus where GnR ...
... dynamic interactions between regulatory signals from the brain, pituitary and gonads, all of them leading to the attainment of reproductive capacity, where a coordinated and timely activation of GnRH neurons must occur. The GnRH neurons extend their neurosecretory axons to the hypothalamus where GnR ...
PDF
... marked by the presence of large (5-15 pm), irregularly shaped terminals that are filled with round synaptic vesicles and mitochondria. Each terminal is characteristically surrounded by dendritic profiles upon which it forms asymmetric synaptic contacts. By virtue of its structure, synaptic relations ...
... marked by the presence of large (5-15 pm), irregularly shaped terminals that are filled with round synaptic vesicles and mitochondria. Each terminal is characteristically surrounded by dendritic profiles upon which it forms asymmetric synaptic contacts. By virtue of its structure, synaptic relations ...
Complete morphologies of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in
... Morphologies of individual forebrain cholinergic neurons A series of 4HT titration experiments with Chat-IRES-CreER;R26IAP mice showed that intraperitoneal (IP) injection of 1–5 µg 4HT at P4-5 resulted in ∼10 forebrain cholinergic neurons labeled per brain. Using this protocol, 67 well-separated for ...
... Morphologies of individual forebrain cholinergic neurons A series of 4HT titration experiments with Chat-IRES-CreER;R26IAP mice showed that intraperitoneal (IP) injection of 1–5 µg 4HT at P4-5 resulted in ∼10 forebrain cholinergic neurons labeled per brain. Using this protocol, 67 well-separated for ...
Primitive Roles for Inhibitory Interneurons in Developing Frog Spinal
... pulse to the tail skin (Fig. 2 B, inset). This excites the touch sensory nerve endings of Rohon-Beard neurons (Fig. 1), and the resulting swimming can be monitored by recording ventral root activity (Fig. 3C). Motoneuron and CPG neuron activity during swimming alternates on the left and right sides ...
... pulse to the tail skin (Fig. 2 B, inset). This excites the touch sensory nerve endings of Rohon-Beard neurons (Fig. 1), and the resulting swimming can be monitored by recording ventral root activity (Fig. 3C). Motoneuron and CPG neuron activity during swimming alternates on the left and right sides ...
Sensation
... An early stage of perception in which neurons in a receptor create an internal pattern of nerve impulses that represent the conditions that stimulated it – either inside or outside the body Perception – A process that makes sensory patterns meaningful and more elaborate Copyright © Allyn and Bacon 2 ...
... An early stage of perception in which neurons in a receptor create an internal pattern of nerve impulses that represent the conditions that stimulated it – either inside or outside the body Perception – A process that makes sensory patterns meaningful and more elaborate Copyright © Allyn and Bacon 2 ...
Volatile Solvents as Drugs of Abuse: Focus on the Cortico
... 2011). However, the intentional misuse of volatile solvents was not reported in clinical case reports or popular press until the mid-twentieth century. The first documented case was in 1946, when a boy, who was being treated for psychotic symptoms at a hospital, admitted to the attending physician t ...
... 2011). However, the intentional misuse of volatile solvents was not reported in clinical case reports or popular press until the mid-twentieth century. The first documented case was in 1946, when a boy, who was being treated for psychotic symptoms at a hospital, admitted to the attending physician t ...
Title Goes here
... regions where the terminals of GABAergic neurons are densely concentrated Boutons that are immunoreactive for glutamate include a high concentration of Zn2+ boutons ...
... regions where the terminals of GABAergic neurons are densely concentrated Boutons that are immunoreactive for glutamate include a high concentration of Zn2+ boutons ...
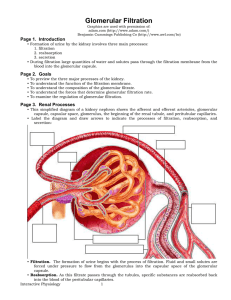
Glomerular Filtration
... • An analogy for this process would be a football player (#60) trying to run for a touchdown. However, his progress to the goal line is slowed by two opposing players (#15 and #28). The runner eventually reaches the goal, but not as easily as he would without the resistance. • Now let’s see what hap ...
... • An analogy for this process would be a football player (#60) trying to run for a touchdown. However, his progress to the goal line is slowed by two opposing players (#15 and #28). The runner eventually reaches the goal, but not as easily as he would without the resistance. • Now let’s see what hap ...
Review - Wesleyan University
... newly sprouted axons arise from injured axons in the dorsal column versus ininjured ventral axons. Nevertheless, many corticospinal axon sprouts occur in the dorsal spinal cord, suggesting origination from the injured dorsal corticospinal tract. Perhaps most excitingly, the injured animals treated w ...
... newly sprouted axons arise from injured axons in the dorsal column versus ininjured ventral axons. Nevertheless, many corticospinal axon sprouts occur in the dorsal spinal cord, suggesting origination from the injured dorsal corticospinal tract. Perhaps most excitingly, the injured animals treated w ...
Short title: Thalamocortical computations during tactile sensation
... thalamic input at baseline, during whisker movement and during touch. We used the model to ...
... thalamic input at baseline, during whisker movement and during touch. We used the model to ...
What Can an Orbitofrontal Cortex- Endowed Animal
... by a simple fact (which was admittedly difficult for an olfactory neuroscientist, such as myself to accept). The fact is, the sense of smell does not require an OFC. A casual glance at the animal kingdom makes this abundantly clear. There are thousands of vertebrate and invertebrate species using th ...
... by a simple fact (which was admittedly difficult for an olfactory neuroscientist, such as myself to accept). The fact is, the sense of smell does not require an OFC. A casual glance at the animal kingdom makes this abundantly clear. There are thousands of vertebrate and invertebrate species using th ...
Massively Parallel Recording of Unit and Local Field
... from large numbers of sites with minimal damage to the nervous tissue. MEMS devices can combine silicon integrated-circuit processing with thin-film microelectrode sensing (see APPENDIX) (Gingerich et al. 2001; Najafi and Wise 1986; Wise and Najafi 1991). In the present experiments, three different ...
... from large numbers of sites with minimal damage to the nervous tissue. MEMS devices can combine silicon integrated-circuit processing with thin-film microelectrode sensing (see APPENDIX) (Gingerich et al. 2001; Najafi and Wise 1986; Wise and Najafi 1991). In the present experiments, three different ...
Giant Fibre Activation of Direct Flight Muscles in
... the wings quickly moved laterally from the closed position to a partially opened position, making an angle of about 45 ° with respect to the long axis of the fly. The wings did not remain open, but closed back to the resting position. The closing occurred in two phases. A rapid initial closing broug ...
... the wings quickly moved laterally from the closed position to a partially opened position, making an angle of about 45 ° with respect to the long axis of the fly. The wings did not remain open, but closed back to the resting position. The closing occurred in two phases. A rapid initial closing broug ...
Distinct or Gradually Changing Spatial and Nonspatial
... many of the ventral, but not dorsal, neurons effectively distinguished between the open and closed arms [Royer et al. (2010), their Fig. 3], distinguished outbound (toward reward location) and inbound trajectories (away from reward location) [Royer et al. (2010), their Figs. 3, 4], and often fired a ...
... many of the ventral, but not dorsal, neurons effectively distinguished between the open and closed arms [Royer et al. (2010), their Fig. 3], distinguished outbound (toward reward location) and inbound trajectories (away from reward location) [Royer et al. (2010), their Figs. 3, 4], and often fired a ...
The Nervous System
... William Shakespeare called the brain “the soul’s frail dwelling house.” Actually, this miraculous organ is more like the main room in a house filled with many alcoves and passageways—the “house” being the nervous system as a whole. Before we can understand the windows, walls, and furniture of this h ...
... William Shakespeare called the brain “the soul’s frail dwelling house.” Actually, this miraculous organ is more like the main room in a house filled with many alcoves and passageways—the “house” being the nervous system as a whole. Before we can understand the windows, walls, and furniture of this h ...
PDF
... auditory nerve (Fig. 2A). There is clearly dichotomy in the diameters of the axons 100 pm from the cell body: axons of type I neurons are thicker than 1pm in diameter, whereas axons of type I1 neurons are thinner than 1 pm. Thus the central axon diameter can be used as the key variable of separation ...
... auditory nerve (Fig. 2A). There is clearly dichotomy in the diameters of the axons 100 pm from the cell body: axons of type I neurons are thicker than 1pm in diameter, whereas axons of type I1 neurons are thinner than 1 pm. Thus the central axon diameter can be used as the key variable of separation ...
The Neurophysiological Basis of Learning and Memory in Advanced
... (Figures 24.4A and 24.4B), a muscarinic receptor antagonist that also blocks the synaptic potential at the neuromuscular junctions of the octopus arm.34 Hexamethonium also blocked both spontaneous and evoked spiking activity recorded from the large neuron axonal bundles (Figures 24.4B and 24.4D). As ...
... (Figures 24.4A and 24.4B), a muscarinic receptor antagonist that also blocks the synaptic potential at the neuromuscular junctions of the octopus arm.34 Hexamethonium also blocked both spontaneous and evoked spiking activity recorded from the large neuron axonal bundles (Figures 24.4B and 24.4D). As ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.