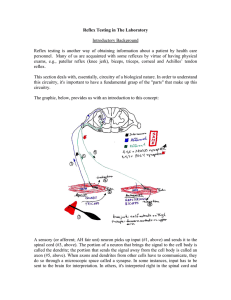
Reflex Testing in The Laboratory
... called the dendrite; the portion that sends the signal away from the cell body is called an axon (#5, above). When axons and dendrites from other cells have to communicate, they do so through a microscopic space called a synapse. In some instances, input has to be sent to the brain for interpretatio ...
... called the dendrite; the portion that sends the signal away from the cell body is called an axon (#5, above). When axons and dendrites from other cells have to communicate, they do so through a microscopic space called a synapse. In some instances, input has to be sent to the brain for interpretatio ...
Biophysics of Extracellular Action Potentials
... include low-amplitude spikes then bias is moderate. If only high amplitude units (> 200 µV) are picked up, then recording will be significantly biased towards the deep layers. The majority of spikes in cortex had a negative peak with a mean of -0.11 mV, but a minority of units (<10%) had a large pos ...
... include low-amplitude spikes then bias is moderate. If only high amplitude units (> 200 µV) are picked up, then recording will be significantly biased towards the deep layers. The majority of spikes in cortex had a negative peak with a mean of -0.11 mV, but a minority of units (<10%) had a large pos ...
Mechanisms Underlying the Cardioinhibitory and Pressor
... were presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. P value less than 0.05 calculated from Student’s t-test was considered statistically significant. ...
... were presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. P value less than 0.05 calculated from Student’s t-test was considered statistically significant. ...
The diaphragm: two physiological muscles in one
... the other hand, Balkowiec et al. (1995) recorded 13 spindle afferents from a single cat phrenic nerve, suggesting a spindle density more typical of skeletal muscle (although, again, their distribution was predominantly, but not exclusively, crural). However, as the projections of the spindle afferen ...
... the other hand, Balkowiec et al. (1995) recorded 13 spindle afferents from a single cat phrenic nerve, suggesting a spindle density more typical of skeletal muscle (although, again, their distribution was predominantly, but not exclusively, crural). However, as the projections of the spindle afferen ...
Similarities between Severe Tinnitus and Chronic Pain
... independent of the peripheral injury that caused the changes in the nervous system to develop. Phantom pain from amputations that are performed under general anesthesia is an example of such sustained changes in the central nervous system that may be the result of overstimulation of neural structure ...
... independent of the peripheral injury that caused the changes in the nervous system to develop. Phantom pain from amputations that are performed under general anesthesia is an example of such sustained changes in the central nervous system that may be the result of overstimulation of neural structure ...
MUSCULOSKELETAL BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF BRACHIAL
... Koelling, and siblings Adam and Ashley. They’ve welcomed me into their family wholeheartedly. I am especially humbled by the generosity they have shown, sharing so much of what they have to make their love known to me. After good days or bad, my one constant joy has been returning home to see my wif ...
... Koelling, and siblings Adam and Ashley. They’ve welcomed me into their family wholeheartedly. I am especially humbled by the generosity they have shown, sharing so much of what they have to make their love known to me. After good days or bad, my one constant joy has been returning home to see my wif ...
Simulating Populations of Neurons - Leeds VLE
... an understanding as to how the software NEST used learning rules to simulate different models connected in various networks. Skills and techniques learnt from the Computational Modelling module (COMP5320M) were used to analyse and pre-process data obtained from simulations. This project provided the ...
... an understanding as to how the software NEST used learning rules to simulate different models connected in various networks. Skills and techniques learnt from the Computational Modelling module (COMP5320M) were used to analyse and pre-process data obtained from simulations. This project provided the ...
Visceral sensitivity and functional dyspepsia
... may have abnormally slow gastric emptying concomitant with abnormalities in gastric electrical activity as shown by the differences between the gammagraphic curves of dyspeptic patients and those of asymptomatic controls. Among the disorders or alterations of sensory perception, hypersensitivity to ...
... may have abnormally slow gastric emptying concomitant with abnormalities in gastric electrical activity as shown by the differences between the gammagraphic curves of dyspeptic patients and those of asymptomatic controls. Among the disorders or alterations of sensory perception, hypersensitivity to ...
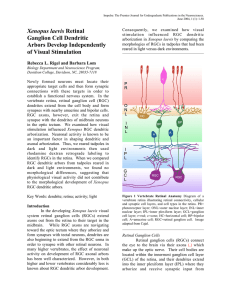
Xenopus laevis Retinal Ganglion Cell Dendritic Arbors Develop
... Neuronal Activity Influences Xenopus laevis RGC Axon Arborization Studies of Xenopus RGCs have shown that, like in mammals and in zebrafish, action potentials are also important for the development of axonal arbor morphology at the tectum. Neuronal activity stabilizes Xenopus RGC axonal arbors. Time ...
... Neuronal Activity Influences Xenopus laevis RGC Axon Arborization Studies of Xenopus RGCs have shown that, like in mammals and in zebrafish, action potentials are also important for the development of axonal arbor morphology at the tectum. Neuronal activity stabilizes Xenopus RGC axonal arbors. Time ...
Sensory nerve conduction studies
... m.abductor hallucis with surface electrodes. When the threshold for a motor response is around 1mA (stimulus duration 0.2 ms) the position of the recording electrode is excellent. Thresholds of more than 3 mA rarely give satisfactory recordings. Placement of reference electrode: Subcutaneously 20-30 ...
... m.abductor hallucis with surface electrodes. When the threshold for a motor response is around 1mA (stimulus duration 0.2 ms) the position of the recording electrode is excellent. Thresholds of more than 3 mA rarely give satisfactory recordings. Placement of reference electrode: Subcutaneously 20-30 ...
Chapter 29 - krigolson teaching
... What neuronal mechanism might underlie this apparent shift in images at the time of saccades? Neurons in the parietal cortex alter their activity preceding saccades in ways that seem remarkably related to the perceptual phenomenon. When a monkey is about to make a saccade, a neuron becomes less sens ...
... What neuronal mechanism might underlie this apparent shift in images at the time of saccades? Neurons in the parietal cortex alter their activity preceding saccades in ways that seem remarkably related to the perceptual phenomenon. When a monkey is about to make a saccade, a neuron becomes less sens ...
Electrical Stimulation of the Horizontal Limb of the Diagonal Band
... twisted together) were placed in the LOT (4.7 mm anterior; 3.4 mm lateral; 5.2 ventral from bregma), in pPC (3.6 mm posterior, 3.0 mm lateral (14° angled laterally); 9 –10 mm ventral from bregma), and in the HDB (0.0 – 0.5 mm posterior, 1.8 –2.2 mm lateral, 8.6 –9.0 mm ventral from bregma). We chose ...
... twisted together) were placed in the LOT (4.7 mm anterior; 3.4 mm lateral; 5.2 ventral from bregma), in pPC (3.6 mm posterior, 3.0 mm lateral (14° angled laterally); 9 –10 mm ventral from bregma), and in the HDB (0.0 – 0.5 mm posterior, 1.8 –2.2 mm lateral, 8.6 –9.0 mm ventral from bregma). We chose ...
Rearrangement of microtubule polarity orientation during conversion
... neurons that regenerated an axon from the tip of the dendrite, 84%–100% of microtubules in the mid-region of the original dendrite were plus end-distal (Figs. 3A, 3B, and 3E; Table 1), indicating that microtubule polarity orientation in the original dendrite changed during 24 h of culture. Although ...
... neurons that regenerated an axon from the tip of the dendrite, 84%–100% of microtubules in the mid-region of the original dendrite were plus end-distal (Figs. 3A, 3B, and 3E; Table 1), indicating that microtubule polarity orientation in the original dendrite changed during 24 h of culture. Although ...
Segregated cholinergic transmission in the ventral tegmental area
... excitatory and inhibitory responses in both DA and non-DA neurons, although the proportions varied slightly. No responses were observed when cholinergic neurons were transduced only with the fluorescent reporter (Supplementary Fig. 6). Stimulation of axons from the PPN produced predominantly excitat ...
... excitatory and inhibitory responses in both DA and non-DA neurons, although the proportions varied slightly. No responses were observed when cholinergic neurons were transduced only with the fluorescent reporter (Supplementary Fig. 6). Stimulation of axons from the PPN produced predominantly excitat ...
CNS 424 Block Educational Framework (Week 1)
... Make a list of the components of the system. Review the basic structure of sympathetic trunk. Describe the source of sympathetic system in the neck and make a list of target organs. Describe the Para vertebral sympathetic ganglia in the abdomen, their locations and target organs. Discuss the relatio ...
... Make a list of the components of the system. Review the basic structure of sympathetic trunk. Describe the source of sympathetic system in the neck and make a list of target organs. Describe the Para vertebral sympathetic ganglia in the abdomen, their locations and target organs. Discuss the relatio ...
the medial division of the medial geniculate body of the cat
... morphologically heterogeneous neurons. The main types, in descending order of frequency, are medium-sized neurons with (1) radiate, (2) tufted, or (3) elongate dendrites; (4) small stellate or radiate neurons, including Golgi type II cells with a locally arborizing, sparsely branching axon collatera ...
... morphologically heterogeneous neurons. The main types, in descending order of frequency, are medium-sized neurons with (1) radiate, (2) tufted, or (3) elongate dendrites; (4) small stellate or radiate neurons, including Golgi type II cells with a locally arborizing, sparsely branching axon collatera ...
Rapid Changes in Synaptic Vesicle Cytochemistry
... described in detail elsewhere (26). By 2 wk in vitro, these cultures had well-developed fascicles of nerve fibers connecting single or small groups of neurons. They were subsequently cultured for a total of 5-9 wk in vitro because prior studies using this culture system have demonstrated that substa ...
... described in detail elsewhere (26). By 2 wk in vitro, these cultures had well-developed fascicles of nerve fibers connecting single or small groups of neurons. They were subsequently cultured for a total of 5-9 wk in vitro because prior studies using this culture system have demonstrated that substa ...
Dynamics of sensory thalamocortical synaptic networks during
... Abstract The thalamocortical network consists of the pathways that interconnect the thalamus and neocortex, including thalamic sensory afferents, corticothalamic and thalamocortical pathways. These pathways are essential to acquire, analyze, store and retrieve sensory information. However, sensory i ...
... Abstract The thalamocortical network consists of the pathways that interconnect the thalamus and neocortex, including thalamic sensory afferents, corticothalamic and thalamocortical pathways. These pathways are essential to acquire, analyze, store and retrieve sensory information. However, sensory i ...
Fein A (2012) Nociceptors and the Perception of Pain.
... nociceptors. We have all probably experienced that pain can be caused by thermal, mechanical and chemical stimuli that produce tissue injury. Several possibilities might explain how these different stimuli could result in the sensation of pain. One possibility is that individual nociceptors are sens ...
... nociceptors. We have all probably experienced that pain can be caused by thermal, mechanical and chemical stimuli that produce tissue injury. Several possibilities might explain how these different stimuli could result in the sensation of pain. One possibility is that individual nociceptors are sens ...
Differential Impairment of Individuated Finger Movements in
... motor system have used heterogeneous patients with relatively nonspecific lesions, and with a wide range of motor and nonmotor abnormalities (Carroll 1965; Wade et al. 1983). Pure motor hemiparesis, a relatively homogeneous clinical syndrome, is characterized by paresis on one side of the body witho ...
... motor system have used heterogeneous patients with relatively nonspecific lesions, and with a wide range of motor and nonmotor abnormalities (Carroll 1965; Wade et al. 1983). Pure motor hemiparesis, a relatively homogeneous clinical syndrome, is characterized by paresis on one side of the body witho ...
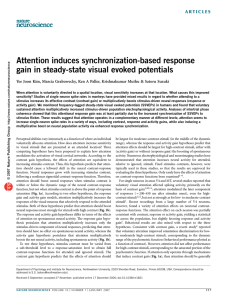
Attention induces synchronization-based response gain in steady
... (or activity) gain in terms of increased phase locking of population activity to stimulus flicker, SSVEP amplitudes might be sensitive enough to demonstrate response (or activity) gain. Indeed, some of the data reported in a prior SSVEP study2 are suggestive of multiplicative attention effects on SS ...
... (or activity) gain in terms of increased phase locking of population activity to stimulus flicker, SSVEP amplitudes might be sensitive enough to demonstrate response (or activity) gain. Indeed, some of the data reported in a prior SSVEP study2 are suggestive of multiplicative attention effects on SS ...
Towards a New Understanding of Chronic Pelvic Pain.
... and 2nd order dorsal horn neurons. Inhibitory neurons release endogenous opioids and inhibitory neurotransmitters like GABA which have an antinociceptive effect. ...
... and 2nd order dorsal horn neurons. Inhibitory neurons release endogenous opioids and inhibitory neurotransmitters like GABA which have an antinociceptive effect. ...
Chapter 14 - Brain and Spinal Cord
... The Adult Human Brain Ranges from 750 cc to 2100 cc Contains almost 97% of the body’s neural tissue Average weight about 1.4 kg (3 lb) Male brains are typically larger but there is no correlation between brain size and intelligence. ...
... The Adult Human Brain Ranges from 750 cc to 2100 cc Contains almost 97% of the body’s neural tissue Average weight about 1.4 kg (3 lb) Male brains are typically larger but there is no correlation between brain size and intelligence. ...
Mismatch Negativity: Different Water in the Same River
... (third waveform in fig. 1). Lavikainen et al. [1995] found two sources for the magnetic N1 response to such a change in frequency and suggested that these represented the normal N1 and an MMN, with the MMN occurring earlier than it would have if the frequency change had been part of a separate devia ...
... (third waveform in fig. 1). Lavikainen et al. [1995] found two sources for the magnetic N1 response to such a change in frequency and suggested that these represented the normal N1 and an MMN, with the MMN occurring earlier than it would have if the frequency change had been part of a separate devia ...
Synchronisation hubs in the visual cortex may arise from strong
... predict that the strength and orientation tuning of synaptic inhibition are heterogeneous across area 17 neurons, which could have important implications for these neurons’ sensory processing capabilities. Furthermore, although our experimental recordings were conducted in the visual cortex, our mod ...
... predict that the strength and orientation tuning of synaptic inhibition are heterogeneous across area 17 neurons, which could have important implications for these neurons’ sensory processing capabilities. Furthermore, although our experimental recordings were conducted in the visual cortex, our mod ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.