Ventral Medial Nucleus Neurons Send Thalamocortical Afferents
... the observation that more than half of their projecting axon fibers were distributed in L1 of the cerebral cortex (Kuramoto et al. 2009). VM neurons had similar input–output organization to those of IZ neurons; both the neuron groups received inhibitory afferents from the basal ganglia and sent effer ...
... the observation that more than half of their projecting axon fibers were distributed in L1 of the cerebral cortex (Kuramoto et al. 2009). VM neurons had similar input–output organization to those of IZ neurons; both the neuron groups received inhibitory afferents from the basal ganglia and sent effer ...
Some Fiber Projections to the Superior Colliculus in the Cat`
... side medial to the cerebral peduncle. This small retinal tract may be identical with the anterior accessory optic tract. Retinal fibers also reach the rostral diencephalic extension of the superior colliculus, the pretectal region. Degenerated fibers were seen to reach this structure laterally by wa ...
... side medial to the cerebral peduncle. This small retinal tract may be identical with the anterior accessory optic tract. Retinal fibers also reach the rostral diencephalic extension of the superior colliculus, the pretectal region. Degenerated fibers were seen to reach this structure laterally by wa ...
Central Control of the Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems and
... into three distinct neural phases in which each phase reflects a “state” of the oscillating network rather than a particular configuration of the motor output. In other words, a cycle phase in this context means a recurring episode when one or more groups of neurons in the network discharge a charac ...
... into three distinct neural phases in which each phase reflects a “state” of the oscillating network rather than a particular configuration of the motor output. In other words, a cycle phase in this context means a recurring episode when one or more groups of neurons in the network discharge a charac ...
Axon Initiation and Growth Cone Turning on Bound Protein Gradients Cellular/Molecular Junyu Mai,
... gradient (10 min diffusive printing with 20 g/ml FITC-IgG). Insets, Definition of the axon initiation and turning angles. The angles varied from ⫹ 90 o to –90 o, with the positive and negative value indicating that the axon was initiated or turned toward the high- and low-density side of the gradie ...
... gradient (10 min diffusive printing with 20 g/ml FITC-IgG). Insets, Definition of the axon initiation and turning angles. The angles varied from ⫹ 90 o to –90 o, with the positive and negative value indicating that the axon was initiated or turned toward the high- and low-density side of the gradie ...
Central Control of the Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems
... et al. (487), who suggest that lungfish, which also have a buccal force pump, have a postinspiratory phase. The mechanisms underlying respiratory rhythmogenesis in mammals are only now being resolved (67, 529, 585), and even less is known about respiratory rhythmogenesis in nonmammalian species. Rec ...
... et al. (487), who suggest that lungfish, which also have a buccal force pump, have a postinspiratory phase. The mechanisms underlying respiratory rhythmogenesis in mammals are only now being resolved (67, 529, 585), and even less is known about respiratory rhythmogenesis in nonmammalian species. Rec ...
- D-Scholarship@Pitt
... Although these studies have provided evidence that synaptic refinement occurs through activity-dependent competition, all were performed by blocking or reducing electrical activity. Therefore, these results could mean that a certain threshold level of activity is required to read pre-determined mole ...
... Although these studies have provided evidence that synaptic refinement occurs through activity-dependent competition, all were performed by blocking or reducing electrical activity. Therefore, these results could mean that a certain threshold level of activity is required to read pre-determined mole ...
University of Groningen Gustatory neural processing in the
... range of taste sensation 106. Moreover, molecules that elicit similar verbal reports of taste from humans or neural activity in gustatory afferent nerves often bear little chemical relation to one another. For example, many mono- and disaccharides taste sweet to humans. Not all sugars however, taste ...
... range of taste sensation 106. Moreover, molecules that elicit similar verbal reports of taste from humans or neural activity in gustatory afferent nerves often bear little chemical relation to one another. For example, many mono- and disaccharides taste sweet to humans. Not all sugars however, taste ...
Substance P and Cholecystokinin-like lmmunoreactive Varicosities
... In recent years, the neuropeptides substance P (SP) and cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) have been suggested as neurotransmitters or neuromodulators of primary afferent neurons. Immunohistochemical studies have provided anatomical evidence in support of this hypothesis. SP-like immunoreactivity ( ...
... In recent years, the neuropeptides substance P (SP) and cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) have been suggested as neurotransmitters or neuromodulators of primary afferent neurons. Immunohistochemical studies have provided anatomical evidence in support of this hypothesis. SP-like immunoreactivity ( ...
Disorders of the Cerebellum and Its Connections
... The cerebellum, which lies just dorsal to the pons and medulla, consists of two highly convoluted lateral cerebellar hemispheres and a narrow medial portion, the vermis. It is connected to the brain by three pairs of dense fiber bundles called the peduncles. Although the structure and function of th ...
... The cerebellum, which lies just dorsal to the pons and medulla, consists of two highly convoluted lateral cerebellar hemispheres and a narrow medial portion, the vermis. It is connected to the brain by three pairs of dense fiber bundles called the peduncles. Although the structure and function of th ...
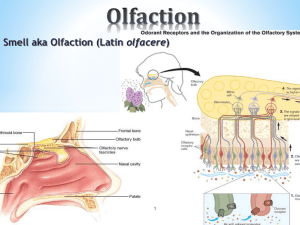
olfaction
... so bundles of axons form right and left olfactory nerves They terminate in the olfactory bulbs – below the frontal lobes of the cerebrum Axons of the olfactory bulbs form the olfactory tract which projects to the primary olfactory area of the cerebral cortex. Some project into the limbic syste ...
... so bundles of axons form right and left olfactory nerves They terminate in the olfactory bulbs – below the frontal lobes of the cerebrum Axons of the olfactory bulbs form the olfactory tract which projects to the primary olfactory area of the cerebral cortex. Some project into the limbic syste ...
Ethanol Potentiation of Glycine-Induced Responses in Dissociated
... with our previous report (Ye, 2000), glycine elicited depolarization and, in some cases, action potentials in VTA neurons from neonatal rats (Fig. 1). This depolarization is explained by a reversal potential for glycine’s action (EGly) that is much more positive (near ⫺25 mV in neonatal neurons) tha ...
... with our previous report (Ye, 2000), glycine elicited depolarization and, in some cases, action potentials in VTA neurons from neonatal rats (Fig. 1). This depolarization is explained by a reversal potential for glycine’s action (EGly) that is much more positive (near ⫺25 mV in neonatal neurons) tha ...
... glial cells, was observed to correlate well with TSE related lessions. This may suggest that, among all neurotrophic factors evaluated, this receptor is involved in end stage brain pathology in BSE. Additionally, the study of the peripheral nervous system neuroregeneration was carried out following ...
Seventeen
... the centrifugal fibers. Other dendrites form dendrodgndritic synapses with mitral cell dendrites. Sorne of these synaptic arrangements are shown irr Figure 77 -2.The complex circuitry of the olfactory bulb recalls that of the retina and indicates thiat, as is the case with visual images, ...
... the centrifugal fibers. Other dendrites form dendrodgndritic synapses with mitral cell dendrites. Sorne of these synaptic arrangements are shown irr Figure 77 -2.The complex circuitry of the olfactory bulb recalls that of the retina and indicates thiat, as is the case with visual images, ...
AXOTOMIZED SPINAL COMMISSURAL INTERNEURONS OF THE ADULT FELINE:
... or CINs) are a class of neuron with axons that project through the ventral commissure to the contralateral spinal cord. My goal was to examine the morphological, molecular, and functional changes that occur to adult feline PCIs following a proximal axotomy. We first determined whether proximally axo ...
... or CINs) are a class of neuron with axons that project through the ventral commissure to the contralateral spinal cord. My goal was to examine the morphological, molecular, and functional changes that occur to adult feline PCIs following a proximal axotomy. We first determined whether proximally axo ...
lecture3-joints
... By the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the term “Joint”. Describe the classification of the 3 types of joints & give an example of each. Describe the characteristics of synovial joints. Describe the classification of synovial joints & give an example of each. List fa ...
... By the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the term “Joint”. Describe the classification of the 3 types of joints & give an example of each. Describe the characteristics of synovial joints. Describe the classification of synovial joints & give an example of each. List fa ...
A role for subplate neurons in the patterning of
... During cerebral cortical development, ingrowing axons from different thalamic nuclei select and invade their cortical targets. The selection of an appropriate target is first evident even before thalamic axons grow into the cortical plate: initially axons accumulate and wait below their cortical tar ...
... During cerebral cortical development, ingrowing axons from different thalamic nuclei select and invade their cortical targets. The selection of an appropriate target is first evident even before thalamic axons grow into the cortical plate: initially axons accumulate and wait below their cortical tar ...
LFP Power Spectra in V1 Cortex: The Graded Effect of Stimulus
... contents of the LFP are actually modulated by stimulus conditions. We studied the neural activity recorded in V1 of anesthetized and paralyzed monkeys to a series of grating patterns of ascending stimulus contrasts. The simultaneously sampled LFP and spike responses from these recordings were analyz ...
... contents of the LFP are actually modulated by stimulus conditions. We studied the neural activity recorded in V1 of anesthetized and paralyzed monkeys to a series of grating patterns of ascending stimulus contrasts. The simultaneously sampled LFP and spike responses from these recordings were analyz ...
After all, it`s still replication: A reply to Jacob on simulation and mirror
... Now, if, as maintained by the classical model of MNs, MNs only code motor acts (motor intentions), they should fire in the same way when a subject observes the Action and the Intention conditions, since in both conditions one and the same motor act is depicted. However, Iacoboni and colleagues disc ...
... Now, if, as maintained by the classical model of MNs, MNs only code motor acts (motor intentions), they should fire in the same way when a subject observes the Action and the Intention conditions, since in both conditions one and the same motor act is depicted. However, Iacoboni and colleagues disc ...
Motor imagery and higher-level cognition: four hurdles before
... 2008, 2009). Using motor imagery can be difficult for some individuals, especially as it is somewhat less natural than visual imagery. Before we can look directly at the implications of motor imagery on cognitive abilities and neural substrates, we first need to account for individual variability in ...
... 2008, 2009). Using motor imagery can be difficult for some individuals, especially as it is somewhat less natural than visual imagery. Before we can look directly at the implications of motor imagery on cognitive abilities and neural substrates, we first need to account for individual variability in ...
Structure of Receptive Fields in Area 3b of Primary Somatosensory
... mm long). Random dot patterns are unbiased in the sense that all possible patterns with the specified dot density are equally likely and the probability of a repeated pattern is virtually zero. The dot density (10 dots/cm 2) was chosen to satisf y two constraints. First, it was large enough that, at ...
... mm long). Random dot patterns are unbiased in the sense that all possible patterns with the specified dot density are equally likely and the probability of a repeated pattern is virtually zero. The dot density (10 dots/cm 2) was chosen to satisf y two constraints. First, it was large enough that, at ...
How PACAP CeA Infusion Alters Mechanical and Thermal Sensitivity
... 1.1 Prevalence of Pain Pain is part of the human experience. Pain has been defined as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage (International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP), 2011). Acute and chron ...
... 1.1 Prevalence of Pain Pain is part of the human experience. Pain has been defined as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage (International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP), 2011). Acute and chron ...
Experience-Dependent Sharpening of Visual Shape Selectivity in
... To measure the broadness of stimulus selectivity, we determined the number of stimuli (of 18) at each orientation that elicited a significant response greater than baseline according to a one-tailed t-test at P < 0.01. For this analysis, lower values indicate sharper tuning (i.e., a neuron that respo ...
... To measure the broadness of stimulus selectivity, we determined the number of stimuli (of 18) at each orientation that elicited a significant response greater than baseline according to a one-tailed t-test at P < 0.01. For this analysis, lower values indicate sharper tuning (i.e., a neuron that respo ...
The Role of Neurotrophins in Neurotransmitter Release
... motoneurons (Baldelli and others 1999). These channel types are known to contribute to fast synaptic transmission at excitatory hippocampal synapses (Gasparini and others 2001). Taken together, these observations suggest that Ca2+ channels known to be involved in neurotransmitter release at small ce ...
... motoneurons (Baldelli and others 1999). These channel types are known to contribute to fast synaptic transmission at excitatory hippocampal synapses (Gasparini and others 2001). Taken together, these observations suggest that Ca2+ channels known to be involved in neurotransmitter release at small ce ...
Different adrenal sympathetic preganglionic
... which the unit could fire more than one time to a paired RVLM stimulus. This response, characteristic of Epi Adr SPNs, is shown in the peristimulus time histogram in Fig. 2A, top. The probability of unit discharge fell below control levels for ⬃80 ms after the RVLM stimulation (mean control discharg ...
... which the unit could fire more than one time to a paired RVLM stimulus. This response, characteristic of Epi Adr SPNs, is shown in the peristimulus time histogram in Fig. 2A, top. The probability of unit discharge fell below control levels for ⬃80 ms after the RVLM stimulation (mean control discharg ...
Anatomy and physiology of the esophageal body
... plexus regulate secretion and the contraction of the muscularis musosae. The significance of a scattered myenteric plexus in the proximal esophageal striated muscle remains unclear.4,5 Arterial blood supply to the esophagus is provided by three sources: branches of the inferior thyroid artery provid ...
... plexus regulate secretion and the contraction of the muscularis musosae. The significance of a scattered myenteric plexus in the proximal esophageal striated muscle remains unclear.4,5 Arterial blood supply to the esophagus is provided by three sources: branches of the inferior thyroid artery provid ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.