L1CAM/Neuroglian controls the axon–axon interactions establishing
... nrg849 (Goossens et al., 2011), with mutations disrupting intracellular protein–protein interactions. To generate specific intracellular mutations, we used a genomic rescue approach (Venken et al., 2009) that allows expression of modified versions of Nrg at endogenous levels in the background of the ...
... nrg849 (Goossens et al., 2011), with mutations disrupting intracellular protein–protein interactions. To generate specific intracellular mutations, we used a genomic rescue approach (Venken et al., 2009) that allows expression of modified versions of Nrg at endogenous levels in the background of the ...
Postoperative Left Prefrontal Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic
... neostigmine and glycopyrrolate. All patients were pretreated for postoperative nausea and vomiting with ondansetron 30 min before emergence from surgery. At the time of arrival in the recovery room, patients were loaded with morphine sulfate up to 0.1 mg/kg ideal body weight based on their clinical ...
... neostigmine and glycopyrrolate. All patients were pretreated for postoperative nausea and vomiting with ondansetron 30 min before emergence from surgery. At the time of arrival in the recovery room, patients were loaded with morphine sulfate up to 0.1 mg/kg ideal body weight based on their clinical ...
Ch. 14 CNS textbook
... to be composed of two major divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The reason for designating two distinct divisions is to make the study of the nervous system easier. In this chapter, we discuss the part of the nervous system that lies at the center of ...
... to be composed of two major divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The reason for designating two distinct divisions is to make the study of the nervous system easier. In this chapter, we discuss the part of the nervous system that lies at the center of ...
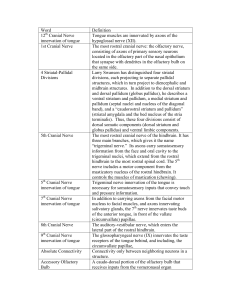
Word Definition 12 Cranial Nerve innervation of
... three distinct groups. In other species there are 1-3 groups. The AOT axons carry information about movement throughout large receptive fields, as occurs during head movements. See “Cortical Neuromodulation during sleep.”In the midbrain reticular formation, e.g., in the cholinergic cells of the midb ...
... three distinct groups. In other species there are 1-3 groups. The AOT axons carry information about movement throughout large receptive fields, as occurs during head movements. See “Cortical Neuromodulation during sleep.”In the midbrain reticular formation, e.g., in the cholinergic cells of the midb ...
Bursting Neurons Signal Input Slope
... the slope in a graded manner. We show how these computations can be understood in terms of the biophysical mechanism of burst generation. There are several examples in the literature suggesting that bursts indeed occur preferentially on positive slopes (Guido et al., 1992; Gabbiani et al., 1996). Ou ...
... the slope in a graded manner. We show how these computations can be understood in terms of the biophysical mechanism of burst generation. There are several examples in the literature suggesting that bursts indeed occur preferentially on positive slopes (Guido et al., 1992; Gabbiani et al., 1996). Ou ...
the Central Nervous System
... A. Basal nuclei (basal ganglia) - involved in motor control 1. group of nuclei deep within the cerebral white matter a. caudate nucleus—arches over thalamus b. putamen c. globus pallidus 2. cooperate with the cerebral cortex in controlling movement 3. start, stop, and regulate intensity of voluntary ...
... A. Basal nuclei (basal ganglia) - involved in motor control 1. group of nuclei deep within the cerebral white matter a. caudate nucleus—arches over thalamus b. putamen c. globus pallidus 2. cooperate with the cerebral cortex in controlling movement 3. start, stop, and regulate intensity of voluntary ...
Chapter 06 Abstract Neuron Models
... behaviors of networks. At the level of neuron modeling, what is immediately of concern to us is Grossberg's comment, "Two seemingly different models can be equivalent from a functional viewpoint if they both generate similar sets of emergent behaviors." In every abstract neuron model some or even al ...
... behaviors of networks. At the level of neuron modeling, what is immediately of concern to us is Grossberg's comment, "Two seemingly different models can be equivalent from a functional viewpoint if they both generate similar sets of emergent behaviors." In every abstract neuron model some or even al ...
Kandel ch. 42 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Mossy fibers originate from nuclei in the spinal cord and brain stem and carry sensory information from the periphery as well as information from the cerebral cortex. They terminate as excitatory synapses on the dendrites of granule cells in the granular layer (Figure 42-4). The axons of the granule ...
... Mossy fibers originate from nuclei in the spinal cord and brain stem and carry sensory information from the periphery as well as information from the cerebral cortex. They terminate as excitatory synapses on the dendrites of granule cells in the granular layer (Figure 42-4). The axons of the granule ...
Title: 공학도를 위한 생물학 (2)
... And common answers to this question are, but the question is it's not a best question. But if you are to ask this question, common answers given are the nervous system is too complex to be explained by a general theory. And because ir performs too many computational functions to be explained by any ...
... And common answers to this question are, but the question is it's not a best question. But if you are to ask this question, common answers given are the nervous system is too complex to be explained by a general theory. And because ir performs too many computational functions to be explained by any ...
The Relation between Dendritic Geometry
... We recorded basic parameters describing the electrical excitability of the neurons that have been typically used in the literature. A sequence of depolarizing 500-ms-long rectangular current pulses of varying amplitudes was applied, and the action potential (AP) sequences were recorded. For analysis ...
... We recorded basic parameters describing the electrical excitability of the neurons that have been typically used in the literature. A sequence of depolarizing 500-ms-long rectangular current pulses of varying amplitudes was applied, and the action potential (AP) sequences were recorded. For analysis ...
A Curious Commentary on a Book on Mirror Neurons and Other
... in a situation of having to rebound free throw shots if the shot misses, which provides a competitive advantage in learning to predict the outcome of others’ shots. This is not the case for expert or novice watchers who do not have to use the visual information to select time-sensitive appropriate a ...
... in a situation of having to rebound free throw shots if the shot misses, which provides a competitive advantage in learning to predict the outcome of others’ shots. This is not the case for expert or novice watchers who do not have to use the visual information to select time-sensitive appropriate a ...
Big Myth or Major Miss? - Perceptual Science Laboratory
... Furthermore, a MNS provides a neurophysiological underpinning for several claims of embodied cognition such as a) perception and action are intimately linked, and b) what appears to be high-‐level or abstra ...
... Furthermore, a MNS provides a neurophysiological underpinning for several claims of embodied cognition such as a) perception and action are intimately linked, and b) what appears to be high-‐level or abstra ...
The Basal Ganglia
... the thalamus and cerebral cortex. These circuits ar The Skel to~otor Circuit Engages Specific Portions largely segregated, bath structurally and functionally. Each circuit originates in a specific area of the of the Cer bral Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and Thalamus cerebral cortex and engages different p ...
... the thalamus and cerebral cortex. These circuits ar The Skel to~otor Circuit Engages Specific Portions largely segregated, bath structurally and functionally. Each circuit originates in a specific area of the of the Cer bral Cortex, Basal Ganglia, and Thalamus cerebral cortex and engages different p ...
Retinal Ganglion Cell Axon Guidance in the Mouse Optic Chiasm
... N IH Image analysis system to measure the area covered by the RGC axons. This measurement takes into account both the number and length of the axons, parameters that could not be accurately measured individually in these three-dimensional cultures. Because outgrowth was not radial, care was taken to ...
... N IH Image analysis system to measure the area covered by the RGC axons. This measurement takes into account both the number and length of the axons, parameters that could not be accurately measured individually in these three-dimensional cultures. Because outgrowth was not radial, care was taken to ...
Neuronal Interaction Dynamics in Cat Primary Visual Cortex
... However, RFs can exhibit complex, nonpredictive behavior dependent on f urther variations of the stimulus parameters. In addition, these complex spatiotemporal response properties can be modified by stimulation displaced from the RF center or from outside the classical RF (Allman et al., 1985; Dinse ...
... However, RFs can exhibit complex, nonpredictive behavior dependent on f urther variations of the stimulus parameters. In addition, these complex spatiotemporal response properties can be modified by stimulation displaced from the RF center or from outside the classical RF (Allman et al., 1985; Dinse ...
Axonal Dopamine Receptors Activate Peripheral Spike
... neurons release transmitter as a graded function of membrane potential and are reciprocally inhibitory (Fig. 2 F) (Russell and Graubard, 1987; Hartline and Graubard, 1992), it is not possible from these experiments alone to determine whether either or both of the neurons is a direct target of the do ...
... neurons release transmitter as a graded function of membrane potential and are reciprocally inhibitory (Fig. 2 F) (Russell and Graubard, 1987; Hartline and Graubard, 1992), it is not possible from these experiments alone to determine whether either or both of the neurons is a direct target of the do ...
Anatomical Changes in Human Motor Cortex and Motor Pathways
... Tractography was performed using mrDiffusion software (Dougherty et al. 2005), based on the diffusion tensor calculated as described above. The corticospinal and the corticopontine tracts were targeted; 4 volumes of interest specified anatomically in each individual in native space: the posterior lim ...
... Tractography was performed using mrDiffusion software (Dougherty et al. 2005), based on the diffusion tensor calculated as described above. The corticospinal and the corticopontine tracts were targeted; 4 volumes of interest specified anatomically in each individual in native space: the posterior lim ...
Single Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons Form Widely Spread
... ac, Anterior commissure; cc, corpus callosum; cp, cerebral peduncle; CPu, caudate–putamen (neostriatum); Hpc, hippocampus; ic, there was no obvious difference between internal capsule; LV, lateral ventricle; ml, medial lemniscus; ot, optic tract; STh, subthalamic nucleus; str, superior thalamic the ...
... ac, Anterior commissure; cc, corpus callosum; cp, cerebral peduncle; CPu, caudate–putamen (neostriatum); Hpc, hippocampus; ic, there was no obvious difference between internal capsule; LV, lateral ventricle; ml, medial lemniscus; ot, optic tract; STh, subthalamic nucleus; str, superior thalamic the ...
Lecture 2: The Spinal Cord
... cord, each bear a spinal ganglion which constitutes the first cell-station of the sensory nerves ...
... cord, each bear a spinal ganglion which constitutes the first cell-station of the sensory nerves ...
Anatomy - Nervous System Test Chpt 9
... 1. What is the function of the nervous system? a. sensory input b. integration c. motor output d. all of the above 2. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. nerve b. neuron c. brain d. spinal cord 3. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in ...
... 1. What is the function of the nervous system? a. sensory input b. integration c. motor output d. all of the above 2. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. nerve b. neuron c. brain d. spinal cord 3. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in ...
Post-pubertal Emergence of Prefrontal Cortical Up
... and required 10--20 min to completely wash out the effects. All data shown were obtained from the stable 2--3 min following drug administration. The doses were selected based on pilot experiments determining dose--response curves for these agents, which revealed that 8 lM NMDA is an effective concen ...
... and required 10--20 min to completely wash out the effects. All data shown were obtained from the stable 2--3 min following drug administration. The doses were selected based on pilot experiments determining dose--response curves for these agents, which revealed that 8 lM NMDA is an effective concen ...
Functional Imaging of Central Nervous System Involvement in
... ger of the affected hand compared with the unaffected hand. In addition, the distance between the S1 representations of the thumb and little finger of the affected hand was significantly shorter compared with the representations of the thumb and little finger of the unaffected hand. However, an ind ...
... ger of the affected hand compared with the unaffected hand. In addition, the distance between the S1 representations of the thumb and little finger of the affected hand was significantly shorter compared with the representations of the thumb and little finger of the unaffected hand. However, an ind ...
Anatomofunctional organization of the ventral primary motor and
... Stevenage, UK) with the following parameters: total train duration, 50 ms; single pulse width, 0.2 ms; and pulse frequency, 330 Hz. The current intensity ranged from 3 to 40 lA and was controlled on an oscilloscope by measuring the voltage drop across a 10 KX resistor in series with the stimulating ...
... Stevenage, UK) with the following parameters: total train duration, 50 ms; single pulse width, 0.2 ms; and pulse frequency, 330 Hz. The current intensity ranged from 3 to 40 lA and was controlled on an oscilloscope by measuring the voltage drop across a 10 KX resistor in series with the stimulating ...
ELECTRODEPOSITION OF ALLOYS, 1930 TO 1940.1 By Ci
... software (Cambridge, U.K.). The average value over a 20-s period was used to evaluate sSNA and arterial blood pressure. Phrenic frequency and phrenic amplitude were determined using a phrenic nerve triggered waveform average over a 100-s period. The sSNA responses to intermittent ADN stimulation and ...
... software (Cambridge, U.K.). The average value over a 20-s period was used to evaluate sSNA and arterial blood pressure. Phrenic frequency and phrenic amplitude were determined using a phrenic nerve triggered waveform average over a 100-s period. The sSNA responses to intermittent ADN stimulation and ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.