Simulations of the Role of the Muscarinic-Activated Calcium- I in Entorhinal Neuronal
... drites lumped together. The addition of the separate initial segment compartment differs from the pyramidal cell. The lengths and cross sections of the three principal dendrite compartments were adjusted to give the dendrite a length constant of 2 (sealed-end condition). The compartment profiles are ...
... drites lumped together. The addition of the separate initial segment compartment differs from the pyramidal cell. The lengths and cross sections of the three principal dendrite compartments were adjusted to give the dendrite a length constant of 2 (sealed-end condition). The compartment profiles are ...
CO2-pH
... application results in Ca2+ release from internal stores (ER). It would be interesting to examine if this also occurs with high levels of CO2 exposure. ...
... application results in Ca2+ release from internal stores (ER). It would be interesting to examine if this also occurs with high levels of CO2 exposure. ...
Neuronal polarity: establishing and maintaining the axon initial
... somatodendritic region after synapse stimulation is called a postsynaptic potential (PSP). Axons also require a fast electric signal transfer, however since axons can be much longer than dendrites this transfer must be more faithful and stronger. Therefore axons have a system that boots the electric ...
... somatodendritic region after synapse stimulation is called a postsynaptic potential (PSP). Axons also require a fast electric signal transfer, however since axons can be much longer than dendrites this transfer must be more faithful and stronger. Therefore axons have a system that boots the electric ...
Local Gene Expression in Axons and Nerve Endings: The Glia
... cells whose cytoplasm resides largely in the axon domain, at distances up to meters away from the nucleus. As a result, the combined mass of cell processes markedly exceeds that of the cell body in many neuronal types and many animal species (Fig. 1). Accordingly, neurons account for half the mammal ...
... cells whose cytoplasm resides largely in the axon domain, at distances up to meters away from the nucleus. As a result, the combined mass of cell processes markedly exceeds that of the cell body in many neuronal types and many animal species (Fig. 1). Accordingly, neurons account for half the mammal ...
NAME:OLUWATIMEHIN OLUWAWEMIMO MATRIC NUMBER :14
... voluntary muscle, and therefore under conscious control. Skeletal muscle is specialized for rapid and forceful contraction of short duration. Skeletal muscle cells contain similar components and structures as other cells but different terms are used to describe those components and structure in skel ...
... voluntary muscle, and therefore under conscious control. Skeletal muscle is specialized for rapid and forceful contraction of short duration. Skeletal muscle cells contain similar components and structures as other cells but different terms are used to describe those components and structure in skel ...
the axon hillock and the initial segment
... finely granular material undercoating the plasma membrane, (b) scattered clusters of ribosomes, and (c) fascicles of microtubules. A similar undercoating occurs beneath the plasma membrane of myelinated axons at nodes of Ranvier. The ribosomes are not organized into Nissl bodies and are too sparsely ...
... finely granular material undercoating the plasma membrane, (b) scattered clusters of ribosomes, and (c) fascicles of microtubules. A similar undercoating occurs beneath the plasma membrane of myelinated axons at nodes of Ranvier. The ribosomes are not organized into Nissl bodies and are too sparsely ...
see p. Mov50 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... because parents are asymptomatic, consanguinity rate is high (ranging 5.6-28% in different populations). ...
... because parents are asymptomatic, consanguinity rate is high (ranging 5.6-28% in different populations). ...
敌獳湯⌠ⴷ8
... contralateral pontine nuclei (and thus, indirectly, from the contralateral cerebral cortex), and the contralateral olivary nuclear complex in the medulla (olive, for short). The olivary fibers are the so-called climbing fibers, which terminate on the Purkinje cells of the cerebellar cortex, climbing ...
... contralateral pontine nuclei (and thus, indirectly, from the contralateral cerebral cortex), and the contralateral olivary nuclear complex in the medulla (olive, for short). The olivary fibers are the so-called climbing fibers, which terminate on the Purkinje cells of the cerebellar cortex, climbing ...
Escape behavior and neuronal responses to looming stimuli in the
... distance of 70·cm at a constant speed of 20·cm·s–1 (Fig.·1B). Thus, for the crab’s eye the stimulus had an apparent size subtending an angle of 4° at its stationary initial position and expanded until covering the entire screen (77° width, 62° height). It should be noted that this definition is some ...
... distance of 70·cm at a constant speed of 20·cm·s–1 (Fig.·1B). Thus, for the crab’s eye the stimulus had an apparent size subtending an angle of 4° at its stationary initial position and expanded until covering the entire screen (77° width, 62° height). It should be noted that this definition is some ...
Biophysical Properties and Responses to Neurotransmitters of
... passive membrane properties of these ganglion neurons were examined and compared with each other. There were significant differences between the properties of neurons in the PG and GG ganglia. The mean membrane time constant, spike threshold, action potential halfwidth, and action potential decay ti ...
... passive membrane properties of these ganglion neurons were examined and compared with each other. There were significant differences between the properties of neurons in the PG and GG ganglia. The mean membrane time constant, spike threshold, action potential halfwidth, and action potential decay ti ...
Chapter 7: Eyes and Ears
... sighted during youth may benefit from this age change since their ability to see distant objects improves. Many individuals have lenses so flat that they cannot focus light even from far objects. This condition may eventually begin to improve because thickening of the lens increases its ability to r ...
... sighted during youth may benefit from this age change since their ability to see distant objects improves. Many individuals have lenses so flat that they cannot focus light even from far objects. This condition may eventually begin to improve because thickening of the lens increases its ability to r ...
Habituation, sensitization and Pavlovian conditioning
... on the parameters of the stimulation protocol (e.g., odor concentration, frequency of odor presentation), a temporary increment in responsiveness might initially be observed. If, however, an appetitive gustatory stimulus (e.g., sugar) is repeated with the same ISI, depending again on the concentrati ...
... on the parameters of the stimulation protocol (e.g., odor concentration, frequency of odor presentation), a temporary increment in responsiveness might initially be observed. If, however, an appetitive gustatory stimulus (e.g., sugar) is repeated with the same ISI, depending again on the concentrati ...
J Comp Physiol (1982) 149: 179 193
... neurons in the vicinity. (d) Different pathways between photoreceptors, and an interneuron under investigation may be revealed by impulse responses consisting of several excitatory and/or inhibitory waves. Impulse responses of VS-cells were recorded in 29 penetrations. The responses are very similar ...
... neurons in the vicinity. (d) Different pathways between photoreceptors, and an interneuron under investigation may be revealed by impulse responses consisting of several excitatory and/or inhibitory waves. Impulse responses of VS-cells were recorded in 29 penetrations. The responses are very similar ...
Identification of the Neuropeptide Transmitter Proctolin in Drosophila
... using a 2-pump HPLC with a 30 cm C-18 Bondapak column. Three kinds of separation were used: (1) a gradient elution of 5-50% acetonitrile against an aqueous buffer of 50 mM ammonium acetate, pH 4.5; (2) a gradient elution of 5-50% acetonitrile in the presence of a constant aqueous 0.1% trifluoroaceti ...
... using a 2-pump HPLC with a 30 cm C-18 Bondapak column. Three kinds of separation were used: (1) a gradient elution of 5-50% acetonitrile against an aqueous buffer of 50 mM ammonium acetate, pH 4.5; (2) a gradient elution of 5-50% acetonitrile in the presence of a constant aqueous 0.1% trifluoroaceti ...
Propagation of cortical synfire activity: survival probability in single
... If all neurons in the ®rst group are activated synchronously, they will cause the neurons of the second group to ®re synchronously and so on. Thus, each activated group will pass a spike volley on to the next group. This process will continue, until either the chain comes to an end, or other (e.g. i ...
... If all neurons in the ®rst group are activated synchronously, they will cause the neurons of the second group to ®re synchronously and so on. Thus, each activated group will pass a spike volley on to the next group. This process will continue, until either the chain comes to an end, or other (e.g. i ...
Nervous System PPT - Bibb County Schools
... If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP Copyright © 2003 Pearso ...
... If the action potential (nerve impulse) starts, it is propagated over the entire axon Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP Copyright © 2003 Pearso ...
Neural Correlates of Perceived Brightness in the Retina, Lateral
... There was no perceived brightness modulation in the central area containing the receptive field in this condition. (3 ) Same as ( 1) with the addition of drifting white (or black) bars over receptive field. Brightness induction was perceived in the area surrounding the bars. ( 4) L uminance modulati ...
... There was no perceived brightness modulation in the central area containing the receptive field in this condition. (3 ) Same as ( 1) with the addition of drifting white (or black) bars over receptive field. Brightness induction was perceived in the area surrounding the bars. ( 4) L uminance modulati ...
THE AREA POSTREMA: A POTENTIAL SITE FOR CIRCADIAN REGULATION BY
... ion substitution experiments revealed a PK2-induced Cl- current was responsible for membrane depolarization, while hyperpolarizations were the result of inhibition of an inwardly rectifying non-selective cation current. In contrast to these differential effects on membrane potential, nearly all neur ...
... ion substitution experiments revealed a PK2-induced Cl- current was responsible for membrane depolarization, while hyperpolarizations were the result of inhibition of an inwardly rectifying non-selective cation current. In contrast to these differential effects on membrane potential, nearly all neur ...
Introduction: Biology Today Chapter 1
... Specialized hair cells in the inner ear sense the orientation and position of the head, as discussed in the learning module for the auditory and vestibular system. ...
... Specialized hair cells in the inner ear sense the orientation and position of the head, as discussed in the learning module for the auditory and vestibular system. ...
Pelvic Pain
... Pain either constant (active) or only on palpation (latent) Motor dysfunction / reduced ROM Associated autonomic dysfunction Sikdar et al 2009, ...
... Pain either constant (active) or only on palpation (latent) Motor dysfunction / reduced ROM Associated autonomic dysfunction Sikdar et al 2009, ...
Functional Connectivity during Surround Suppression in
... One common property among visual sensory neurons, that has been attributed frequently to horizontal intra-areal connections, is surround suppression, also known as size tuning. Surround suppression, found initially in the retina [1], has since been found and studied extensively in all subsequent vis ...
... One common property among visual sensory neurons, that has been attributed frequently to horizontal intra-areal connections, is surround suppression, also known as size tuning. Surround suppression, found initially in the retina [1], has since been found and studied extensively in all subsequent vis ...
File
... 26) The simplest animals to display cephalization and centralization of the nervous system are A) sponges. B) flatworms. C) cnidarians. D) echinoderms. Answer: B Topic: 28.10 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 27) The brain and sensory system of a bilaterally symmetric organism function most like A) th ...
... 26) The simplest animals to display cephalization and centralization of the nervous system are A) sponges. B) flatworms. C) cnidarians. D) echinoderms. Answer: B Topic: 28.10 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 27) The brain and sensory system of a bilaterally symmetric organism function most like A) th ...
File
... 26) The simplest animals to display cephalization and centralization of the nervous system are A) sponges. B) flatworms. C) cnidarians. D) echinoderms. Answer: B Topic: 28.10 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 27) The brain and sensory system of a bilaterally symmetric organism function most like A) th ...
... 26) The simplest animals to display cephalization and centralization of the nervous system are A) sponges. B) flatworms. C) cnidarians. D) echinoderms. Answer: B Topic: 28.10 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 27) The brain and sensory system of a bilaterally symmetric organism function most like A) th ...
The Interoceptive, or Visceral, Sensations
... The viscera are generally insensitive to the usual stimuli that cause pain, but spasm, inflammation, trauma, pressure, distention, or tension on the viscera may produce severe pain, some of which results from involvement of the surrounding tissues. Pain endings are found in the parietal pleura over ...
... The viscera are generally insensitive to the usual stimuli that cause pain, but spasm, inflammation, trauma, pressure, distention, or tension on the viscera may produce severe pain, some of which results from involvement of the surrounding tissues. Pain endings are found in the parietal pleura over ...
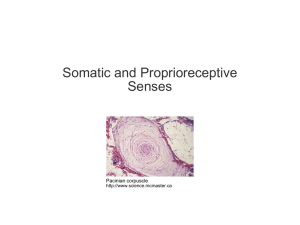
Somatic and Special Senses
... brain interprets sensory impulses • Impulse is read depending on what area of the brain receives it • One area may be sound and one area may be touch ...
... brain interprets sensory impulses • Impulse is read depending on what area of the brain receives it • One area may be sound and one area may be touch ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.