Lemniscal recurrent and transcortical influences on
... rhythmic oscillations of the membrane potential that made it difficult to study the synaptic responses. Membrane depolarization close to −20 mV was necessary to uncover the EPSPs responsible of the presumed recurrent spikes. These short-latency spikes could be blocked in five CL cells in which they ...
... rhythmic oscillations of the membrane potential that made it difficult to study the synaptic responses. Membrane depolarization close to −20 mV was necessary to uncover the EPSPs responsible of the presumed recurrent spikes. These short-latency spikes could be blocked in five CL cells in which they ...
PDF+Links
... area (morphometric parameter), as well as intensity of their staining (ROD — relative optical density, semiquantitative densitometric parameter developed by the software) was done at 400 ´ magnification. All consecutive sections of each series were analyzed. The neuronal counts were summarized using ...
... area (morphometric parameter), as well as intensity of their staining (ROD — relative optical density, semiquantitative densitometric parameter developed by the software) was done at 400 ´ magnification. All consecutive sections of each series were analyzed. The neuronal counts were summarized using ...
Lecture 3 Figure 1
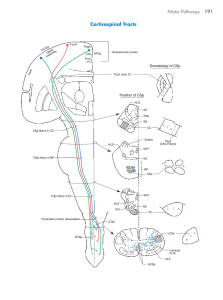
... lesioned side and away from the side of the hemiplegia. In addition to a contralateral hemiplegia, common cranial nerve findings in capsular lesions may include 1) deviation of the tongue toward the side of the weakness and away from the side of the lesion when protruded and 2) paralysis of facial mu ...
... lesioned side and away from the side of the hemiplegia. In addition to a contralateral hemiplegia, common cranial nerve findings in capsular lesions may include 1) deviation of the tongue toward the side of the weakness and away from the side of the lesion when protruded and 2) paralysis of facial mu ...
W3005 1/29/0 Prof
... molecules depending on the biochemical state of the cell.The ability of developing axons to grow towards some brain regions and away from others was recognized very early in experiments on the retinotectal system of frogs. As we saw in Bill Harris’ experiment, the optic tectum is a major target for ...
... molecules depending on the biochemical state of the cell.The ability of developing axons to grow towards some brain regions and away from others was recognized very early in experiments on the retinotectal system of frogs. As we saw in Bill Harris’ experiment, the optic tectum is a major target for ...
Co-activation of VTA DA and GABA neurons mediates nicotine
... results demonstrate that both positive and negative motivational values are transmitted through the dopamine (DA) neuron, but that the concerted activity of DA and GABA systems is necessary for the reinforcing actions of nicotine through burst firing of DA neurons. This work identifies the GABAergic i ...
... results demonstrate that both positive and negative motivational values are transmitted through the dopamine (DA) neuron, but that the concerted activity of DA and GABA systems is necessary for the reinforcing actions of nicotine through burst firing of DA neurons. This work identifies the GABAergic i ...
Inhibitory interneurons in a cortical column form hot zones of
... Only on the basis of such prevalence numbers is it possible to interpret data on single-cell physiology (1–8) and synaptic connections of pairs of neurons (9–12) at the circuit level. The distribution of cortical neurons and INs has therefore been the objective of several studies over the past decad ...
... Only on the basis of such prevalence numbers is it possible to interpret data on single-cell physiology (1–8) and synaptic connections of pairs of neurons (9–12) at the circuit level. The distribution of cortical neurons and INs has therefore been the objective of several studies over the past decad ...
diencephalon - Loyola University Medical Education Network
... a.) Identify the specific (or relay) nuclei of the thalamus, source of their afferents and which ones project to: i. Prefrontal cortex ii. Primary motor cortex iii. Somatic sensory cortex iv. Primary visual cortex v. Primary auditory cortex b.) Name the association nuclei of the thalamus and define ...
... a.) Identify the specific (or relay) nuclei of the thalamus, source of their afferents and which ones project to: i. Prefrontal cortex ii. Primary motor cortex iii. Somatic sensory cortex iv. Primary visual cortex v. Primary auditory cortex b.) Name the association nuclei of the thalamus and define ...
Chapter 2 – Action potential - Fun-Mooc
... sodium channel opening threshold because the threshold is about 50. In and response to this bolt of potential, we record a current which is no longer rectangular but which shows a descending leg, a peak, and an ascending leg. This is a negative inward current. This is an inward + charge current. And ...
... sodium channel opening threshold because the threshold is about 50. In and response to this bolt of potential, we record a current which is no longer rectangular but which shows a descending leg, a peak, and an ascending leg. This is a negative inward current. This is an inward + charge current. And ...
Disentangling pleasure from incentive salience and
... duce increases in incentive salience or Pavlovian-triggered motivation (here called “wanting” in shorthand) (1, 31, 35–37). A neurochemical distinction has been made between opioid stimulation of the NAc hotspot, which amplifies hedonic impact (liking) as well as motivation (wanting) for reward, and ...
... duce increases in incentive salience or Pavlovian-triggered motivation (here called “wanting” in shorthand) (1, 31, 35–37). A neurochemical distinction has been made between opioid stimulation of the NAc hotspot, which amplifies hedonic impact (liking) as well as motivation (wanting) for reward, and ...
The Inferior Parietal Lobule Is the Target of Output from the Superior
... intraparietal sulcus that projects to the F EF (Andersen et al., 1985). A previous anatomical study confirmed that LI P occupies a similar location in the Cebus monkey (Tian and Lynch, 1996). To guide the HSV1 injections visually into the posterior bank of the intraparietal sulcus, in some animals w ...
... intraparietal sulcus that projects to the F EF (Andersen et al., 1985). A previous anatomical study confirmed that LI P occupies a similar location in the Cebus monkey (Tian and Lynch, 1996). To guide the HSV1 injections visually into the posterior bank of the intraparietal sulcus, in some animals w ...
lmmunocytochemical Mapping of 18236, A Brain
... distribution in pontine, cerebellar, cortical, and limbic structures (Sutcliffe et al., 1983). The detailed cytological analysis of the distribution of this polypeptide, presented here, suggests that the 18236 protein may mark sequences of connected neurons within recognized circuits of the olfactor ...
... distribution in pontine, cerebellar, cortical, and limbic structures (Sutcliffe et al., 1983). The detailed cytological analysis of the distribution of this polypeptide, presented here, suggests that the 18236 protein may mark sequences of connected neurons within recognized circuits of the olfactor ...
Evolutionary roots offreedom
... tum leap. All relevant variables (complexity, time, "vocabulary," and so on) increase by several orders of magnitude. Along with it, variability increases immensely, so do the options for choice among alternatives. In fact, those comparative increases over other species are so large that the argumen ...
... tum leap. All relevant variables (complexity, time, "vocabulary," and so on) increase by several orders of magnitude. Along with it, variability increases immensely, so do the options for choice among alternatives. In fact, those comparative increases over other species are so large that the argumen ...
Cortico-Basal Ganglia Interactions in Huntington`s Disease
... of pathology in HD has been challenged by several studies. The critical involvement of the cerebral cortex in both “motor” and “limbic” circuits, as outlined above, suggests that some of the clinical symptoms of the disease are, in part, attributed to cortical dysfunction and degeneration. Accumulat ...
... of pathology in HD has been challenged by several studies. The critical involvement of the cerebral cortex in both “motor” and “limbic” circuits, as outlined above, suggests that some of the clinical symptoms of the disease are, in part, attributed to cortical dysfunction and degeneration. Accumulat ...
Significance of Neural Crest in Tooth Development
... encounter a relatively cell-free environment rich in extracellular matrix molecules. In this environment, they undergo extensive migrations along several well-defined pathways. These migrations are determined by intrinsic properties of the neural crest cells and features of the external environment ...
... encounter a relatively cell-free environment rich in extracellular matrix molecules. In this environment, they undergo extensive migrations along several well-defined pathways. These migrations are determined by intrinsic properties of the neural crest cells and features of the external environment ...
Clarke`s column neurons as the focus of a corticospinal corollary circuit
... motor command centers in the CNS1. Proprioceptive afferent input from the limbs is relayed to cortical motor centers along diverse ascending relay pathways, the most prominent of which engage the spinocerebellar system2–4. In mammals, there are a dozen or so distinct classes of spinocerebellar neuro ...
... motor command centers in the CNS1. Proprioceptive afferent input from the limbs is relayed to cortical motor centers along diverse ascending relay pathways, the most prominent of which engage the spinocerebellar system2–4. In mammals, there are a dozen or so distinct classes of spinocerebellar neuro ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Hemoglobin breaks down into bilirubin which is normally cleared from the body by the liver Newborns have an immature liver so bilirubin will build up and cause jaundice of body and of brain Infant will have diminished reflexes, lethargy, reduced muscle tone, and a high pitched ...
... Hemoglobin breaks down into bilirubin which is normally cleared from the body by the liver Newborns have an immature liver so bilirubin will build up and cause jaundice of body and of brain Infant will have diminished reflexes, lethargy, reduced muscle tone, and a high pitched ...
Morphological Changes in the Hippocampus Following Nicotine and
... Fig. 1. Histological analyses of the hippocampus. A. Hippocampus (the arrows show the borders of investigated areas): CA1 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus, hilus of the dentate gyrus, DB DG - dorsal blade of the dentate gyrus, VB DG - ventral blades of the dentate gyrus. NADPH-diaphorase staining. D ...
... Fig. 1. Histological analyses of the hippocampus. A. Hippocampus (the arrows show the borders of investigated areas): CA1 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus, hilus of the dentate gyrus, DB DG - dorsal blade of the dentate gyrus, VB DG - ventral blades of the dentate gyrus. NADPH-diaphorase staining. D ...
C6.4 PPT - Destiny High School
... Neuron Types by Function • sensory neurons (afferent) – send impulses toward CNS – Impulses from the skin and organs to the spinal cord and brain. – Provides information about the external and internal environments. ...
... Neuron Types by Function • sensory neurons (afferent) – send impulses toward CNS – Impulses from the skin and organs to the spinal cord and brain. – Provides information about the external and internal environments. ...
Anatomy - Nervous System Test Chpt 9
... c. motor output d. all of the above 2. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. nerve b. neuron c. brain d. spinal cord 3. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in its environment? a. a threshold b. an action potential c. a nerve signal d. a d ...
... c. motor output d. all of the above 2. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. nerve b. neuron c. brain d. spinal cord 3. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in its environment? a. a threshold b. an action potential c. a nerve signal d. a d ...
Guide to the CERAD Form
... The following sections relate variables from the STATA database, in which data are archived, to entries on the CERAD forms completed for each CC75C brain donor. ...
... The following sections relate variables from the STATA database, in which data are archived, to entries on the CERAD forms completed for each CC75C brain donor. ...
Functional Properties of Corticotectal Neurons in the Monkey`s
... field that could drive saccadic eye movements and neural pathways by which these signals could reach brain stem oculomotor centers. However, to understand how the cerebral cortex controls a specific behavior, it is not sufficient to know the types of activity in the cortex and the anatomical project ...
... field that could drive saccadic eye movements and neural pathways by which these signals could reach brain stem oculomotor centers. However, to understand how the cerebral cortex controls a specific behavior, it is not sufficient to know the types of activity in the cortex and the anatomical project ...
HB-GAM (pleiotrophin) reverses inhibition of neural
... HB-GAM/pleiotrophin was initially isolated as a heparin-binding neurite outgrowth-promoting factor for central neurons8,9. Its expression peaks during the first 3–4 weeks of postnatal development in rat brain10 corresponding to heightened plasticity of the juvenile brain11. The expression level at t ...
... HB-GAM/pleiotrophin was initially isolated as a heparin-binding neurite outgrowth-promoting factor for central neurons8,9. Its expression peaks during the first 3–4 weeks of postnatal development in rat brain10 corresponding to heightened plasticity of the juvenile brain11. The expression level at t ...
Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord
... • spinothalamic tract (sensory fibres subserving pain and temperature enter at each segment, synapse, and the second order neuron crosses to join the spinothalamic tract) • posterior (dorsal) column tract (sensory fibres subserving position, vibration and discriminative touch enter and directly join ...
... • spinothalamic tract (sensory fibres subserving pain and temperature enter at each segment, synapse, and the second order neuron crosses to join the spinothalamic tract) • posterior (dorsal) column tract (sensory fibres subserving position, vibration and discriminative touch enter and directly join ...