download file
... were especially helpful in recording neuronal responses. Rolan’s neat and methodically ...
... were especially helpful in recording neuronal responses. Rolan’s neat and methodically ...
Cerebellar control of visceral responses–possible mechanisms
... Electrical stimulation within the fastigial nucleus, even though a necessary step in exploration of the cerebellar autonomic control mechanisms, no doubt produces a very stereotyped and poorly differentiated excitation of fastigial neurons and adjacent nervous pathways. Such excitations are, for nat ...
... Electrical stimulation within the fastigial nucleus, even though a necessary step in exploration of the cerebellar autonomic control mechanisms, no doubt produces a very stereotyped and poorly differentiated excitation of fastigial neurons and adjacent nervous pathways. Such excitations are, for nat ...
Separate Representations of Target and Timing Cue Locations in
... oculomotor network and both are connected to several other areas such as temporal and lateral prefrontal cortices (Andersen 1995; Huerta and Kaas 1990; Lynch and Tian 2006). LIP sits at the interface between sensory and motor cortices (Andersen and Buneo 2002), whereas SEF is in the frontal cortex. ...
... oculomotor network and both are connected to several other areas such as temporal and lateral prefrontal cortices (Andersen 1995; Huerta and Kaas 1990; Lynch and Tian 2006). LIP sits at the interface between sensory and motor cortices (Andersen and Buneo 2002), whereas SEF is in the frontal cortex. ...
Glia-Derived D-Serine Controls NMDA Receptor Activity and
... synaptic changes. Such a contribution of astrocytes to synaptic metaplasticity fuels the emerging concept that astrocytes are dynamic partners of brain signaling. INTRODUCTION There is strong evidence for reciprocal communication between neurons and glia (Fields and Stevens-Graham, 2002; Haydon, 200 ...
... synaptic changes. Such a contribution of astrocytes to synaptic metaplasticity fuels the emerging concept that astrocytes are dynamic partners of brain signaling. INTRODUCTION There is strong evidence for reciprocal communication between neurons and glia (Fields and Stevens-Graham, 2002; Haydon, 200 ...
Stimulus Dependence of Local Field Potential Spectra: Experiment
... offer important insights into sensory neural representations. However, gaining such insight requires developing data-driven computational models that can identify and disambiguate the neural contributions to the LFP. Here, we investigated how networks of excitatory and inhibitory integrate-and-fire ...
... offer important insights into sensory neural representations. However, gaining such insight requires developing data-driven computational models that can identify and disambiguate the neural contributions to the LFP. Here, we investigated how networks of excitatory and inhibitory integrate-and-fire ...
191 Advances in Anatomy Embryology and Cell Biology
... sections (e.g., Lewis 1968)—several marker proteins, revealed by immunohistochemistry, visualize proliferating cells. Two commonly used markers are Ki67 and phosphohistone H3. The antigen Ki67 is present in all phases of the cell cycle except G0 , and the transition from a proliferative to nonprolif ...
... sections (e.g., Lewis 1968)—several marker proteins, revealed by immunohistochemistry, visualize proliferating cells. Two commonly used markers are Ki67 and phosphohistone H3. The antigen Ki67 is present in all phases of the cell cycle except G0 , and the transition from a proliferative to nonprolif ...
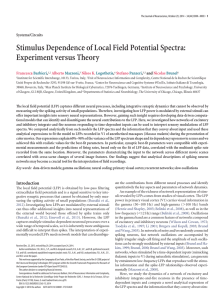
BOOK 1: Nervous system anatomy and function
... some but not all ions can move across. The neuron can additionally change which ions move across. When ions move across the cell membrane, the membrane potential changes due to the addition (or subtraction) of charges. Thus, during an action potential, the neuronal membrane allows positively charged ...
... some but not all ions can move across. The neuron can additionally change which ions move across. When ions move across the cell membrane, the membrane potential changes due to the addition (or subtraction) of charges. Thus, during an action potential, the neuronal membrane allows positively charged ...
Huntingtin Aggregation Kinetics and Their Pathological
... protein. Mutant Huntingtin forms intracellular aggregates within neurons, although it is unclear whether aggregates or more soluble forms of the protein represent the pathogenic species. To examine the link between aggregation and neurodegeneration, we generated Drosophila melanogaster transgenic st ...
... protein. Mutant Huntingtin forms intracellular aggregates within neurons, although it is unclear whether aggregates or more soluble forms of the protein represent the pathogenic species. To examine the link between aggregation and neurodegeneration, we generated Drosophila melanogaster transgenic st ...
Midbrain Dopamine Neurons Encode a Quantitative Reward
... shading at the top of each block indicating the largest available reward. Note that the subject manages, in general, to select delays that yield rewards, but also note that the size of the reward earned on each trial varies across the range of possible reward values. To quantify this behavior, Figur ...
... shading at the top of each block indicating the largest available reward. Note that the subject manages, in general, to select delays that yield rewards, but also note that the size of the reward earned on each trial varies across the range of possible reward values. To quantify this behavior, Figur ...
Circadian Organization in Hemimetabolous Insects
... suggest the existence of a secondary oscillator for the locomotor rhythm in the central brain. After bilateral removal of the optic lobe, some crickets showed residual rhythms that gradually disappeared within several days (Tomioka, 1985). Optic lobeless crickets showed locomotor rhythms in light da ...
... suggest the existence of a secondary oscillator for the locomotor rhythm in the central brain. After bilateral removal of the optic lobe, some crickets showed residual rhythms that gradually disappeared within several days (Tomioka, 1985). Optic lobeless crickets showed locomotor rhythms in light da ...
Neural Networks
... SNIPE 1 is a well-documented JAVA library that implements a framework for neural networks in a speedy, feature-rich and usable way. It is available at no cost for non-commercial purposes. It was originally designed for high performance simulations with lots and lots of neural networks (even large on ...
... SNIPE 1 is a well-documented JAVA library that implements a framework for neural networks in a speedy, feature-rich and usable way. It is available at no cost for non-commercial purposes. It was originally designed for high performance simulations with lots and lots of neural networks (even large on ...
Dopamine Receptor–Mediated Mechanisms Involved in the
... the tungsten wire electrode, either D1- or D2-class DA receptor antagonist was injected (total volume õ1 ml, at a rate of 1 ml/ 5–10 min). SCH23390 (10 mg/ ml in saline, 31 mM, pH 5.7; RBI) or cis-flupenthixol (30 mg/ ml in saline, 59 mM, pH 6.6; RBI) were used as the D1-class antagonists. ( 0 )-Sul ...
... the tungsten wire electrode, either D1- or D2-class DA receptor antagonist was injected (total volume õ1 ml, at a rate of 1 ml/ 5–10 min). SCH23390 (10 mg/ ml in saline, 31 mM, pH 5.7; RBI) or cis-flupenthixol (30 mg/ ml in saline, 59 mM, pH 6.6; RBI) were used as the D1-class antagonists. ( 0 )-Sul ...
Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors in Aplysia californica and Molecular
... electrophysiological recordings from individual cells. Large neurons also allow for nucleic acid isolation from few cells, allowing for targeted studies on subsets of neurons. Glutamate (L-Glu) is the principal fast excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS) of nearly all animal ...
... electrophysiological recordings from individual cells. Large neurons also allow for nucleic acid isolation from few cells, allowing for targeted studies on subsets of neurons. Glutamate (L-Glu) is the principal fast excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS) of nearly all animal ...
Neurally Plausible Model of Robot Reaching Inspired by Infant
... inputs during our weekly meetings. I appreciate that he would always answer my questions and correct my mistakes without judgment. Also, I would like to thank the members of my Ph.D. committee, Dr. Daniela Corbetta, Dr. James Plank and Dr. Lynne Parker, for their valuable and constructive feedback o ...
... inputs during our weekly meetings. I appreciate that he would always answer my questions and correct my mistakes without judgment. Also, I would like to thank the members of my Ph.D. committee, Dr. Daniela Corbetta, Dr. James Plank and Dr. Lynne Parker, for their valuable and constructive feedback o ...
Overo Lethal White Foal Syndrome
... phenotypes in humans, pigs, and rodents.3 The KIT locus is linked to those that encode albumin and vitamin D–binding protein.3 Genes that influence melanocyte development and migration have long been considered important in inheritance of an overo pattern, with the favored model being one in which o ...
... phenotypes in humans, pigs, and rodents.3 The KIT locus is linked to those that encode albumin and vitamin D–binding protein.3 Genes that influence melanocyte development and migration have long been considered important in inheritance of an overo pattern, with the favored model being one in which o ...
Calcium homeostasis in aging neurons
... Ca2+ dependent. Synchronous release driven by the precisely timed presynaptic Ca2+ current results in a large, fast postsynaptic response (Llinas et al., 1981; Sabatini and Regehr, 1996), whereas the slower asynchronous component, resulting from residual Ca2+ remaining in the terminal after an actio ...
... Ca2+ dependent. Synchronous release driven by the precisely timed presynaptic Ca2+ current results in a large, fast postsynaptic response (Llinas et al., 1981; Sabatini and Regehr, 1996), whereas the slower asynchronous component, resulting from residual Ca2+ remaining in the terminal after an actio ...
CHAPTER 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Carry messages from the central nervous system to muscles and glands Usually have one long axon that runs from the spinal cord to the muscle or gland Carry input from sense organs to the central nervous system Have long dendrites that carry input from the sense organ to the brain or spinal cord Copy ...
... Carry messages from the central nervous system to muscles and glands Usually have one long axon that runs from the spinal cord to the muscle or gland Carry input from sense organs to the central nervous system Have long dendrites that carry input from the sense organ to the brain or spinal cord Copy ...
VIP in Neurological Diseases: More Than A Neuropeptide
... proinflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins that contribute to the wound-healing response and debris elimination. However, continuous presence of these mediators involves gliosis and neuronal cell death. In chronic CNS damage, as in multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer´s disease or Parkinson´s disease, sp ...
... proinflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins that contribute to the wound-healing response and debris elimination. However, continuous presence of these mediators involves gliosis and neuronal cell death. In chronic CNS damage, as in multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer´s disease or Parkinson´s disease, sp ...
Structure and Central Connections Of PERIPHERAL OLFACTORY
... and duct cells of Bowman’s glands, the major source of mucus in the olfactory epithelium. The third cell type is the poorly understood microvillar cell located at the surface of the epithelium. Microvillar cells, which look similar to the so-called brush cells found throughout the upper and lower a ...
... and duct cells of Bowman’s glands, the major source of mucus in the olfactory epithelium. The third cell type is the poorly understood microvillar cell located at the surface of the epithelium. Microvillar cells, which look similar to the so-called brush cells found throughout the upper and lower a ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.