CH1101 General and Physical Chemistry 2012 Basic
... , except for one or two small points. The third time you go through it, you know you don’t understand it, but by that time you are so used to it it doesn’t bother you anymore.’ - Arnold Sommerfeld. ...
... , except for one or two small points. The third time you go through it, you know you don’t understand it, but by that time you are so used to it it doesn’t bother you anymore.’ - Arnold Sommerfeld. ...
Name____________________ Pd________ Date__________
... Calculate each of the following problems by using one or more of the following conversion factors: 1 mole = molar mass (g), 1 mole = 22.4 L @ STP, 1 mole = 6.02x10 23 molecules, atoms, particles, etc ...
... Calculate each of the following problems by using one or more of the following conversion factors: 1 mole = molar mass (g), 1 mole = 22.4 L @ STP, 1 mole = 6.02x10 23 molecules, atoms, particles, etc ...
ReviewPackage_ElectricityMagnetism
... o Neutrons do not have a charge A positively charged body has more protons than electrons. A negatively charged body has more electrons than protons. Electrical charges are measured in coulomb (C). A single electron or protons has a charge of only 1.602 X 10 -19C because they are so small. For ...
... o Neutrons do not have a charge A positively charged body has more protons than electrons. A negatively charged body has more electrons than protons. Electrical charges are measured in coulomb (C). A single electron or protons has a charge of only 1.602 X 10 -19C because they are so small. For ...
Physical concept of the surface tension of the liquid until some time
... physics and physical chemistry. A conclusion of this «unpacking» model is that of a reliable agreement with the molecular - kinetic theory of ideal gases. Namely, the theoretical development of the relationship of heat capacity values for one-, two - and triatomic gases. An impact of the spatial arr ...
... physics and physical chemistry. A conclusion of this «unpacking» model is that of a reliable agreement with the molecular - kinetic theory of ideal gases. Namely, the theoretical development of the relationship of heat capacity values for one-, two - and triatomic gases. An impact of the spatial arr ...
Practice Final fall 2012
... 2. The object in the sky that lies very nearly on an extension of the earth's axis is A. the sun. B. Orion. C. Mercury. D. Polaris 3. In which one or more of the following is the earth assumed to be the center of the universe? A. the Ptolemaic system B. the Copernican system C. Kepler's laws of plan ...
... 2. The object in the sky that lies very nearly on an extension of the earth's axis is A. the sun. B. Orion. C. Mercury. D. Polaris 3. In which one or more of the following is the earth assumed to be the center of the universe? A. the Ptolemaic system B. the Copernican system C. Kepler's laws of plan ...
Solid State Physics
... • Formed by strong, localized bonds with stable, closed-shell structures. • Larger cohesive energies than for ionic solids (4-7 eV/atom). – Leads to higher melting and boiling points. • Low electrical conductivity. – Due to energy band gap that charged carriers must overcome in order to conduct. ...
... • Formed by strong, localized bonds with stable, closed-shell structures. • Larger cohesive energies than for ionic solids (4-7 eV/atom). – Leads to higher melting and boiling points. • Low electrical conductivity. – Due to energy band gap that charged carriers must overcome in order to conduct. ...
Characteristisation of a recirculating flow using ultrasonic Doppler velocimetry
... 2.2 Description of the velocimetry method The ultrasonic transducer is placed in one of the sidewalls in the horizontal direction, which is a 4-MHz probe, 8mm in diameter. According to relationship between wavelength and frequency λ f = c , c being the sound speed in the liquid metal, we deduce that ...
... 2.2 Description of the velocimetry method The ultrasonic transducer is placed in one of the sidewalls in the horizontal direction, which is a 4-MHz probe, 8mm in diameter. According to relationship between wavelength and frequency λ f = c , c being the sound speed in the liquid metal, we deduce that ...
1. Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn
... fusion reactor, a gas fo heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collision of nuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the r ...
... fusion reactor, a gas fo heavy hydrogen is fully ionized into deuteron nuclei and electrons. This collision of nuclei and electrons is known as plasma. The nuclei move randomly in the reactor core and occasionally come close enough for nuclear fusion to take place. Usually, the temperatures in the r ...
Introduction to even-denominator FQHE: composite fermions
... FQHE: Review of Laughlin states • Laughlin quasiparticle • Laughlin wave function describes ground state of charge e electrons • Where do charge e/m anyons come from? • Excitations create anyons. What causes excitations? ...
... FQHE: Review of Laughlin states • Laughlin quasiparticle • Laughlin wave function describes ground state of charge e electrons • Where do charge e/m anyons come from? • Excitations create anyons. What causes excitations? ...
1 PHY831 - Subject Exam Dec. 14th 2011, 10am - 1pm
... (iii) The first thing to note is that T anh(3βJm2 ) for ferromagnetic interactions (i.e. J > 0) is always positive, so there are no negative m solutions to the mean field equation. This is completely different than the pair interaction case where there is symmetry in the solutions for positive and n ...
... (iii) The first thing to note is that T anh(3βJm2 ) for ferromagnetic interactions (i.e. J > 0) is always positive, so there are no negative m solutions to the mean field equation. This is completely different than the pair interaction case where there is symmetry in the solutions for positive and n ...
Examination WS 00/01 - KIT
... b) at a given temperature, the larger the band gap, the higher the electrical conductivity. c) electrons can be excited into conduction band only when the excitation energy is at lease equal to the band gap. 17. For electrical conduction, which one is true? a) Free electrons participate in the condu ...
... b) at a given temperature, the larger the band gap, the higher the electrical conductivity. c) electrons can be excited into conduction band only when the excitation energy is at lease equal to the band gap. 17. For electrical conduction, which one is true? a) Free electrons participate in the condu ...
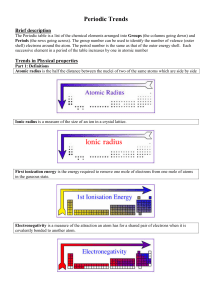
Topic 3 Periodicity notes SL - Chemical Minds
... Part 2: Physical properties down a group Going down a group, the atomic radius and ionic radius increase due to an increase in the number of electron shells surrounding the nucleus. The ionisation energy and electronegativity decrease because i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction b ...
... Part 2: Physical properties down a group Going down a group, the atomic radius and ionic radius increase due to an increase in the number of electron shells surrounding the nucleus. The ionisation energy and electronegativity decrease because i) there is a decrease in the electrostatic attraction b ...
High Pressure CO2 Adsorption: Challenges and
... suitable materials for CO2 adsorption than the commonly used liquid amine as long as regeneration and efficiency of the material is concerned. Polybenzimidazole (PBI) and SBA15 have been considered as best options, since these materials have high thermal stability, mechanically robust molecular natu ...
... suitable materials for CO2 adsorption than the commonly used liquid amine as long as regeneration and efficiency of the material is concerned. Polybenzimidazole (PBI) and SBA15 have been considered as best options, since these materials have high thermal stability, mechanically robust molecular natu ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).