How Atoms Bond: Ionic Bonds
... close: atoms aren’t even big enough to be microscopic. As eensy as atoms are, they’re made up of even smaller particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons. A diagram of an atom looks like this: “shells” surrounding a center, or nucleus. Inside the nucleus are all of that atom’s protons (and neutrons) ...
... close: atoms aren’t even big enough to be microscopic. As eensy as atoms are, they’re made up of even smaller particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons. A diagram of an atom looks like this: “shells” surrounding a center, or nucleus. Inside the nucleus are all of that atom’s protons (and neutrons) ...
Chemistry 20 – Unit 2 – Gases – FITB Notes Topic A
... 1. The gas molecules are in constant ________ motion, where they move in a straight line until they _______ with another particle or the wall of the container 2. The gas molecules are “______________” (they have mass but __________, and act like point spheres) 3. The only interaction between molecul ...
... 1. The gas molecules are in constant ________ motion, where they move in a straight line until they _______ with another particle or the wall of the container 2. The gas molecules are “______________” (they have mass but __________, and act like point spheres) 3. The only interaction between molecul ...
N241774
... indicative of the proper interpretation of these headings at the international level. See T.D. 89-80, 54 Fed. Reg. 35127 (Aug. 23, 1989). EN 39.09 (3) Polyurethanes is relevant to your products and provides: This class includes all polymers produced by the reaction of polyfunctional isocyanates with ...
... indicative of the proper interpretation of these headings at the international level. See T.D. 89-80, 54 Fed. Reg. 35127 (Aug. 23, 1989). EN 39.09 (3) Polyurethanes is relevant to your products and provides: This class includes all polymers produced by the reaction of polyfunctional isocyanates with ...
Measurements - Effingham County Schools
... not involve a change in the identity of the substance o Grinding, cutting, melting, and boiling ...
... not involve a change in the identity of the substance o Grinding, cutting, melting, and boiling ...
section_3.2
... The number of each type of atom is indicated by a subscript written to the right of the element symbol ...
... The number of each type of atom is indicated by a subscript written to the right of the element symbol ...
Metallic Crystal Structure
... regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged with respect to one another. A crystalline material is one in which the atoms are situated in a repeating or periodic array over large atomic distances; that is, long-range order exists, such that upon solidification, the atoms will position themselve ...
... regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged with respect to one another. A crystalline material is one in which the atoms are situated in a repeating or periodic array over large atomic distances; that is, long-range order exists, such that upon solidification, the atoms will position themselve ...
Chapter 3
... Enthalpy is the total energy we would need, to create a system out of nothing and put it in an environment with constant pressure P. Or, if we could completely annihilate a system, H is the energy we could recover: the system’s energy plus the work done by the collapsing atmosphere. However, we usu ...
... Enthalpy is the total energy we would need, to create a system out of nothing and put it in an environment with constant pressure P. Or, if we could completely annihilate a system, H is the energy we could recover: the system’s energy plus the work done by the collapsing atmosphere. However, we usu ...
... This paper presents an analytical formalism that allows for a description of a variety of non linear optical phenomena occurring when an electromagnetic wave propagates through a nematic liquid crystal. First, by using only thermodynamic and symmetry properties, a closed set of hydrodynamic equation ...
Review IV
... 14.2 Energetics in Solution?: Dissociation in solution into Ions, Ion-Dipole forces Solutions of Solids Dissolved in Water A. Solubility and Saturation 1. Saturated: solvent holding as much solute as it can 2. Unsaturated: solvent can hold more solute 3. Supersaturated: solvent holding more than the ...
... 14.2 Energetics in Solution?: Dissociation in solution into Ions, Ion-Dipole forces Solutions of Solids Dissolved in Water A. Solubility and Saturation 1. Saturated: solvent holding as much solute as it can 2. Unsaturated: solvent can hold more solute 3. Supersaturated: solvent holding more than the ...
Physical Properties
... • The nature of the bonds within a substance can predict and explain some of its properties. This is particularly true for physical properties. • We’ll consider three of these properties: – Melting and boiling points – Solubility ...
... • The nature of the bonds within a substance can predict and explain some of its properties. This is particularly true for physical properties. • We’ll consider three of these properties: – Melting and boiling points – Solubility ...
Features of spin-orbit-induced dynamics in magnetic nanofilms
... The prospects of the creation of new layered magnetic nanostructures possessing by the property of the field and current-govern magnetic dynamics with ultimately small energy consumption as base elements for nanodevices of an information technology with high bit densities and high-frequency radiatio ...
... The prospects of the creation of new layered magnetic nanostructures possessing by the property of the field and current-govern magnetic dynamics with ultimately small energy consumption as base elements for nanodevices of an information technology with high bit densities and high-frequency radiatio ...
CHAPTER I
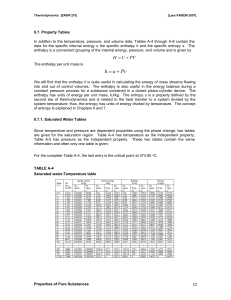
... second law of thermodynamics and is related to the heat transfer to a system divided by the system temperature; thus, the entropy has units of energy divided by temperature. The concept of entropy is explained in Chapters 6 and 7. II.7.1. Saturated Water Tables Since temperature and pressure are dep ...
... second law of thermodynamics and is related to the heat transfer to a system divided by the system temperature; thus, the entropy has units of energy divided by temperature. The concept of entropy is explained in Chapters 6 and 7. II.7.1. Saturated Water Tables Since temperature and pressure are dep ...
CHM 151LL: States of Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes
... and that have not reacted with each other to form a pure substance. Mixtures can be separated into their individual compounds by physical methods, that is, by methods that don’t require the breaking or making of chemical bonds. Common separation methods include filtration, decanting, distillation, e ...
... and that have not reacted with each other to form a pure substance. Mixtures can be separated into their individual compounds by physical methods, that is, by methods that don’t require the breaking or making of chemical bonds. Common separation methods include filtration, decanting, distillation, e ...
Patent-description-adapted
... plasma is sometimes referred to as being hot if it is nearly fully ionized, or cold if only a small fraction (for example 1%) of the gas molecules are ionized (but other definitions of the terms hot plasma and cold plasma are common). Even in a "cold" plasma the electron temperature is still typical ...
... plasma is sometimes referred to as being hot if it is nearly fully ionized, or cold if only a small fraction (for example 1%) of the gas molecules are ionized (but other definitions of the terms hot plasma and cold plasma are common). Even in a "cold" plasma the electron temperature is still typical ...
Oobleck Worksheet - Science Education at Jefferson Lab
... properties, on the other hand, have more to do with the atomic or molecular composition of matter. Chemical properties deal with how substances react with other such as water, air or fire. ...
... properties, on the other hand, have more to do with the atomic or molecular composition of matter. Chemical properties deal with how substances react with other such as water, air or fire. ...
chapter1-bur.2388380..
... Chemistry. From the word alchemy, from Old French alkemie, from Middle Latin alkimia, from Arabic al-kimiya, from Greek khemeioa (found about 300 AD in a decree of Diocletian against "the old writings of the Egyptians"), all meaning "alchemy." Perhaps from an old name for Egypt (Khemia, literally "l ...
... Chemistry. From the word alchemy, from Old French alkemie, from Middle Latin alkimia, from Arabic al-kimiya, from Greek khemeioa (found about 300 AD in a decree of Diocletian against "the old writings of the Egyptians"), all meaning "alchemy." Perhaps from an old name for Egypt (Khemia, literally "l ...
2 - Partnership for Effective Science Teaching and Learning
... dropped rock has a natural tendency to fall to the floor. When two atoms are close to each other and their electrons are of the correct type, it is more energetically favorable for them to come together and share electrons (become "bonded") than it is for them to exist as individual, separate atoms. ...
... dropped rock has a natural tendency to fall to the floor. When two atoms are close to each other and their electrons are of the correct type, it is more energetically favorable for them to come together and share electrons (become "bonded") than it is for them to exist as individual, separate atoms. ...
Many_8 - USU physics
... plane waves: e.g., eipx ± e−ipx , in the x -direction. The first term corresponds to momentum + p in the x -direction, the second to momentum − p in the x -direction. If an electric field is turned on in the +x -direction, say, the magnitude of the momentum (and hence energy) in the first term w ...
... plane waves: e.g., eipx ± e−ipx , in the x -direction. The first term corresponds to momentum + p in the x -direction, the second to momentum − p in the x -direction. If an electric field is turned on in the +x -direction, say, the magnitude of the momentum (and hence energy) in the first term w ...
Operation Principle of a Twist-Nematic Liquid Crystal Display
... There are many types of liquid crystal displays, each with unique properties. The most common LCD that is used for everyday items like watches and calculators is called the twisted nematic (TN) display. This device consists of a nematic liquid crystal sandwiched between two plates of glass. A specia ...
... There are many types of liquid crystal displays, each with unique properties. The most common LCD that is used for everyday items like watches and calculators is called the twisted nematic (TN) display. This device consists of a nematic liquid crystal sandwiched between two plates of glass. A specia ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).