ChinaPresentation1
... 4 Wall conditioning 5 Sputtering physical and chemical 6 Divertor physics ...
... 4 Wall conditioning 5 Sputtering physical and chemical 6 Divertor physics ...
Kinetic-Molecular theory of Matter/Ch10, Gases/Ch11 –Column
... 5) Using the KE equation, explain why balloons filled with helium (molar mass 4g/mol) deflate faster than those filled with air (molar mass 29g/mol) 6) What is an ideal gas? Do any actually exist? Why do we care about them? ...
... 5) Using the KE equation, explain why balloons filled with helium (molar mass 4g/mol) deflate faster than those filled with air (molar mass 29g/mol) 6) What is an ideal gas? Do any actually exist? Why do we care about them? ...
Supercritical clouds
... magnetic flux is frozen-in. • Solution: only (molecular) ions are tied to field lines. • Ambipolar diffusion: field lines can slip through the neutrals, allowing supercritical cores to form. • Long diffusion timescale means inefficient star formation. ...
... magnetic flux is frozen-in. • Solution: only (molecular) ions are tied to field lines. • Ambipolar diffusion: field lines can slip through the neutrals, allowing supercritical cores to form. • Long diffusion timescale means inefficient star formation. ...
Entropy change due to mixing , T . Evaluate
... A collection of free nucleons is enclosed in a box of volume V. The energy of a single nucleon of momentum p is p = p2/2m + mc2 where mc2=1000MeV. a) Pretending that there is no conservation law for the number of nucleons, calculate the partition function at temperature T. (Nucleons are fermions). ...
... A collection of free nucleons is enclosed in a box of volume V. The energy of a single nucleon of momentum p is p = p2/2m + mc2 where mc2=1000MeV. a) Pretending that there is no conservation law for the number of nucleons, calculate the partition function at temperature T. (Nucleons are fermions). ...
Introduction NOTES AND PROBLEM SET 1
... 1. Two hard spheres (with diameters σ) are fixed at the distance L. Other 3 similar spheres are free to move along the line connecting the first two spheres. Determine the dependence of average density of the spheres on the distance from the leftmost sphere (similar system with 4 spheres in total wa ...
... 1. Two hard spheres (with diameters σ) are fixed at the distance L. Other 3 similar spheres are free to move along the line connecting the first two spheres. Determine the dependence of average density of the spheres on the distance from the leftmost sphere (similar system with 4 spheres in total wa ...
Topic 3 Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Bonding and
... • Ionic solids are usually soluble in water because the dipole on water interacts with the ionic charges –> negative end of the dipole coordinates to the cation –> strength of interaction increases with decreasing cation size and increasing charge ...
... • Ionic solids are usually soluble in water because the dipole on water interacts with the ionic charges –> negative end of the dipole coordinates to the cation –> strength of interaction increases with decreasing cation size and increasing charge ...
Magnetic field in matter
... material (magnetization) to generate macroscopic current densities, which give rise to a magnetic field modifying the external B-field… Try to see what is the field configuration at equilibrium Try to describe the system in terms of controllable quantities ...
... material (magnetization) to generate macroscopic current densities, which give rise to a magnetic field modifying the external B-field… Try to see what is the field configuration at equilibrium Try to describe the system in terms of controllable quantities ...
IONS, ACIDS, BASES, AND pH
... Hydrogen ions are critical in a number of biological processes. HYDROGEN ION = PROTON. An acid is any compound (solid, liquid, or gas) that results in the dissociation of hydrogen ions in water. Proton pumps in the lining of your stomach maintain a strongly acidic environment to aid in digestion and ...
... Hydrogen ions are critical in a number of biological processes. HYDROGEN ION = PROTON. An acid is any compound (solid, liquid, or gas) that results in the dissociation of hydrogen ions in water. Proton pumps in the lining of your stomach maintain a strongly acidic environment to aid in digestion and ...
Document
... iv. Most elements are solids. v. Several are gaseous. vi. Only two elements are liquids at 25oC. vii. Some elements form diatomic molecules, two atoms combined into a molecule. j. 3.10 Ions i. A charged particle, called an ion, can be produced by adding or removing one or more electrons from an atom ...
... iv. Most elements are solids. v. Several are gaseous. vi. Only two elements are liquids at 25oC. vii. Some elements form diatomic molecules, two atoms combined into a molecule. j. 3.10 Ions i. A charged particle, called an ion, can be produced by adding or removing one or more electrons from an atom ...
pt.1 - MAGNETISM.eu
... - First maximise the spin by adding the spin angular momenta of the electrons, consistent with Pauli’s principle (the spins of two electrons occupying the same orbital must be opposite) to yield the total spin angular momentum S - Next, couple orbital angular momenta of the individual electrons to g ...
... - First maximise the spin by adding the spin angular momenta of the electrons, consistent with Pauli’s principle (the spins of two electrons occupying the same orbital must be opposite) to yield the total spin angular momentum S - Next, couple orbital angular momenta of the individual electrons to g ...
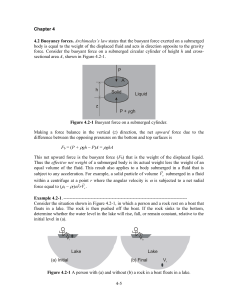
Chapter 4
... Since the volume of water in the lake is constant, and the total displaced volume is reduced, the level of the surface falls. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4.3 Pressure in Response to External Forces The only stress that can exist in a fl ...
... Since the volume of water in the lake is constant, and the total displaced volume is reduced, the level of the surface falls. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4.3 Pressure in Response to External Forces The only stress that can exist in a fl ...
thus
... one containing atoms of the element A and the other containing atoms of element B. When the two crystals are placed in contact with one another, the spontaneous process which occurs is the diffusion of A atoms into the crystal B lattice sites and diffusion of the B atoms into the crystal A lattice. ...
... one containing atoms of the element A and the other containing atoms of element B. When the two crystals are placed in contact with one another, the spontaneous process which occurs is the diffusion of A atoms into the crystal B lattice sites and diffusion of the B atoms into the crystal A lattice. ...
Surface Polymerisation (Polymer) 1 Plasma Enhanced Chemical
... collisions is too low to get a complete thermalization in the degrees of freedom of the system. This means that the electrons remain the particles with the highest energy, and create through collisions with the neutral species a large number of reactive species, while the gas temperature remains low ...
... collisions is too low to get a complete thermalization in the degrees of freedom of the system. This means that the electrons remain the particles with the highest energy, and create through collisions with the neutral species a large number of reactive species, while the gas temperature remains low ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).