New Liquid Crystalline Tolanes from (-)
... The design and synthesis of new chiral liquid crystals has experienced a great growth, especially of ferroelectric liquid crystals (FLCs). This is due to practical applications of FLCs as high resolution displays and in photonical technologies for storage and reproduction of information based on non ...
... The design and synthesis of new chiral liquid crystals has experienced a great growth, especially of ferroelectric liquid crystals (FLCs). This is due to practical applications of FLCs as high resolution displays and in photonical technologies for storage and reproduction of information based on non ...
FORMAT Bulletin - University of Canberra
... radius' to be of the order of 10-13 cm. In the normal atom, the assembly of corpuscles forms a system which is electical neutral. Detached corpuscles behave like negative ions, each carrying a constant negative charge and having a very small mass. September/October 1996 ...
... radius' to be of the order of 10-13 cm. In the normal atom, the assembly of corpuscles forms a system which is electical neutral. Detached corpuscles behave like negative ions, each carrying a constant negative charge and having a very small mass. September/October 1996 ...
Le Châtelier`s Principle
... 6. Bromine vapour reacts with chlorine gas to produce bromine monochloride gas. What effect would pressure have on this equilibrium? Br2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ 2 BrCl(g) since there are the same number of gas molecules on each side of the equation pressure will have no effect on this equilibrium 7. List and ...
... 6. Bromine vapour reacts with chlorine gas to produce bromine monochloride gas. What effect would pressure have on this equilibrium? Br2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ 2 BrCl(g) since there are the same number of gas molecules on each side of the equation pressure will have no effect on this equilibrium 7. List and ...
107 - Bossier Parish Community College
... 13. recognize the interrelationship of the structure of matter and its chemical and physical properties. (B,C) 14. differentiate between intensive and extensive properties. (B,C) 15. determine if a change in matter is physical or chemical. (B,C) 16. recognize and differentiate the characteristics o ...
... 13. recognize the interrelationship of the structure of matter and its chemical and physical properties. (B,C) 14. differentiate between intensive and extensive properties. (B,C) 15. determine if a change in matter is physical or chemical. (B,C) 16. recognize and differentiate the characteristics o ...
Name
... Charged particles at rest are not affected by static magnetic fields. However, when such charged particles are in motion, they are deflected by magnetic fields. The discovery that flowing electrons are affected by magnets was a pivotal discovery at the turn of the 20th century. Today, many common techno ...
... Charged particles at rest are not affected by static magnetic fields. However, when such charged particles are in motion, they are deflected by magnetic fields. The discovery that flowing electrons are affected by magnets was a pivotal discovery at the turn of the 20th century. Today, many common techno ...
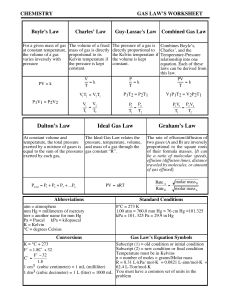
Gas Law`s Worksheet - Willamette Leadership Academy
... 14. A bubble of helium gas has a volume of 0.650 mL near the bottom of a large aquarium where the pressure is 1.54 atm and the temperature is 12°C. Determine the bubble’s volume upon rising near the top where the pressure is 1.01 atm and 16°C. 15. At what temperature Celsius will 19.4 g of molecular ...
... 14. A bubble of helium gas has a volume of 0.650 mL near the bottom of a large aquarium where the pressure is 1.54 atm and the temperature is 12°C. Determine the bubble’s volume upon rising near the top where the pressure is 1.01 atm and 16°C. 15. At what temperature Celsius will 19.4 g of molecular ...
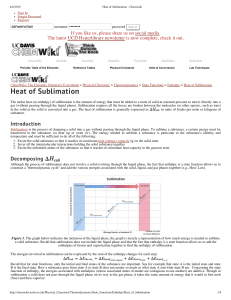
Heat of Sublimation - Chemwiki
... Bond energy is the amount of energy that a group of atoms must absorb so that it can undergo a phase change (going from a state of lower energy to a state of higher energy). It is measured in which is the enthalpy associated with a specific substance at a specific phase change. Common types of enth ...
... Bond energy is the amount of energy that a group of atoms must absorb so that it can undergo a phase change (going from a state of lower energy to a state of higher energy). It is measured in which is the enthalpy associated with a specific substance at a specific phase change. Common types of enth ...
Document
... PbO, ZrO2, and TiO2 in the form of a solid solution. PbO is significantly more volatile than the other two oxides. As a result if PZT films are heated during processing then significant Pb loss can occur, leading to a change in film stoichiometry and dramatically different properties. If Pb loss is ...
... PbO, ZrO2, and TiO2 in the form of a solid solution. PbO is significantly more volatile than the other two oxides. As a result if PZT films are heated during processing then significant Pb loss can occur, leading to a change in film stoichiometry and dramatically different properties. If Pb loss is ...
UNIT 3 VOCABULARY MATCHING and mole problems
... ____ 2.) equal to the number of protons in an atom; whole number on the Periodic Table ____ 3.) equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom ____ 4.) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube ____ 5.) atoms of the same element, but have different masses ____ 6.) negat ...
... ____ 2.) equal to the number of protons in an atom; whole number on the Periodic Table ____ 3.) equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom ____ 4.) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube ____ 5.) atoms of the same element, but have different masses ____ 6.) negat ...
Magnetic Fields in Matter
... Magnetic Fields in Matter Introduction We have seen that separating charges creates an electric field that in turn exerts a force on other charges. In the same way, MOVING charges (i.e., a current) creates a magnetic field that exerts forces on other currents. So it seems straightforward that magnet ...
... Magnetic Fields in Matter Introduction We have seen that separating charges creates an electric field that in turn exerts a force on other charges. In the same way, MOVING charges (i.e., a current) creates a magnetic field that exerts forces on other currents. So it seems straightforward that magnet ...
Nanochemistry Lecture 1
... What’s special with Nano? The properties of nanomaterials deviate from those of single crystals or polycrystals (bulk). For example, the fundamental properties like electronic, magnetic, optical, chemical and biological Surface properties: energy levels, electronic structure, and reactivity are diff ...
... What’s special with Nano? The properties of nanomaterials deviate from those of single crystals or polycrystals (bulk). For example, the fundamental properties like electronic, magnetic, optical, chemical and biological Surface properties: energy levels, electronic structure, and reactivity are diff ...
A Non-thermal Pasteurization Method Using Plasma
... A Non-thermal Pasteurization Method Using Plasma Researchers at the University of Minnesota have developed a non-thermal pasteurization system that effectively kills pathogens like bacteria and viruses, without producing impurities that can damage food nutrients, flavors, or colors. There are many m ...
... A Non-thermal Pasteurization Method Using Plasma Researchers at the University of Minnesota have developed a non-thermal pasteurization system that effectively kills pathogens like bacteria and viruses, without producing impurities that can damage food nutrients, flavors, or colors. There are many m ...
Equilibrium Thermodynamics
... Adiabatic Processes and Heat - It is possible to increase the internal energy U of a system by doing work W on this system. For example, mechanical work done by the friction force transfers energy to the tires of a car. As a result, the atoms in tires vibrate at larger amplitudes and the tires warm ...
... Adiabatic Processes and Heat - It is possible to increase the internal energy U of a system by doing work W on this system. For example, mechanical work done by the friction force transfers energy to the tires of a car. As a result, the atoms in tires vibrate at larger amplitudes and the tires warm ...
Nuclear quantum effects in molecular dynamics simulations
... Molecular dynamics (MD) is a powerful numerical method to investigate properties of condensed matter systems. Interatomic forces are calculated using either force fields or ab initio schemes, such as density functional theory (DFT), while the dynamics of the nuclei is based on classical mechanics. T ...
... Molecular dynamics (MD) is a powerful numerical method to investigate properties of condensed matter systems. Interatomic forces are calculated using either force fields or ab initio schemes, such as density functional theory (DFT), while the dynamics of the nuclei is based on classical mechanics. T ...
Chapter 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement
... To calculate the density, we must know both the mass and the volume of the gas. The mass of the gas is just the difference in the masses of the full and empty container: (837.6 – 836.2) g = 1.4 g In subtracting numbers, we determine the number of significant figures in our result by counting decimal ...
... To calculate the density, we must know both the mass and the volume of the gas. The mass of the gas is just the difference in the masses of the full and empty container: (837.6 – 836.2) g = 1.4 g In subtracting numbers, we determine the number of significant figures in our result by counting decimal ...
Validation of an Automated High Throughput Plasma Protein
... Human Plasma (Male, Pooled (N≥5), EDTA K3 treated, Fasted) Mouse Plasma (Male, Pooled (N≥5), EDTA K3 treated, Fasted) Rat Plasma (Male, Pooled (N≥5), EDTA K3 treated, Fasted) ...
... Human Plasma (Male, Pooled (N≥5), EDTA K3 treated, Fasted) Mouse Plasma (Male, Pooled (N≥5), EDTA K3 treated, Fasted) Rat Plasma (Male, Pooled (N≥5), EDTA K3 treated, Fasted) ...
Atoms Introduction
... 1.) Which of the following is true about an individual atom? a.) An individual atom should be considered to be a solid. b.) An individual atom should be considered to be a liquid. c.) an individual atom should be considered to be a gas. d.) The state of the atom depends on which element it is. e.) A ...
... 1.) Which of the following is true about an individual atom? a.) An individual atom should be considered to be a solid. b.) An individual atom should be considered to be a liquid. c.) an individual atom should be considered to be a gas. d.) The state of the atom depends on which element it is. e.) A ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).