Kein Folientitel
... The evolution equation for the current density, j, is derived by use of the electron equation of motion and called generalized Ohm‘s law. It results from a subtraction of the ion and electron equation of motion. The non-linear advection terms cancel in lowest order. The result is: ...
... The evolution equation for the current density, j, is derived by use of the electron equation of motion and called generalized Ohm‘s law. It results from a subtraction of the ion and electron equation of motion. The non-linear advection terms cancel in lowest order. The result is: ...
Slayt 1
... charges of the ions in an ionic compound. The result of this bond is a neutral compound. Metals and non-metals usually combine by forming ionic bonds. http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/animations/chang_7e_esp/bom1s2_11.swf ...
... charges of the ions in an ionic compound. The result of this bond is a neutral compound. Metals and non-metals usually combine by forming ionic bonds. http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/animations/chang_7e_esp/bom1s2_11.swf ...
A MICROWAVE SPECTROSCOPY
... Reports of June 3, 1946 and April 15, 1947 has been designed and is under construction The magnet frame of one magnet for one inhomogeneous field has been completed and the second is being machined ...
... Reports of June 3, 1946 and April 15, 1947 has been designed and is under construction The magnet frame of one magnet for one inhomogeneous field has been completed and the second is being machined ...
K - UCSB Physics
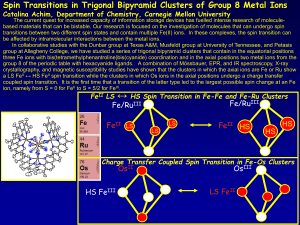
... 1, 2, 1),8–15 hexagonal insulators (Na/Li)2 IrO3 ,16–21 a large family of pyrochlores, R2 Ir2 O7 ,2 some spinel-related structures.25,26 Close to iridates in the periodic table are several osmium such as NaOsO3 27 and Cd2 Os2 O7 ,28 which experimentally display MITs. Apart from thes ...
... 1, 2, 1),8–15 hexagonal insulators (Na/Li)2 IrO3 ,16–21 a large family of pyrochlores, R2 Ir2 O7 ,2 some spinel-related structures.25,26 Close to iridates in the periodic table are several osmium such as NaOsO3 27 and Cd2 Os2 O7 ,28 which experimentally display MITs. Apart from thes ...
The" fingers" of the physics
... be found in that extraordinary period of discoveries and contradictions that characterized the end of the XIX century. In 1873, the scientific community was upset by the publication of the Treatise on electricity and magnetism by J.C. Maxwell, principally because not many had the necessary knowledge ...
... be found in that extraordinary period of discoveries and contradictions that characterized the end of the XIX century. In 1873, the scientific community was upset by the publication of the Treatise on electricity and magnetism by J.C. Maxwell, principally because not many had the necessary knowledge ...
Document
... • It would take you over 1,000,000,000,000 (1 Trillion) years to count the number of atoms in a single grain of sand ...
... • It would take you over 1,000,000,000,000 (1 Trillion) years to count the number of atoms in a single grain of sand ...
LN_ch01
... State of matter is dependent on temperature, pressure, strength of forces between particles Chapter 1 | Slide 11 ...
... State of matter is dependent on temperature, pressure, strength of forces between particles Chapter 1 | Slide 11 ...
Chemistry (B) Final Exam Study Guide 3
... molecules in which atoms are joined in the same order but differ in the arrangements of their atoms in space arrangement in which substituted groups are on opposite sides of a double bond compounds that differ in the orientation of groups around a double bond carbon atom to which four different atom ...
... molecules in which atoms are joined in the same order but differ in the arrangements of their atoms in space arrangement in which substituted groups are on opposite sides of a double bond compounds that differ in the orientation of groups around a double bond carbon atom to which four different atom ...
Magnetism and Matter
... Magnetic field or magnetic flux density B will form at some point in space when an external free current loop is switched on or magnetic material is placed at that location. A charge, q moving with velocity, v generates a field, B in a perpendicular direction of its velocity vector. By Lorentz force ...
... Magnetic field or magnetic flux density B will form at some point in space when an external free current loop is switched on or magnetic material is placed at that location. A charge, q moving with velocity, v generates a field, B in a perpendicular direction of its velocity vector. By Lorentz force ...
Unit 1 Matter and Change HOMEWORK
... 1. What is matter? _____Anything that has mass and takes up space _________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. What is matter? _____Anything that has mass and takes up space _________________________________________________________ ...
phase transition parameters in liquid mixtures with apparent
... fact that for both types of mixtures, the temperature dependence of NDE related to critical fluctuations is described by a power law with the same values of the critical exponents [3]. On the other hand, analysis of the phase diagrams (T,x)p showing the melting points Tm as functions of concentrati ...
... fact that for both types of mixtures, the temperature dependence of NDE related to critical fluctuations is described by a power law with the same values of the critical exponents [3]. On the other hand, analysis of the phase diagrams (T,x)p showing the melting points Tm as functions of concentrati ...
Ezio Fornero, Kinetic Theory
... have v2 = vx2 + vy2 + vz2 . We are interested to average values calculated on all the molecules; since in a chaotic motion there aren’t privileged directions of motion, the mean values of vx , vy and vz will be equal on the whole set of the molecules, thus we’ll have = =
[ = me ...
... have v2 = vx2 + vy2 + vz2 . We are interested to average values calculated on all the molecules; since in a chaotic motion there aren’t privileged directions of motion, the mean values of vx , vy and vz will be equal on the whole set of the molecules, thus we’ll have
Period #2 Notes: Electronic Structure of Atoms
... Melting temperature of Zr2C: Tm=3500°C • Observe: the higher the degree of ionization in the compounds, the stronger the compound. • Also, when an atom gives up its outermost electrons to become a cation, its radius decreases. • Similarly, when an atom attracts electrons to become an anion, its radi ...
... Melting temperature of Zr2C: Tm=3500°C • Observe: the higher the degree of ionization in the compounds, the stronger the compound. • Also, when an atom gives up its outermost electrons to become a cation, its radius decreases. • Similarly, when an atom attracts electrons to become an anion, its radi ...
The halogens
... element at room temperature and one of only six elements on the periodic table that are liquid at or close to room temperature. The pure chemical element has the physical form of a diatomic molecule, Br2. It is a dense, mobile, reddish-brown liquid, that evaporates easily at standard temperature and ...
... element at room temperature and one of only six elements on the periodic table that are liquid at or close to room temperature. The pure chemical element has the physical form of a diatomic molecule, Br2. It is a dense, mobile, reddish-brown liquid, that evaporates easily at standard temperature and ...
Towards an efficient microsystem for the real
... Furthermore, TSILs (or TSOSs) can be dissolved in roomtemperature ILs giving binary solutions combining all abovementioned benefits. ...
... Furthermore, TSILs (or TSOSs) can be dissolved in roomtemperature ILs giving binary solutions combining all abovementioned benefits. ...
Solutions!
... Shows the relationship of grams of solute that may be dissolved at various temperatures. ...
... Shows the relationship of grams of solute that may be dissolved at various temperatures. ...
density of water at room temperature
... Physical properties are the properties that do not change the chemical identity or nature of matter. Chemical properties are properties or changes that do change the chemical nature of matter. The more properties we can identify for a substance, the better we know the nature of that substance. These ...
... Physical properties are the properties that do not change the chemical identity or nature of matter. Chemical properties are properties or changes that do change the chemical nature of matter. The more properties we can identify for a substance, the better we know the nature of that substance. These ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).