Investigation of the Electron Energy Distribution Function in Hollow
... dip in the profile of the electron distribution function in the energy range ε = 2–4 eV and, accordingly, to produce the inverse distribution with df (ε)/dε > 0. The formation of a dip is associated with both the vibrational excitation of N2 molecules and the characteristic features of a hollow-cath ...
... dip in the profile of the electron distribution function in the energy range ε = 2–4 eV and, accordingly, to produce the inverse distribution with df (ε)/dε > 0. The formation of a dip is associated with both the vibrational excitation of N2 molecules and the characteristic features of a hollow-cath ...
Basics of Material Sciences - E
... Subshells have same energy but different _______ (1) Size (2) Shape (3) Orientation (4) All ...
... Subshells have same energy but different _______ (1) Size (2) Shape (3) Orientation (4) All ...
The Mole: A Measurement of Matter
... The Mole: A Measurement of Matter Describe how Avogadro’s number is related to a mole of any substance Solve problems involving mass in grams, amount in moles, and number of atoms of an element ...
... The Mole: A Measurement of Matter Describe how Avogadro’s number is related to a mole of any substance Solve problems involving mass in grams, amount in moles, and number of atoms of an element ...
Semiconductor
... covalent bond structure and therefore a hole in the valence band of the energy level diagram. Every impurity atom will produce a hole in the valence band. These holes will drift to produce an electrical current if a voltage is applied to the material and the P type semiconductor is a much better con ...
... covalent bond structure and therefore a hole in the valence band of the energy level diagram. Every impurity atom will produce a hole in the valence band. These holes will drift to produce an electrical current if a voltage is applied to the material and the P type semiconductor is a much better con ...
Gas Chromatography 1 C i ( bil h ) Carrier gas (mobile phase
... solvent <20°C, after 30s (splitless time) a fast increase in the temperature to 20°C above solvent’s boiling point. Fast transfer from gas to liquid and again to the gas phase sharpens the elution band. ...
... solvent <20°C, after 30s (splitless time) a fast increase in the temperature to 20°C above solvent’s boiling point. Fast transfer from gas to liquid and again to the gas phase sharpens the elution band. ...
Atoms, elements and Compounds
... (i) element cannot be broken into anything simpler by chemical means OR made up of one type of atom only ...
... (i) element cannot be broken into anything simpler by chemical means OR made up of one type of atom only ...
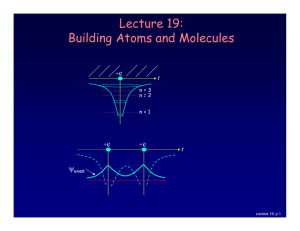
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... • Electrons do not pile up in the lowest energy state. It’s more like filling a bucket with water. • They are distributed among the energy levels according to the Exclusion Principle. • Particles that obey this principle are called “fermions”. Protons and neutrons are also fermions, but photons are ...
... • Electrons do not pile up in the lowest energy state. It’s more like filling a bucket with water. • They are distributed among the energy levels according to the Exclusion Principle. • Particles that obey this principle are called “fermions”. Protons and neutrons are also fermions, but photons are ...
Powerpoints - University of Pittsburgh
... having a very few simple properties: they consist of very many spatially localized, independent components, fixed in number. ...
... having a very few simple properties: they consist of very many spatially localized, independent components, fixed in number. ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint Presentation
... • Every substance has its own unique set of physical and chemical properties. • Observations of properties may vary depending on the conditions of the immediate environment. • It is important to state the specific conditions in which observations are made because both chemical and physical propertie ...
... • Every substance has its own unique set of physical and chemical properties. • Observations of properties may vary depending on the conditions of the immediate environment. • It is important to state the specific conditions in which observations are made because both chemical and physical propertie ...
File
... magnets, have been known to have the property of attracting tiny pieces of metal. This attractive property is called magnetism. ...
... magnets, have been known to have the property of attracting tiny pieces of metal. This attractive property is called magnetism. ...
expansion and diffusion of a laser plasma in a magnetic field
... plasma is the investigation of the possibility of filling magnetic traps with hot plasma produced by laser irradiation of individual solid particles in vacuum. That relatively few experiments have been performed in this field is apparently due to a number of specific difficulties that arise when exp ...
... plasma is the investigation of the possibility of filling magnetic traps with hot plasma produced by laser irradiation of individual solid particles in vacuum. That relatively few experiments have been performed in this field is apparently due to a number of specific difficulties that arise when exp ...
Temperature
... Any macroscopic body composed of a large number of particles has internal energy U associated with internal degrees of freedom . (e.g kinetic energy of molecules in a volume of gas, vibrational energy of atoms in a crystal. The internal energy U(T) is in general a complicated function of T and is di ...
... Any macroscopic body composed of a large number of particles has internal energy U associated with internal degrees of freedom . (e.g kinetic energy of molecules in a volume of gas, vibrational energy of atoms in a crystal. The internal energy U(T) is in general a complicated function of T and is di ...
... Big Idea 2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules and the forces between them. Transformations of matter can be observed in multiple ways that are generally categorized as either chemical or physical change. T ...
1.1.4 Amount of Substance / The Mole
... and found that the ratios of volumes of the reacting gases were small integer numbers e.g two volumes of hydrogen react with one of oxygen to produce two volumes of water ...
... and found that the ratios of volumes of the reacting gases were small integer numbers e.g two volumes of hydrogen react with one of oxygen to produce two volumes of water ...
Diagnostics
... involving the existence of measurement units. These units are essentially arbitrary; i.e. create and agree to use them. ...
... involving the existence of measurement units. These units are essentially arbitrary; i.e. create and agree to use them. ...
Chapter 3
... frequency - the number of waves that pass a specific point within a given time; usually expressed in cycles per second or hertz (Hz) ...
... frequency - the number of waves that pass a specific point within a given time; usually expressed in cycles per second or hertz (Hz) ...
State of matter

In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).